CA Foundation Exam > CA Foundation Notes > Accounting for CA Foundation > Mind Map: Depreciation and Amortisation
Mind Map: Depreciation and Amortisation | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
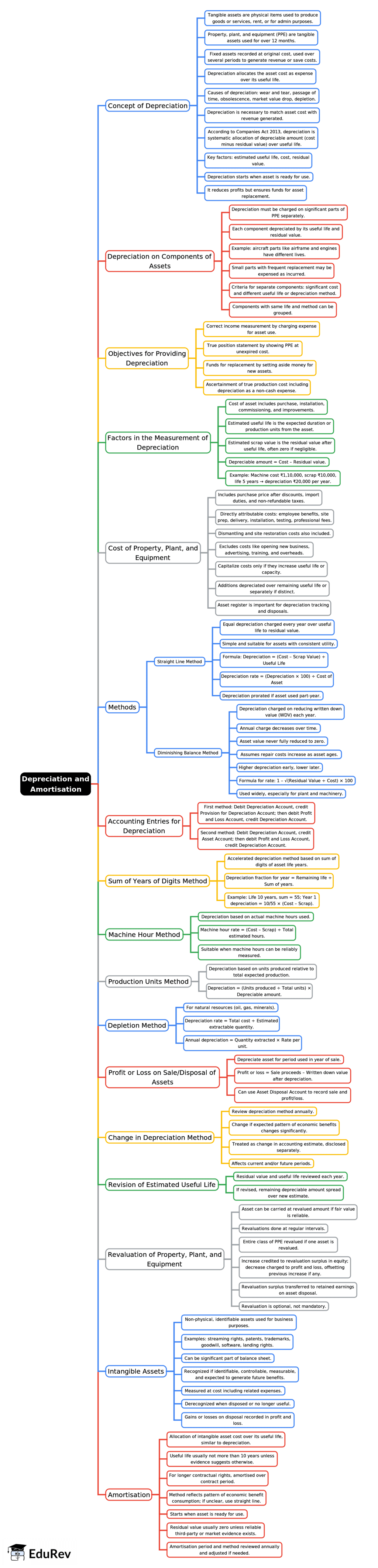
The document Mind Map: Depreciation and Amortisation | Accounting for CA Foundation is a part of the CA Foundation Course Accounting for CA Foundation.
All you need of CA Foundation at this link: CA Foundation
|
68 videos|265 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Depreciation and Amortisation - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What is the difference between depreciation and amortisation? |  |
Ans.Depreciation refers to the reduction in the value of tangible fixed assets over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or other factors. It is applicable to physical assets like machinery, buildings, and vehicles. Amortisation, on the other hand, is the process of gradually writing off the cost of intangible assets, such as patents, copyrights, or goodwill, over their useful life. Both processes help businesses allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life for accounting and tax purposes.
| 2. How are depreciation and amortisation calculated? |  |
Ans.Depreciation can be calculated using various methods, including straight-line, declining balance, or units of production. The straight-line method divides the cost of the asset by its useful life, while the declining balance method applies a fixed percentage to the asset's remaining value each year. Amortisation is typically calculated using the straight-line method, where the cost of the intangible asset is divided by its estimated useful life, resulting in equal annual expense amounts.
| 3. Why is it important for businesses to account for depreciation and amortisation? |  |
Ans.Accounting for depreciation and amortisation is crucial because it affects a company's financial statements and tax liabilities. By recording these expenses, businesses can reflect the true value of their assets on their balance sheets, leading to more accurate financial reporting. Additionally, depreciation and amortisation reduce taxable income, providing potential tax benefits. This practice also helps in strategic planning and budgeting by understanding asset replacement needs.
| 4. What are the common methods of depreciation used in accounting? |  |
Ans.The most common methods of depreciation include:
1. Straight-line method: Allocates an equal expense amount each year over the asset's useful life.
2. Declining balance method: Accelerates depreciation by applying a fixed percentage to the asset's remaining book value.
3. Units of production method: Bases depreciation on the actual usage or output of the asset, making it more variable depending on production levels.
Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the nature of the asset and the company's financial strategy.
| 5. Are there any specific tax implications associated with depreciation and amortisation? |  |
Ans.Yes, there are significant tax implications. Depreciation and amortisation reduce taxable income, which can lower a business's overall tax liability. Different jurisdictions may have specific rules regarding what can be depreciated or amortised and the methods allowed. Additionally, certain assets may qualify for accelerated depreciation under tax laws, allowing businesses to write off a larger portion of the asset's cost in the first few years of its life, thus providing immediate tax relief.
Related Searches
















