CA Foundation Exam > CA Foundation Notes > Accounting for CA Foundation > Mind Map: Capital and Revenue Expenditures and Receipts
Mind Map: Capital and Revenue Expenditures and Receipts | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
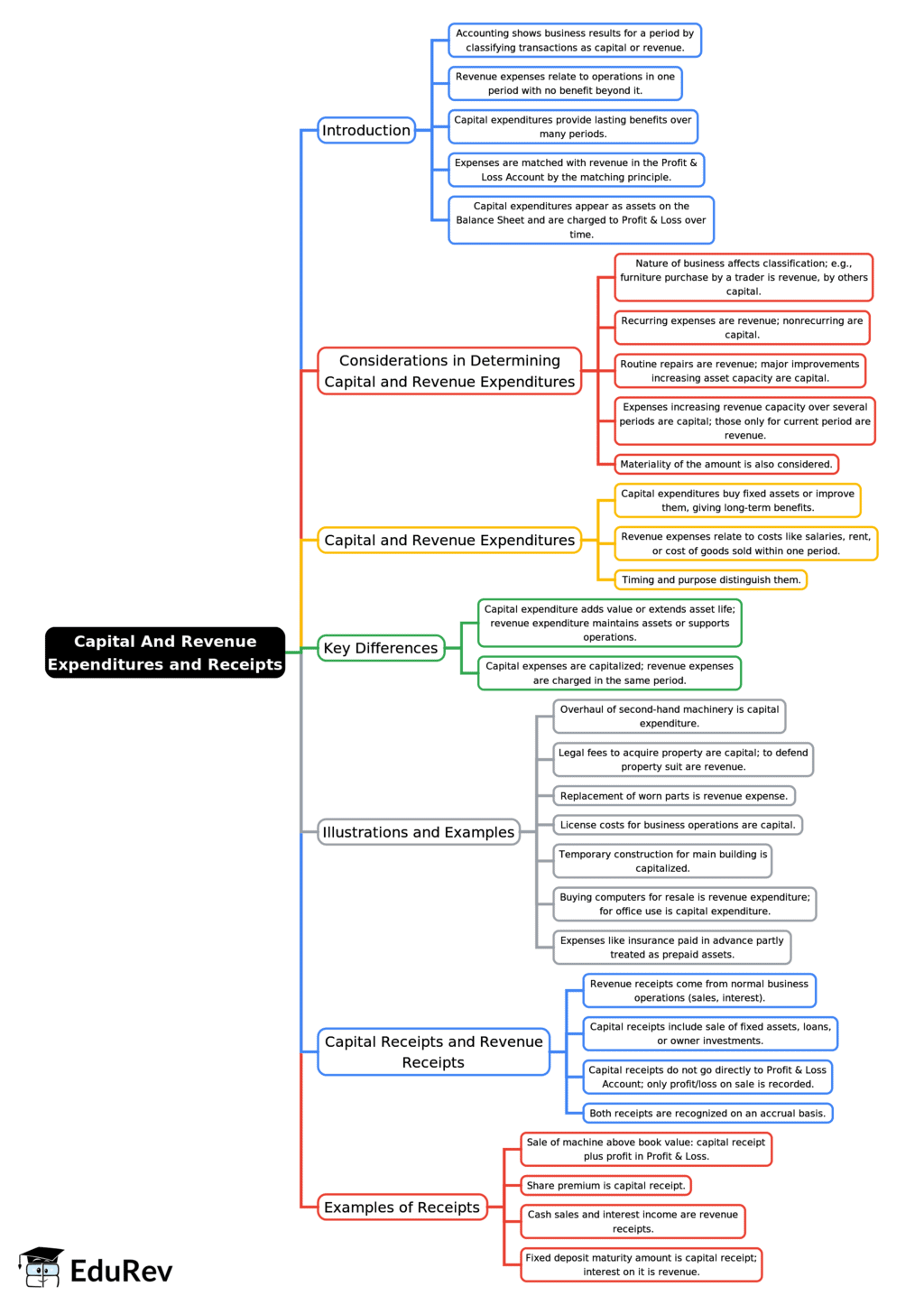
The document Mind Map: Capital and Revenue Expenditures and Receipts | Accounting for CA Foundation is a part of the CA Foundation Course Accounting for CA Foundation.
All you need of CA Foundation at this link: CA Foundation
|
68 videos|265 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Capital and Revenue Expenditures and Receipts - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What are capital expenditures and how do they differ from revenue expenditures? |  |
Ans. Capital expenditures refer to the funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, or maintain physical assets such as property, buildings, or equipment. These expenditures are typically long-term investments that provide benefits over multiple years. In contrast, revenue expenditures are short-term expenses that are necessary for the day-to-day functioning of a business, such as rent, utilities, and wages. The key difference lies in the duration of the benefits: capital expenditures provide long-term value, while revenue expenditures are consumed within a single accounting period.
| 2. Can you give examples of capital and revenue receipts? |  |
Ans. Capital receipts are funds received by a business that lead to an increase in the owner's equity or liabilities. Examples include the sale of fixed assets, loans taken, or issuing shares. On the other hand, revenue receipts are the income generated from normal business operations, such as sales revenue, interest received, or rental income. These receipts do not affect the capital structure of the business but contribute to its profitability.
| 3. How are capital and revenue expenditures treated in financial statements? |  |
Ans. Capital expenditures are recorded as assets on the balance sheet and are subject to depreciation over their useful life, which allocates the cost of the asset over time. Revenue expenditures, however, are recorded as expenses on the income statement in the period they are incurred, directly affecting the net income. This distinction is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis.
| 4. What impact do capital and revenue expenditures have on cash flow? |  |
Ans. Capital expenditures typically result in a significant outflow of cash upfront, impacting the cash flow in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement. These expenditures may lead to increased future cash flows as the assets contribute to revenue generation. Revenue expenditures, conversely, are usually smaller, recurring expenses that affect cash flow in the operating activities section, reflecting the ongoing costs required to maintain business operations.
| 5. Why is it important to distinguish between capital and revenue expenditures? |  |
Ans. Distinguishing between capital and revenue expenditures is essential for accurate financial reporting, tax calculations, and budgeting. Proper classification affects a company's profit margins, tax liabilities, and financial ratios. Misclassifying these expenditures can lead to misinformed business decisions, affecting overall financial health and operational efficiency. Understanding the difference ensures compliance with accounting standards and aids in strategic planning.
Related Searches





















