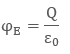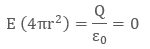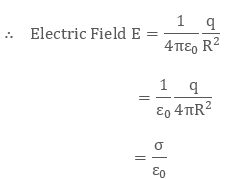Magnetism & Gauss’s Law | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Introduction to Magnetism and Gauss’s Law
The property of magnet to attract or repel other substance is known as Magnetism. We know that, there exist an imaginary magnetic field lines around a magnet which is the main source, responsible for the behaviour of the magnets. When these magnetic field lines penetrates through an area perpendicularly, then (The average of the magnetic field lines) X (the area through which it penetrates) is known as Magnetic Flux. Gauss law in magnetism states that the magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero.
Electrostatics
In physics, electrostatics deals with the study of electric charges that are stationary i.e. they are slow moving or have very less acceleration. With respect to the static charges
Coulomb stated that “The magnitude of electrostatic force of interaction between two point charges is directly proportional to the scalar multiplication of the magnitude of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them”. This law is known as Coulomb’s Law.
Electric Field
A charge particle is always surrounded by a field in which other charge particles can experience its force. In other words, the region where a charge particle can exert force on other charge particle is known as Electric Field. It is a vector quantity which means that it has both magnitude as well as direction. For a positive charge the line of force is directed outwards while for a negative charge the lines of force is directed inwards.
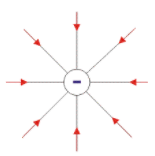 Lines of Force Due to and Isolated -ve charge
Lines of Force Due to and Isolated -ve charge
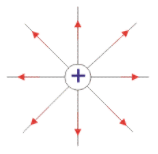 Lines of Force Due to and Isolated +e charge
Lines of Force Due to and Isolated +e charge
Gauss’s Law in Electrostatics
Theorem: Gauss’s Law states that “The net electric flux through any closed surface is equal to 1/ times the net electric charge within that closed surface (or imaginary Gaussian surface)”.
∫ E.ds = q/ϵ
Explanation: In the fig 1.1 two charges +2Q and -Q is enclosed within a closed surface S, and a third charge +3Q is placed outside the closed surface. The net electric flux through the closed surface S will be given by,
ᶲs = ∑ q/ϵ
that is, = (+2Q + (-Q))/ϵ
= Q/ϵ
Since the charge +3Q is placed outside the closed surface, therefore this charge will not be taken into consideration while applying gauss theorem
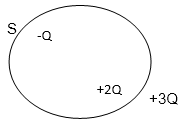
(Here the imaginary closed Gaussian surface is considered to be a circle
Application of Gauss’s Law
Three types of Application of Gauss’s Law
- Electric Field intensity due to Infinitely long uniformly Charged Wire
- Electric Field due to Plane Sheet
- Electric Field due to Spherical shell
- Electric Field intensity due to infinitely long uniformly charged wire
Let us consider a long linear wire of length L with uniformly distributed positive charge λ. Then by applying Gauss Law,
Then by applying Gauss Law,
∫E.ds = q/ϵ
= λL/ϵ
ᶲ = E2πrL
E =λ/2πrϵ
Where r is the perpendicular distance from the charged wire. - Electric Field due to Plane Sheet
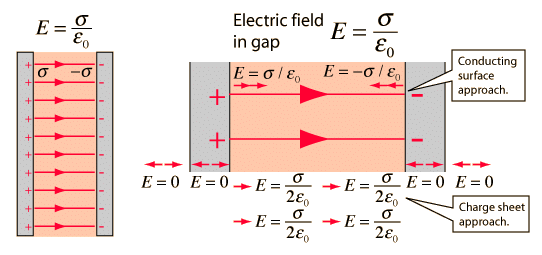
- Electric field due to thin infinite plane sheet with uniform surface charge density.
 In case of an infinite sheet charge, a cylindrical Gaussian surface is considered, such that the electric field is perpendicular to the surface. As a result of which only the ends of the Gaussian surface will constitute the magnetic flux.
In case of an infinite sheet charge, a cylindrical Gaussian surface is considered, such that the electric field is perpendicular to the surface. As a result of which only the ends of the Gaussian surface will constitute the magnetic flux. - Electric field due to two parallel sheets of equal and opposite charge at any point.
Let us assume that the two parallel plates with equal and opposite charge, is at equilibrium which means that the field is perpendicular to the surface and have zero electric field inside the conductor. Then by applying gauss law we can find the electric field between the two plates, which is given in the below diagram.
- Electric field due to thin infinite plane sheet with uniform surface charge density.
- Electric Field due to Spherical Shell
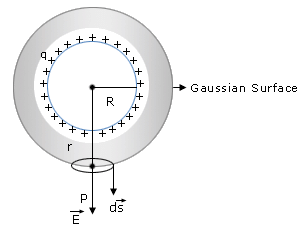
Let us consider a sphere of radius R with positive charge (q) distributed uniformly all over the surface. To calculate the electric field on the surface of the shell(inside and outside), a spherical Gaussian surface is taken into consideration.- Electric field outside the shell: To calculate the electric field outside the shell, we consider the radius of Gaussian surface r is greater than the radius of shell R that is,( r > R)

