Map Based Questions: Climates of India | Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q.1: Monsoon Winds and Rainfall Patterns
a) On a blank map of India, draw arrows to show the direction of the southwest monsoon winds during summer (June to mid-July). Why their western slopes receive heavy rainfall while the Deccan Plateau to the east receives less.
b) On the same map, draw arrows to show the direction of the northeast monsoon winds during winter.
Ans:
a) Southwest Monsoon: Draw arrows from the Indian Ocean (southwest) moving northward across India, starting at the southern tip (early June) and covering the subcontinent by mid-July.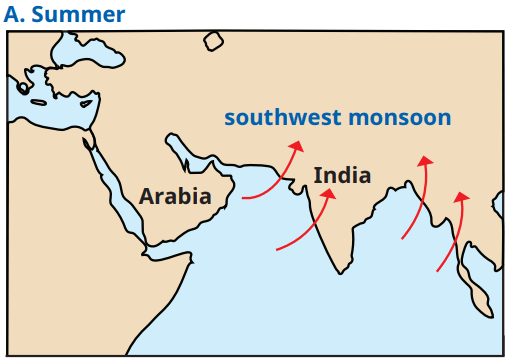
Western Ghats: Label along the western coast. Their western slopes receive heavy rainfall because they act as a barrier, forcing moisture-laden monsoon winds to rise, cool, and condense into rain. The Deccan Plateau to the east lies in the rain shadow, receiving less rainfall due to the barrier effect.
b) Northeast Monsoon: Draw arrows from the land (northeast) toward the Bay of Bengal in winter. Highlight parts of east and south India (e.g., Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh) that receive rainfall as these winds pick up moisture over the Bay of Bengal.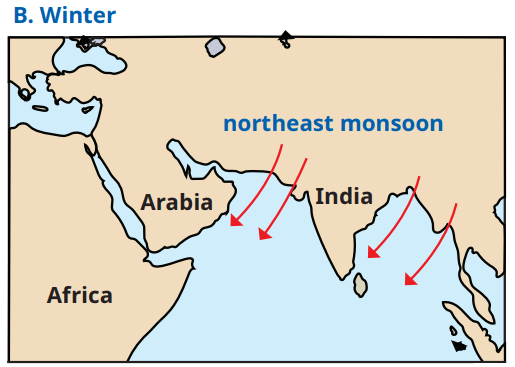
Q.2: Locate Mawsynram in Meghalaya on the map. Why does this area receive the highest average annual rainfall in the world (approximately 11,000 mm)?
Ans: Locate in Meghalaya (northeast India). It receives the highest rainfall (11,000 mm) due to its position in the path of moisture-laden southwest monsoon winds, which are forced upward by the Khasi Hills, causing heavy precipitation.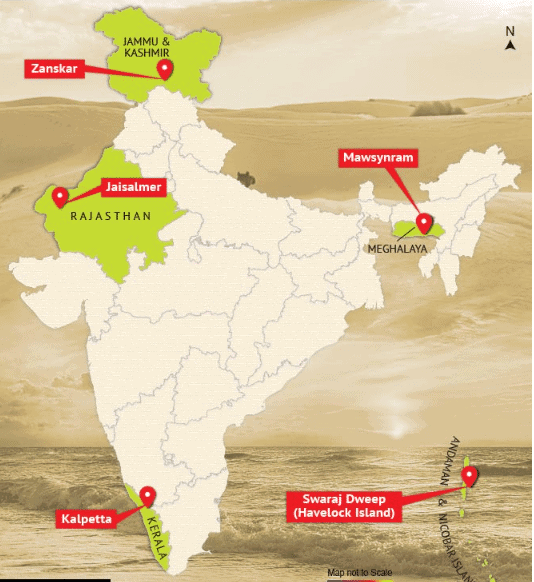
Q3: Look at a map of India given at the end of this book. Identify the climate for these cities—Leh, Chennai, Delhi and Jaipur. For each city, identify its climate type (e.g., alpine, tropical, subtropical, arid, etc.) Explain how the geographical location of each city (e.g., near the sea, in the mountains, or in a desert) influences its climate.
Ans:
Leh: Climate: Alpine. Location: In the Himalayas (high altitude). Influence: High altitude causes cold, snowy winters and cool summers due to low air density and distance from the Earth’s heated surface.
Chennai: Climate: Tropical. Location: Southern peninsula, near the sea. Influence: Proximity to the sea moderates temperatures, and low latitude near the Equator keeps it warm year-round.
Delhi: Climate: Subtropical. Location: Northern plains. Influence: Far from the sea and at a moderate latitude, it experiences very hot summers and cold winters.
