Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Q1: Explain the sublimation process with a labelled diagram.
Ans: Sublimation is the process in which a solid directly changes into the gaseous state without passing through the liquid state, and vice versa. It is a physical and reversible change.
Substances that show sublimation: Camphor, ammonium chloride, naphthalene, iodine, etc.
Activity to demonstrate sublimation (using ammonium chloride):
Take a small amount of ammonium chloride and crush it.
Place it in a china dish.
Cover the dish with an inverted funnel.
Plug the narrow stem of the funnel with cotton.
Gently heat the dish and observe.
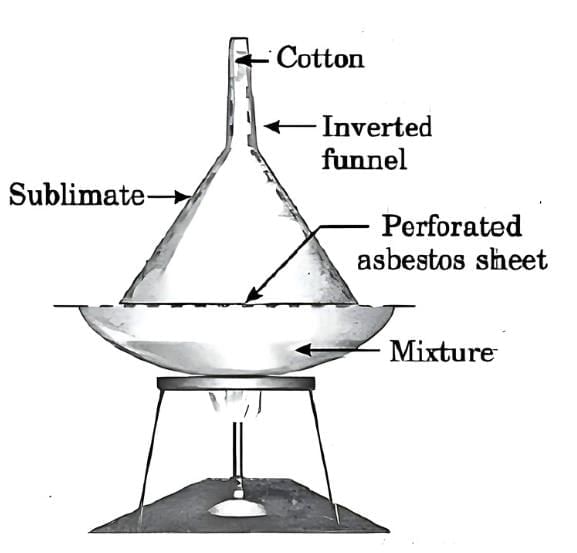 Separation of ammonium chloride and salt by sublimation
Separation of ammonium chloride and salt by sublimation
Observation:
White fumes of ammonium chloride rise and deposit as white crystals on the upper inner side of the funnel, directly changing from solid to gas and back to solid without becoming liquid.
Conclusion:
This confirms that ammonium chloride undergoes sublimation.
Equation:
NH₄Cl (solid) ⇌ NH₄Cl (vapour)
Q2: What are colloids? Give their characteristics.
Ans: A colloid is a type of heterogeneous mixture in which the size of particles is intermediate between those in true solutions and suspensions. The particle size in a colloid ranges from 1 nm to 1000 nm. These particles are not visible to the naked eye but are big enough to scatter light.
Examples of colloids:
Milk, fog, smoke, butter, jelly, and ink.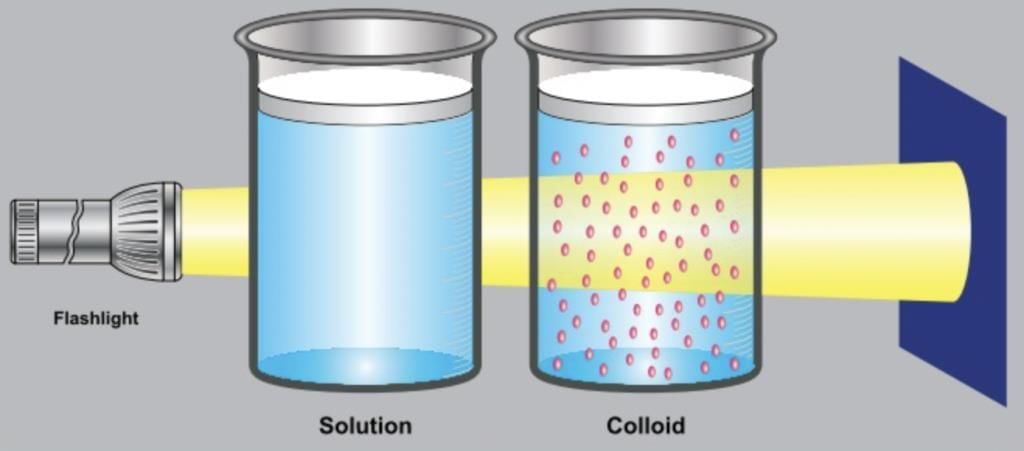
Characteristics of colloids:
- Heterogeneous mixture: Colloids appear homogeneous to the naked eye but are actually heterogeneous in nature.
- Tyndall Effect: When a beam of light passes through a colloid, the path of light becomes visible due to scattering by colloidal particles. This is known as the Tyndall effect.
- Brownian Motion: Colloidal particles show random zigzag motion due to continuous collisions with molecules of the dispersion medium.
- Stability: Colloidal particles do not settle down on standing, hence colloids are relatively stable.
- Cannot be filtered easily: Colloidal particles cannot be separated using ordinary filter paper. However, they can be separated using centrifugation.
- Particle size: The size of colloidal particles is larger than that in a true solution but smaller than that in a suspension.
Thus, Colloids are an important type of mixture found in everyday life, and they exhibit special properties like the Tyndall effect and Brownian motion, making them unique.
Q3: How much water should be mixed with 12 ml of alcohol to obtain 12% of alcohol? Calculate.
Ans: Given:
Volume of solute (alcohol) = 12 ml
Desired concentration = 12%
Let the final volume of solution = x ml
Using the formula for concentration: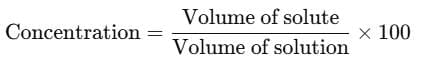
Substitute the values: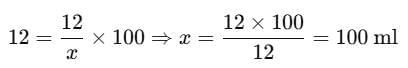
Therefore, the total volume of the solution should be 100 ml.
So, Volume of water = Volume of Solution - Volume of Alcohol ( Solute) 100 − 12 = 88 ml
To obtain a 12% alcohol solution, 88 ml of water should be mixed with 12 ml of alcohol.
Q4: Give the difference between colloidal solutions and suspensions.
Ans:
| Feature | Colloidal Solution | Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 1 nm to 1000 nm | More than 1000 nm |
| Appearance | Appears homogeneous but is heterogeneous | Clearly heterogeneous |
| Visibility of particles | Particles not visible to the naked eye | Particles are visible |
| Stability | Stable, does not settle on standing | Unstable, settles on standing |
| Filtration | Cannot be filtered by filter paper | Can be separated by filtration |
| Tyndall effect | Shows Tyndall effect | May or may not show Tyndall effect |
Q5: Give the difference between true solutions and colloidal solutions.
Ans:
| Feature | True Solution | Colloidal Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Less than 1 nm | Between 1 nm and 1000 nm |
| Appearance | Homogeneous | Appears homogeneous but is heterogeneous |
| Visibility of particles | Particles not visible | Particles not visible but scatter light |
| Stability | Very stable | Relatively stable |
| Tyndall effect | Does not show | Shows Tyndall effect |
| Filtration | Cannot be filtered | Cannot be filtered with normal filter paper |
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
| 1. What is meant by 'pure matter'? |  |
| 2. How can we determine if a substance is pure? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of mixtures? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to understand the purity of matter? |  |
| 5. Can pure substances be separated into simpler substances? |  |
















