Laxmikanth Summary: Directive Principles of State Policy | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Part IV of the Indian Constitution deals with Directive Principles of our State Policy (DPSP). The provisions contained in this Part cannot be enforced by any court, but these principles are fundamental in the governance of the country and it shall be the duty of the State to apply these principles in making laws.

Features of the Directive Principles of Policy
- Definition:
- Directive Principles of State Policy are ideals for the government while making laws.
- They guide legislative, executive, and administrative actions.
- Scope:"State" in this context includes central and state governments, local authorities, and other public bodies (Article 36).
- Historical Connection:
- Similar to the "Instrument of Instructions" in the 1935 Government of India Act.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar equated them, stating they are instructions to the legislature and executive.
- Comprehensive Program:
- Encompasses economic, social, and political aspects.
- Aims for justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity, aligning with the Constitution's Preamble.
- Focuses on creating a 'welfare state,' not a 'police state.'
- Non-Justiciability:
- Not legally enforceable by courts.
- Government isn't compelled to implement them.
- Despite non-justiciability, Article 37 emphasizes their fundamental role in governance.
- Judicial Role:
- Courts can't force implementation but consider them while assessing laws.
- If a law aligns with Directive Principles, it may be deemed 'reasonable' under constitutional scrutiny (Article 14 or 19).
Classification of the Directive Principles
The Constitution does not contain any classification of Directive Principles. However, based on their content and direction, they can be classified into three broad categories, viz, socialistic, Gandhian and liberal-intellectual.

Socialistic Principles
Reflects socialist principles, aiming for a democratic socialist state. Focuses on social and economic justice, steering towards awelfare state.
- Article 38: Promotes people's welfare, striving for a just social, economic, and political order.
- Article 39: Ensures citizens' right to adequate livelihood, fair distribution of resources, and prevention of wealth concentration.
- Article 39A: Promotes equal justice and provides free legal aid to the poor.
- Article 41: Guarantees the right to work, education, and public assistance during unemployment, old age, sickness, and disability.
- Article 42: Provides just and humane working conditions and maternity relief.
- Article 43: Secures a living wage, decent standard of life, and cultural opportunities for workers.
- Article 43A: Encourages worker participation in industrial management.
- Article 47: Aims to improve public health, raise nutrition levels, and enhance people's standard of living.
Gandhian Principles
Based on Gandhian ideology, reflecting ideas from Gandhi's vision during the national movement.
- Article 40: Organize village panchayats, empowering them for self-government.
- Article 43: Promote cottage industries in rural areas, either individually or cooperatively.
- Article 43B: Encourage the formation of cooperative societies with voluntary participation, democratic control, and professional management.
- Article 46: Promote the educational and economic interests of marginalized groups (SCs, STs, and others), protecting them from social injustice and exploitation.
- Article 47: Prohibit the consumption of harmful intoxicants.
- Article 48: Forbid the slaughter of cows, calves, and other useful cattle, aiming to enhance their breeds.
Liberal-Intellectual Principles
Reflects liberal principles, emphasizing individual rights and progressive governance.
- Article 44: Ensure a uniform civil code for all citizens across the country.
- Article 45: Provide early childhood care and education for children until the age of six.
- Article 48: Organize agriculture and animal husbandry using modern and scientific methods.
- Article 48A: Protect and improve the environment, safeguarding forests and wildlife.
- Article 49: Preserve monuments, places, and objects of artistic or historic importance declared national.
- Article 50: Separate the judiciary from the executive in public services of the State.
- Article 51: Promote international peace, maintain just and honourable relations between nations, respect international law and treaties, and encourage arbitration for settling international disputes.
