JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Mind Map: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
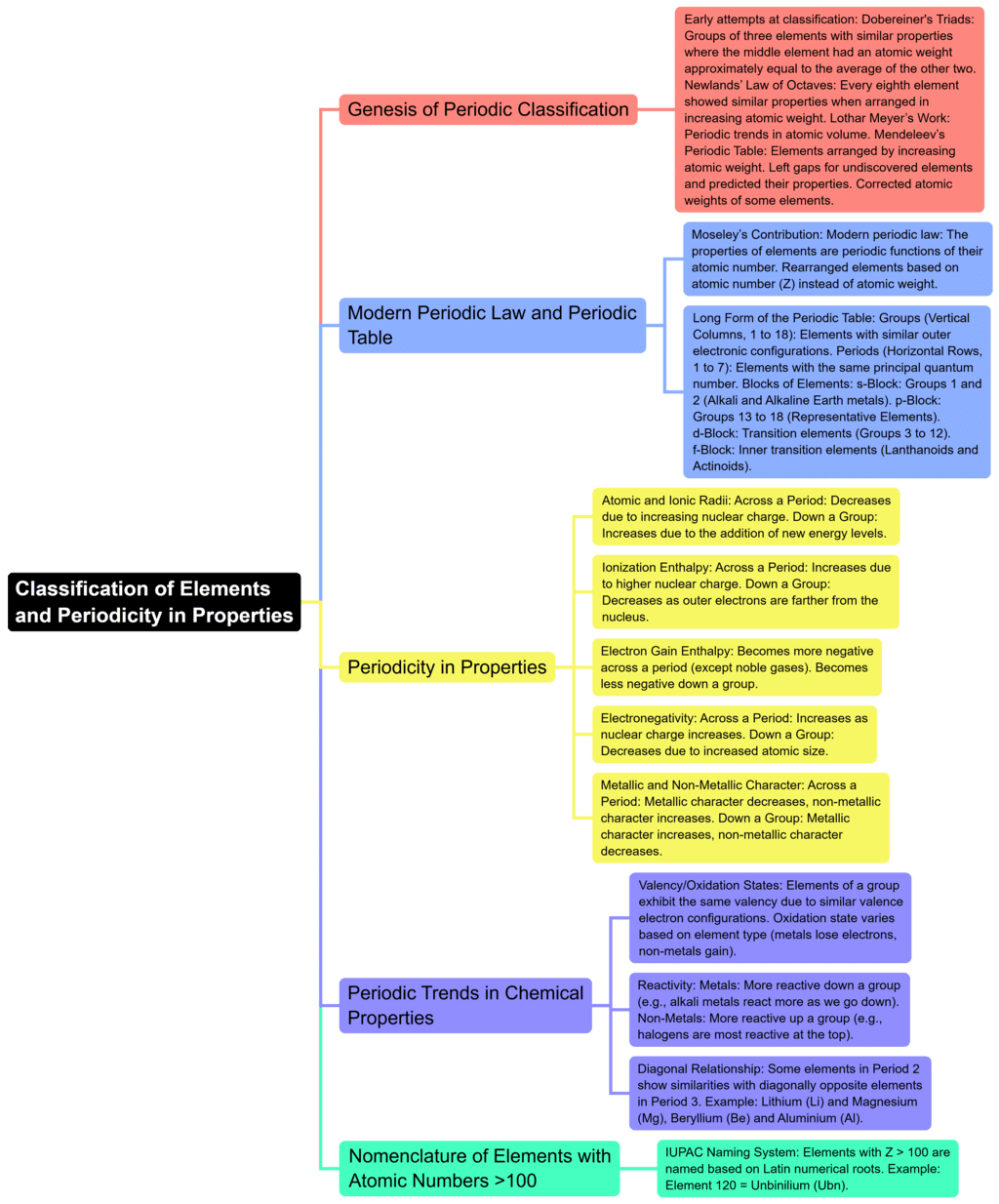
The document Mind Map: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
334 videos|656 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the major classifications of elements in the periodic table? |  |
Ans.Elements in the periodic table are primarily classified into three categories: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals, which are located on the left side and center of the table, are typically characterized by high conductivity, malleability, and ductility. Nonmetals, found on the right side, are generally poor conductors and can be gases, liquids, or brittle solids at room temperature. Metalloids exhibit properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals, making them useful in various applications such as semiconductors.
| 2. How does atomic size change across a period and down a group in the periodic table? |  |
Ans.Atomic size decreases from left to right across a period due to the increasing positive charge in the nucleus, which attracts electrons more strongly and pulls them closer to the nucleus. Conversely, atomic size increases down a group because additional electron shells are added, which outweighs the increase in nuclear charge, resulting in larger atomic radii.
| 3. What is the significance of ionization energy and how does it vary in the periodic table? |  |
Ans.Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. It generally increases across a period from left to right due to increased nuclear charge and decreased atomic radius, making it harder to remove an electron. However, ionization energy decreases down a group because the outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and are shielded by inner electrons, making them easier to remove.
| 4. What trends in electronegativity can be observed in the periodic table? |  |
Ans.Electronegativity, which measures an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond, increases across a period from left to right due to increasing nuclear charge. It decreases down a group because the increasing distance between the nucleus and valence electrons reduces the nucleus's ability to attract bonding electrons. Consequently, fluorine is the most electronegative element, while elements in the lower groups tend to have lower electronegativities.
| 5. How do the properties of alkali metals differ from those of alkaline earth metals? |  |
Ans.Akali metals (Group 1) are known for their high reactivity, low densities, and low melting points, becoming more reactive as you move down the group. They have one valence electron, which they lose easily to form positive ions (M⁺). In contrast, alkaline earth metals (Group 2) are less reactive, have higher melting points, and are denser than alkali metals. They have two valence electrons, which they can lose to form divalent ions (M²⁺), making them less reactive compared to alkali metals.
Related Searches
















