Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Crop Production And Management
Q.1. Describe various methods of agricultural practices involved in crop production and management.
Ans. Various methods of agricultural practices involved in crop production and management are:
- Preparation of soil by tilling and leveling.
- Sowing of seeds into prepared soil.
- Adding manure and fertilizers for replenishment and enrichment of soil and healthy growth of crops.
- The supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called irrigation.
- Protecting from weeds by using weedicides.
- Harvesting of crops by machines.
- Proper storage to protect them from the harmful effects of pests and microorganisms.
Q.2. Define irrigation and its various methods and explain the two methods which conserve water.
Ans. Irrigation is the artificial application of water to crops at different intervals. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil, and season to season.
Two methods of irrigation are
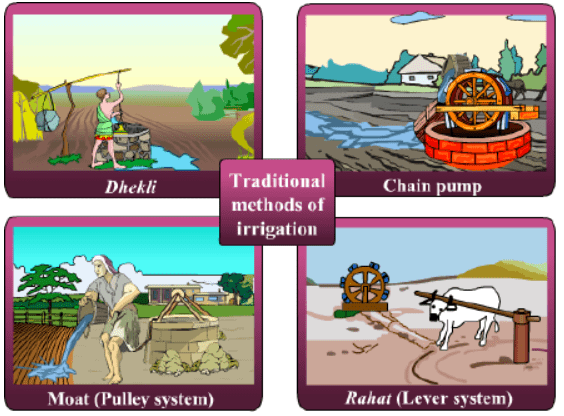
1. Traditional method of irrigation involves cattle or human labor and thus are cheaper than modern methods of irrigation, various traditional ways of irrigation are:
(a) Moat (pulley system)
(b) Chain pump
(c) Dhekli
(d) Rahat (Lever system)
2. Modern methods of irrigation help us to use water economically, involves the following methods:
(a) Sprinkler system: In this system, perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it sprinkles from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
Example: Sprinkler system is used mostly on uneven land.
 Sprinkler system
Sprinkler system
(b) Drip system: In this system, water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called a drip system. It is the best technique for watering plants, trees, and gardens. This system provides water to plants drop by drop, and water is not wasted at all.
Example: watering fruit plants, gardens, and trees.
 Drip SystemQ.3. Describe the importance of weedicides, manures, and fertilizers in good agricultural practice.
Drip SystemQ.3. Describe the importance of weedicides, manures, and fertilizers in good agricultural practice.
Ans. Weeds: Weeds are unwanted plants that grow along with crop plants and compete with them for water, nutrients, space, and light. Thus, they affect the growth of crop plants. Some of the weeds are poisonous for animals and human beings and they interfere even in the harvesting of crop plants.
Example: Wild oats, grass.

Weedicides: These are chemicals that are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds, they do not damage the crops. Weedicides are diluted with water and are sprayed in the field by a sprayer to kill the weeds.
Example: 2,4-D
 Weedicides
Weedicides
Manure and fertilizers are added to the soil to replenish it with nutrients to ensure the healthy growth of plants. Manures like animal waste, plant residues, and fertilizers like urea, and NPK are used for this purpose.

Q.4. Explain harvest festivals.
Ans. A Harvest Festival is an annual celebration that occurs around the time of the main harvest of a given region. The efforts of the farmer of past seasons borne fruit in the form of crops laden with grain, at this point, they celebrate harvest festivals to express their joy and happiness. Special festivals associated with the harvest season are Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya, and Bhogali Bihu.
Q.5. Explain how continuous plantation of crops in a field affects the quality of soil.
Ans. Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons. Growing the same type of crops in the same place for many years in a row disproportionately depletes the soil of certain nutrients. With rotation, a crop that leaches the soil of one kind of nutrient is followed during the next growing season by a dissimilar crop that returns that nutrient to the soil or draws a different ratio of nutrients. For example, rice is followed by cotton.
Q.6. Differentiate between mixed cultivation and crop rotation
Ans.
| Mixed Cultivation | Crop Rotation |
| 1. Simultaneous growth of different crops in one field. 2. Maximize space utilization and diversity in a single season. 3. Different crop types are grown together simultaneously. 4. Not necessarily designed to manage specific nutrient needs. 5. Diverse crops can disrupt pest and disease cycles. For example, Wheat and pea plants grown together in the same field. | 1. Sequential planting of different crops in the same field over time. 2. Preserve soil fertility and manage pest and disease cycles. 3. Successive crops with varying nutrient needs are grown in sequence. 4. Tailored to optimize soil health and nutrient balance for each crop. 5. Alternating crops can break pest and disease cycles and reduce reliance on chemicals. For example, Corn followed by legumes (e.g., soybeans) to restore nitrogen in the soil. |
Q.7. Write a brief note on ‘Animal Husbandry’.
Ans. Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals by humans for profit. In animal husbandry, genetic qualities and behavior are considered to be advantageous to humans for further development. Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years since the first domestication of animals. Humans are dependent on animals in many ways. The animals are domesticated by humans for many purposes. Depending on the usefulness of domestic animals, they are categorized as:
- Meat and Egg yielding animals like pigs, sheep, fish, poultry, goats and duck.
- Milk-yielding animals or dairy animals like cows, buffalo and goats.
- Wool and skin-yielding animals like sheep, goats, camel, buffaloes and cows. Skins are used as leather for different articles.
 Animal Husbandry
Animal Husbandry
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Crop Production And Management
| 1. What are the essential nutrients required for crop production? |  |
| 2. What are some common pests that affect crop production and how can they be managed? |  |
| 3. How does irrigation impact crop production? |  |
| 4. What are some sustainable practices that can be adopted for crop production? |  |
| 5. How can farmers improve soil fertility for better crop production? |  |

