New Directive Principles
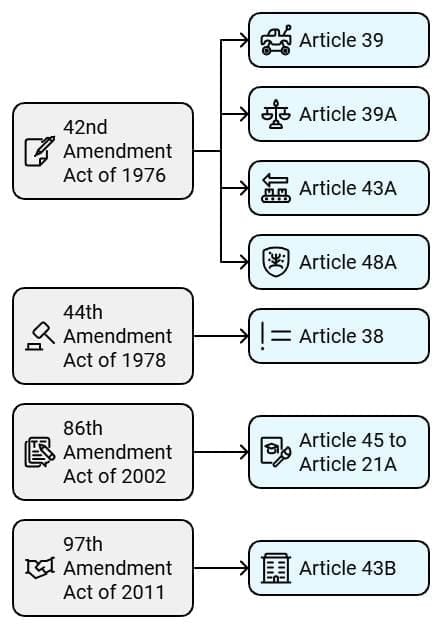
42nd Amendment Act of 1976:
Added four new Directive Principles to the original list.
- Article 39: Secure opportunities for healthy child development.
- Article 39A: Promote equal justice and provide free legal aid to the poor.
- Article 43A: Take steps to involve workers in industry management.
- Article 48A: Protect and improve the environment, safeguarding forests and wildlife.
44th Amendment Act of 1978:
- Added another Directive Principle.
- Article 38: Requires the State to minimize inequalities in income, status, facilities, and opportunities.
86th Amendment Act of 2002:
- Changed the subject of Article 45, making elementary education a fundamental right under Article 21A.
- Requires the State to provide early childhood care and education for all children until the age of six.
97th Amendment Act of 2011:
- Added a new Directive Principle related to cooperative societies.
- Article 43B: Requires the state to promote voluntary formation, autonomous functioning, democratic control, and professional management of cooperative societies.
Sanction Behind Directive Principles of Policy
- B.N. Rau's Recommendation:
- Constitutional Advisor B.N. Rau suggested dividing individual rights into two categories: justiciable and non-justiciable.
- Fundamental Rights (justiciable) were placed in Part III, while Directive Principles (non-justiciable) went to Part IV.
- Nature of Directive Principles:
- Non-justiciable in nature, meaning they can't be legally enforced by courts.
- Constitution (Article 37) emphasizes their fundamental role in governance, making it the state's duty to apply them while making laws.
- Moral Obligation and Political Force:
- Imposes a moral obligation on the state authorities for application.
- The real force behind them is political, driven by public opinion.
- Importance Stressed by Leaders:
- Leaders like Alladi Krishna Swamy Ayyar emphasized that no responsible government can lightly ignore the Directive Principles.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar highlighted that a government relying on popular vote can't afford to ignore these principles.
- Non-Enforceability Reasons:
- Made non-justiciable and legally non-enforceable due to practical considerations:
- Insufficient financial resources.
- Diversity and backwardness in the country.
- Newly independent India needed flexibility in deciding how and when to implement them.
- Pragmatic Approach:Constitution makers believed in awakened public opinion rather than relying solely on court procedures for enforcing these principles.
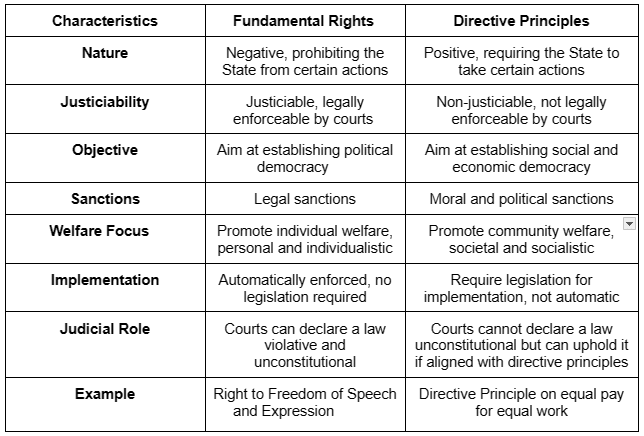
Distinction Between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
Criticism of the Directive Principles
The Directive Principles of State Policy have been criticised by some members of the Constituent Assembly as well as other constitutional and political experts on the following grounds:
- No Legal Force:
- Critics say Directive Principles are criticized because they cannot be legally enforced.