Then by applying integral form of gauss law,
φE = ∮(Ecos θ)ds
= E ∮ ds
= E (4π2) - Electric field inside the charged shell: Electric field inside the shell can be calculated by considering a cylindrical Gaussian surface of radius r. Now in case of electric field inside the shell, we assume that the radius of Gaussian surface r is smaller than the Radius of the shell R that is, (r < R). Then the electric flux through the Gaussian surface is given by,
φE = ∮(Ecosθ )ds = E (4π2)
According to Gauss's law,
Since all the charge lies outside the Gaussian surface therefore the net charge is zero.
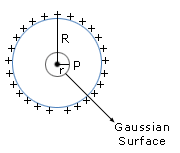
Therefore the electric field is zero at all points inside the shell. - Electric field on the surface of shell: In this case we consider that the radius of Gaussian surface is equal to the radius of shell that is, r = R


is the surface charge density on the shell.
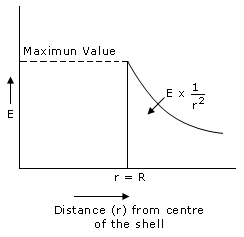
From the above observation it is seen that the electric field inside the shell is zero and electric field is maximum at the surface of the shell.
- Electric field outside the shell: To calculate the electric field outside the shell, we consider the radius of Gaussian surface r is greater than the radius of shell R that is,( r > R)
Magnetostatics
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields where the current is not changing with time that is, it is steady. The magnetic field produced by a steady current is given by
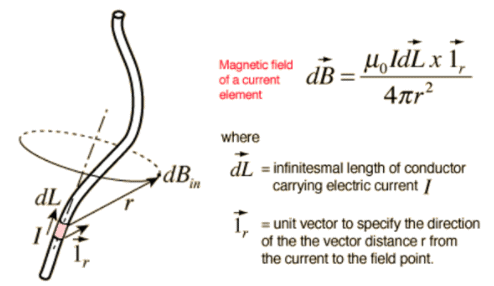
This is known as Biot- Savarts Law.
Biot-savart law states that:
The magnetic field due to current carrying conductor is directly proportional to a) the magnitude of current b) length of element dL c) sine of angle between r and dL and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between source and the field point. Therefore the total magnetic field due to current carrying conductor is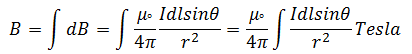
Gauss Law in Magnetism
Gauss law in magnetism states that the magnetic flux through a closed surface is zero. The integral form of gauss law is given by
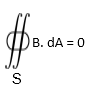
Where S is any closed surface.
Ampere’s Law
While the gauss theorem strictly deals with the electric field lines, Amperes law deals with the magnetic field lines. Ampere’s law states that the line integral of magnetic field along a closed hypothetical loop (an amperian loop) is equal to μ times the current enclosed by loop where μ is the permeability of the free space.
Difference between Biot- Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Law
Both ampere’s law and Biot-Savart’s law help us to calculate the magnitude of magnetic field lines but the basic difference between the biot-savart law and amperes law is that in ampere’s law a symmetric amperian loop is considered along a straight line charge. In other words amperes law is used for symmetrical distribution of currents, while Biotsavart’s law is used for both symmetrical and asymmetrical distribution of currents.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q.1. What is electromagnetism in physics?
Ans. In physics, electromagnetism is defined as the production of magnetic field lines by the motion of electrons in a current carrying conductor. For Example: solenoid
Q2. What is gauss law of Magnetism?
Ans. Gauss law of magnetism states that the net magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero. The integral form of gauss law is given by
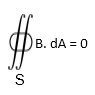
Where S is any closed surface.
Q.3. Do magnetic lines always form closed loops?
Ans. Yes, Magnetic lines always form closed loops. Field line always start from the north pole and ends in the south pole. The magnetic field lines are stronger near the poles.
Q.4. What is gauss law?
Ans. Gauss’s law states that “The net electric flux through any closed surface is equal to 1/ times the net electric charge within that closed surface (or imaginary Gaussian surface)”.
∫E.ds = q/ϵ
|
289 videos|635 docs|184 tests
|
FAQs on Magnetism & Gauss’s Law - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is magnetism and how does it relate to Gauss's Law? |  |
| 2. How does Gauss's Law for magnetism differ from Gauss's Law for electricity? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of magnetism in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How can Gauss's Law for magnetism be useful in studying magnetic fields? |  |
| 5. Can Gauss's Law for magnetism be violated in any situation? |  |

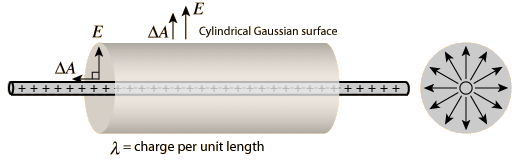 Then by applying Gauss Law,
Then by applying Gauss Law,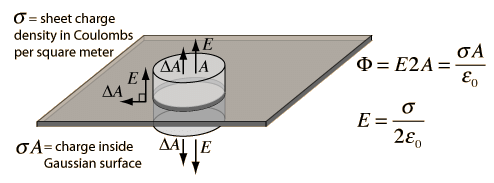 In case of an infinite sheet charge, a cylindrical Gaussian surface is considered, such that the electric field is perpendicular to the surface. As a result of which only the ends of the Gaussian surface will constitute the magnetic flux.
In case of an infinite sheet charge, a cylindrical Gaussian surface is considered, such that the electric field is perpendicular to the surface. As a result of which only the ends of the Gaussian surface will constitute the magnetic flux.