JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Electrochemistry
Mind Map: Electrochemistry | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
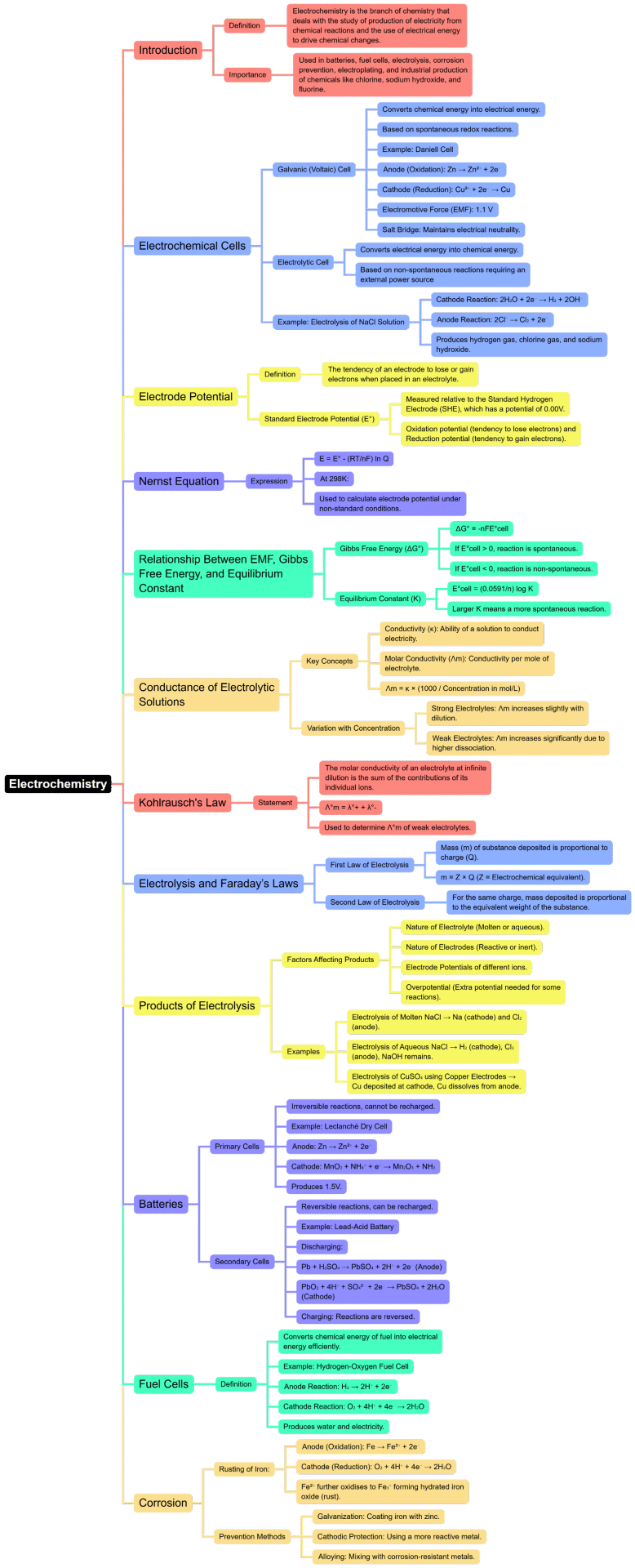
The document Mind Map: Electrochemistry | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Electrochemistry - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is electrochemistry and why is it important for JEE? |  |
Ans. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the relationship between electricity and chemical reactions. It is important for the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) because it covers fundamental concepts such as redox reactions, electrochemical cells, and applications like batteries and corrosion. Understanding these concepts is crucial for solving problems in physical chemistry and for scoring well in the exam.
| 2. What are the key concepts of electrochemistry that are frequently asked in JEE? |  |
Ans. Key concepts include Faraday's laws of electrolysis, Nernst equation, types of electrochemical cells (galvanic and electrolytic), standard electrode potentials, and the concept of cell potential. Mastery of these topics helps in solving numerical problems and understanding theoretical questions that often appear in the JEE.
| 3. How do I calculate the cell potential using the Nernst equation? |  |
Ans. The Nernst equation is given by E = E° - (RT/nF) * ln(Q), where E is the cell potential, E° is the standard cell potential, R is the universal gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred, F is Faraday's constant, and Q is the reaction quotient. To calculate cell potential, you need to know the standard potentials and the concentrations of the reactants and products.
| 4. What are galvanic and electrolytic cells, and how do they differ? |  |
Ans. Galvanic cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions, whereas electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous reactions. In galvanic cells, the anode is negative and the cathode is positive, while in electrolytic cells, the anode is positive and the cathode is negative. Understanding these differences is crucial for solving related problems in JEE.
| 5. How can I prepare effectively for electrochemistry in JEE? |  |
Ans. To prepare effectively, focus on understanding the fundamental concepts, practicing numerical problems, and familiarizing yourself with the common types of questions asked in JEE. Use NCERT textbooks, reference books, and previous years' question papers for practice. Additionally, conducting group study sessions and discussing difficult topics can enhance your understanding and retention of electrochemistry concepts.
Related Searches





