- Described as 'pious superfluities,' like a 'cheque on a bank' only payable when resources permit.
- Compared to New Year's resolutions that are broken quickly.
- Illogically Arranged:
- Critics argue that Directive Principles are not logically organized.
- Notproperly classified; mix important and less important issues.
- Sir Ivor Jennings says they lack a consistent philosophy.
- Conservative:
- Sir Ivor Jennings believes Directive Principles are based on 19th-century England's political philosophy.
- Expresses Fabian Socialism without socialism.
- Thought to be suitable for the 20th century but might become outdated for the 21st century.
- Constitutional Conflict:
- K. Santhanam highlights potential conflicts between different levels of government.
- Possibility of conflict between the Centre and states, President and Prime Minister, and governor and chief minister.
- Centre can direct states on Directive Principles, leading to the potential dismissal of state governments.
- President canreject billsviolating Directive Principles, causing conflict with the Prime Minister.
- Similar conflicts may occur between the governor and chief minister at the state level.
Utility of Directive Principles
Declared Fundamental:
- The Constitution states that Directive Principles are fundamental to governing the country.
- L.M. Singhvi calls them the "life-giving provisions" and the essence of the Constitution's social justice philosophy.
Positive Opinions:
- M.C. Chagla believes following Directive Principles would make India a heavenly place.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar values them for emphasizing"economic democracy"alongside political democracy.
- Granville Austin sees them as fostering social revolution by creating necessary conditions.
Moral Precepts and EducativValue:
- Sir RN. Rau views Directive Principles as"moral precepts"with educational value.
- M.C. Setalvad, former Attorney General, sees them as an "Instrument of Instructions" for authorities.
Significance and Usefulness:
- Directive Principles serve as general recommendations reminding authorities of constitutional principles.
- Act as guiding lights for courts in exercising judicial review to determine constitutional validity.
- Form the background for all state actions and guide the courts.
- Amplify the Preamble's resolve to secure justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity for all citizens.
Roles Played by Directive Principles:
- Facilitate stability and continuity in policies despite changes in the ruling party.
- Supplementary to citizens' fundamental rights, filling in social and economic rights.
- The implementation creates a favourable atmosphere for citizens to enjoy fundamental rights fully.
- Enable the opposition to influence and control the government by pointing out non-compliance with Directives.
- Serve as a crucial test for evaluating the government's performance, allowing citizens to scrutinize policies and programs.
- Act as a common political manifesto, guiding legislative and executive actions regardless of political ideology.
Conflict Between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
- Champakam Dorairajan Case (1951):
- In case of conflict between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles, Fundamental Rights prevail.
- Fundamental Rights can be amended by Parliament, leading to the First, Fourth, and Seventeenth Amendment Acts.
- Golaknath Case (1967):
- Supreme Court ruled Fundamental Rights are "sacrosanct" and cannot be amended for Directive Principles.
- Parliament reacted with the 24th and 25th Amendment Acts, asserting power to amend Fundamental Rights.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973):
- Second provision of Article 31C, giving immunity to laws implementing socialistic Directive Principles, declared unconstitutional.
- First provision upheld, stating laws implementing specified Directive Principles won't be void for violating certain Fundamental Rights.
- 42nd Amendment Act (1976):
- Extended protection of Article 31C to any law implementing Directive Principles.
- Declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in Minerva Mills case (1980).
- Minerva Mills Case (1980):
- Reaffirmed Fundamental Rights' supremacy over Directive Principles.
- Emphasized the Constitution's balance between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles as essential.
- Goals of Directive Principles should be achieved without compromising the means provided by Fundamental Rights.
- Current Position:
- Fundamental Rights have supremacy over Directive Principles.
- Parliament can amend Fundamental Rights to implement Directive Principles without damaging the Constitution's basic structure.
Implementation of Directive Principles
- Planning Commission and NITI Aayog (1950-2015):
- Planning Commission (1950) and NITI Aayog (2015) aimed at planned development.
