Lab Manual: Resistors in Series - Class 10 PDF Download
Objective
To determine the equivalent resistance of two resistors, when connected in series combination.
Materials Required
Two standard resistance coils (or resistors), ammeter (0-1.5A), voltmeter (0-1.5V), one-way key, low resistance rheostat, connecting wires, a piece of sand paper and ceil or battery eliminator.
Theory/Principle
The end-to-end connection of two or more resistors is said to be series combination, if they. provide only one path to the flow of current, i.e. same current would be flown through each resistor.
Consider V be the potential difference by one DC source across the combination of unknown resistances R1 and R2 [as shown in Fig. 1(b)]. Fig.1 (a) Two resistors AB and CD are placed one after the other
Fig.1 (a) Two resistors AB and CD are placed one after the other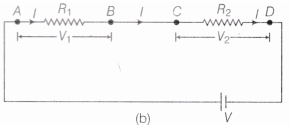 Fig.1 (b) Two resistors AB and CD are connected in a series combination
Fig.1 (b) Two resistors AB and CD are connected in a series combination
If V1 and V2 be the potential differences measured by the voltmeter across each resistor, then
V = V1 + V2 ………(i)
According to Ohm’s law,
V1 = IR1, V2 = IR2
and V = IRs ……..(ii)
where, Rs = Equivalent resistance of R1 and R2 in series combination.
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
IRs = IR1 + IR2
⇒ Rs = R1 + R2
Thus, the equivalent resistance of the series combination is equal to the sum of the individual resistances connected in the series circuit.
Procedure
- Note the least count and the zero error (if any) of the given ammeter and voltmeter.
- Clean the ends of connecting wires using a sand paper.
- Find the values of two given resistances R1 and R2 by the procedure given in Experiment 5.
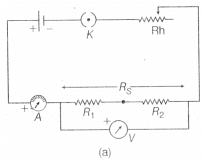 Fig. 2 (a) Circuit diagram of resistors in series
Fig. 2 (a) Circuit diagram of resistors in series
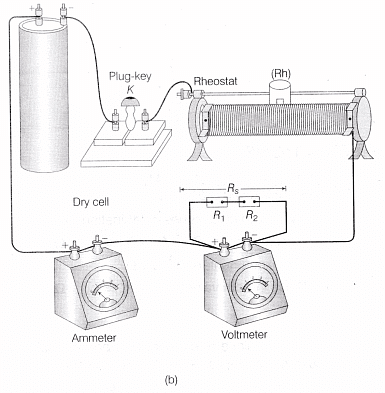 Fig. 2 (b) Block diagram of resistors in series
Fig. 2 (b) Block diagram of resistors in series
- Connect the resistances in series as shown in block diagram or circuit diagram given in Fig. 2.
- Put the plug in the key and take the readings of ammeter and voltmeter (as done in Experiment 5).
- Repeat the step 5 three times by changing the position of the sliding contact of the rheostat (as done in Experiment 5).
- Tabulate the readings and find the ratio of V and I. It will give the equivalent resistance of the combination.
Observation
- Least count of ammeter = …………. A
- Zero error of ammeter = ………… A
- Least count of voltmeter = ………… V
- Zero error of voltmeter = …………. V
- Zero correction in ammeter reading = ………. A
- Zero correction in voltmeter reading = ……… V
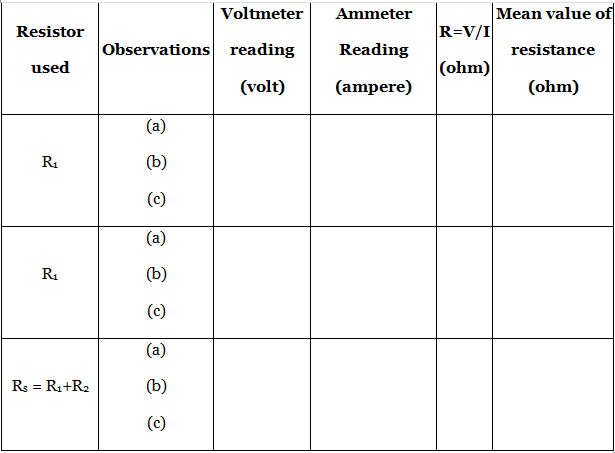
Calculations
- Mean value of R1 = ………. Ω
- Mean value of R2 = ……….. Ω
- Equivalent value of series combination,
- By calculation, R’s = R1 + R2 = ………… Ω
- By experiment, Rs = ………… Ω
Difference in both values, Rs - R’s = ……… Ω
Result
- There is a close agreement between the calculated value and the value obtained by the experiment.
Hence, Rs = R1 + R2 is verified. - Equivalent resistance, Rs = …………. Ω
Percentage Error
It can be found by using the following relation:
Percentage Error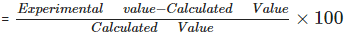
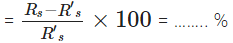
It shows that the percentage error is within the experimental error.
Precautions
- Remove the dust and other insulating particles from the ends of connecting wire, by rubbing it with sand paper.
- All the connections should be tight and properly done as per the circuit diagram.
- Take out the plug from the plug key in between the two observations.
- A low resistance rheostat should be used in the circuit to obtain a large variation in the current.
- The thick copper connecting wires should be used in the circuit.
- The positive terminal of the ammeter and voltmeter must be connected to the positive terminal of the battery or battery eliminator.
- Never connect the two terminals of the cell without any resistance.
- The pointers of the ammeter and voltmeter should be at zero mark when no current flows through them.
- Current should be passed through the circuit for a short time while taking observations; otherwise current would cause unnecessary heating in the circuit. Heating may change the resistance of resistors.
- The ammeter should be connected in series with the combination of resistors such that the current enters at the positive terminal and leaves at the negative terminal of the ammeter.
- Voltmeter should always be connected in parallel to the combination of resistors.
Sources of Error
- Reading error may be possible while observing the pointer of ammeter and voltmeter.
- Thick connecting wires may not be available at the time of performing the experiment.
- Area of cross-section of resistance may not be uniform across the length of the wire.
- The high resistance rheostat may be used.
- Current may be allowed for the longer period through the circuit.
- The terminal screws of the given instruments may not be tighten properly.