Jaipur: Climate: Arid. Location: Near the Thar Desert. Influence: Far from the sea and flat topography lead to extremely hot days, cool nights, and little rainfall.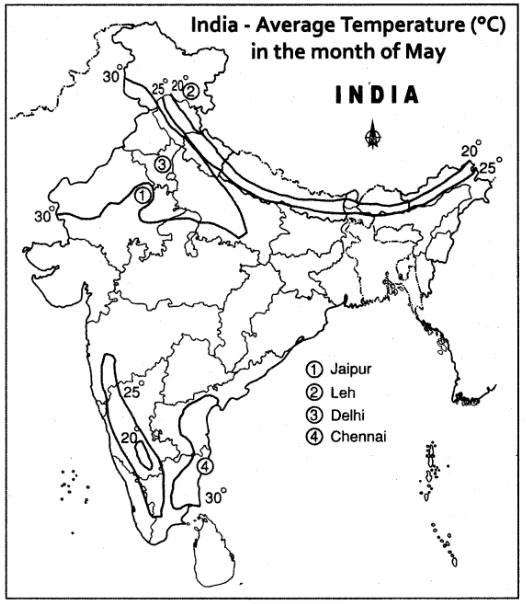
Q.4 Impact of Topography on Climate
a) Locate the Western Ghats and the Himalayas on the map. How do these mountain ranges influence the climate of the surrounding areas? For example, explain their role in the monsoon rainfall distribution or protection from certain winds.
b) Mark the Thar Desert and explain why its flat topography contributes to its arid climate.
Ans:
a) Western Ghats: Locate along the western coast. They act as a barrier, causing heavy rainfall on their western slopes during the southwest monsoon by forcing winds to rise and condense, while the Deccan Plateau to the east receives less rain.
Himalayas: Locate in northern India. They protect the subcontinent from cold desert winds of Central Asia, keeping northern India relatively warmer in winter, and cause orographic rainfall in some areas.
b) Thar Desert: Mark in western Rajasthan. Its flat topography offers no barrier to hot, dry winds from the west (e.g., from Arabia), leading to minimal rainfall and an arid climate.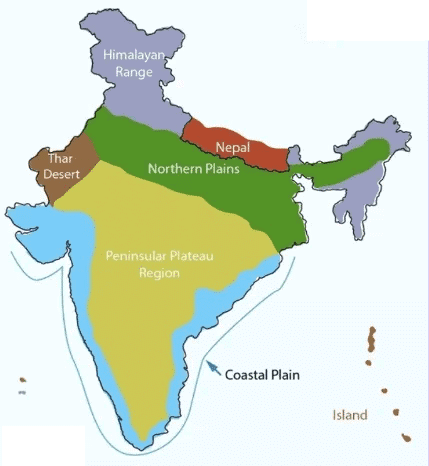
Q.5: Comparing Coastal and Inland Climates: On the map, locate Mumbai and Nagpur. Compare their climates by noting their proximity to the sea and the resulting temperature ranges (use data from the chapter: Mumbai’s range is about 14°C, Nagpur’s is about 34°C).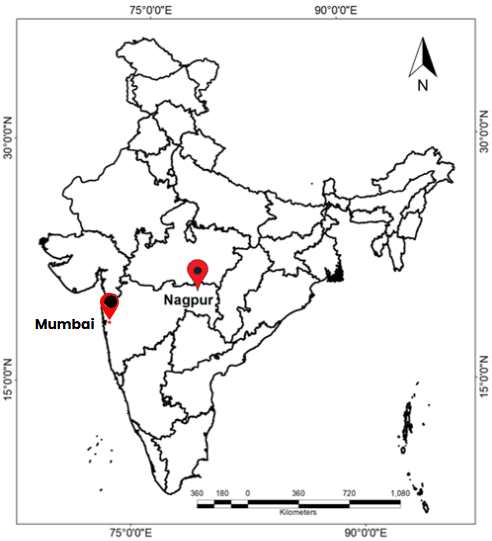
Ans: Mumbai and Nagpur: Locate Mumbai on the western coast and Nagpur in central India.
- Mumbai: Tropical wet climate, temperature range ~14°C (summers ~32°C, winters ~18°C) due to proximity to the sea, which moderates temperatures.
- Nagpur: Semi-arid climate, temperature range ~34°C (summers ~44°C, winters ~10°C) due to its inland location, far from the sea’s moderating effect.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Map Based Questions: Climates of India - Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the major types of climates found in India? |  |
| 2. How does the monsoon affect the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What factors influence the climate variations across different regions of India? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the Himalayas in influencing India's climate? |  |
| 5. How do human activities impact the climate in India? |  |
