- Successive Five Year Plans focused on socio-economic justice and reducing inequalities.
- Land Reforms:
- States enacted laws for agrarian changes, including intermediary abolition and tenancy reforms.
- Ceilings on land holdings, surplus land distribution, and promotion of cooperative farming.
- Labor Welfare Acts:
- Various Acts like Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Wages Act, and Child Labour Prohibition Act.
- Enacted to protect labor rights, with the government banning child labor in 2006.
- Women's Rights Acts:Maternity Benefit Act (1961) and Equal Remuneration Act (1976) safeguard women workers.
- Financial Resource Utilization:
- Nationalization of life insurance (1956) and fourteen leading banks (1969).
- Abolition of Privy Purses (1971) and other financial measures for common good.
- Legal Aid and Justice System:
- Legal Services Authorities Act (1987) for free legal aid and Lok Adalats for conciliation.
- Panchayati Raj system (1992) introduced for local self-governance.
- Cottage Industries Development:Various boards and commissions established for the development of cottage industries.
- Rural Development Programs:
- Multiple programs like Community Development, Jawahar Rozgar Yojana, and NREGA launched.
- Aimed at raising the standard of living in rural areas.
- Environmental Conservation Acts:
- Wildlife (Protection) Act (1972), Forest (Conservation) Act (1980), and Water and Air Acts.
- Established Pollution Control Boards for environmental protection.
- Modernization of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry:
- Improved agricultural inputs, seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation facilities.
- Modernizing animal husbandry on scientific lines.
- Reservation for Weaker Sections:
- Reservations in education, government services, and representative bodies for SCs, STs, and other weaker sections.
- Acts like Untouchability (Offences) Act, now Protection of Civil Rights Act, enacted for protection.
- National Commissions for Social Groups:
- Establishment of national commissions for backward classes, minorities, women, and child rights.
- 103rd Amendment Act (2019) provided 10% reservation for Economically Weaker Sections (EWSs).
- Judicial Reforms:Criminal Procedure Code (1973) separated judiciary from the executive in public services.
- Monument and Archaeological Protection:Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act (1951) for protection.
- Public Health Initiatives:
- Establishment of primary health centers and hospitals nationwide.
- Special programs for disease eradication.
- Anti-Cow Slaughter Laws:Some states enacted laws prohibiting the slaughter of cows, calves, and bullocks.
Old Age Pension Schemes:Some states initiated pension schemes for people above 65 years.
Foreign Policy for Peace:India follows non-alignment and panchsheel for international peace and security.
Directives Outside Part IV
Apart from the Directives included in Part IV, there are some other Directives contained in other Parts of the Constitution. They are:
- Reservation for SCs and STs in Services (Article 335):
- Members of Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) have claims to services and posts.
- Consideration given while making appointments, balancing with the efficiency of administration.
- Mother-Tongue Instruction for Linguistic Minorities (Article 350-A):
- States and local authorities should strive to provide facilities for instruction in the mother tongue at the primary stage.
- Focus on children belonging to linguistic minority groups.
- Promotion and Development of Hindi (Article 351):
- Union's duty to promote and develop the Hindi language.
- The aim is for Hindi to serve as a medium of expression for the diverse culture of India.
- These directives are non-justiciable, meaning they cannot be legally enforced by the courts.
- Despite being non-justiciable, the judiciary pays equal attention to them, emphasizing the holistic reading of the Constitution.
- The goal is to balance the interests of SCs and STs, linguistic minorities, and the promotion of Hindi with administrative efficiency and cultural diversity.
|
147 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Directive Principles of State Policy - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main features of the Directive Principles of State Policy in India? |  |
| 2. How are the Directive Principles classified? |  |
| 3. What is the distinction between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy? |  |
| 4. What are some criticisms of the Directive Principles of State Policy? |  |
| 5. How do Directive Principles conflict with Fundamental Rights? |  |

















