NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Physiology > Mind Map: Gastrointestinal Physiology
Mind Map: Gastrointestinal Physiology | Physiology - NEET PG PDF Download
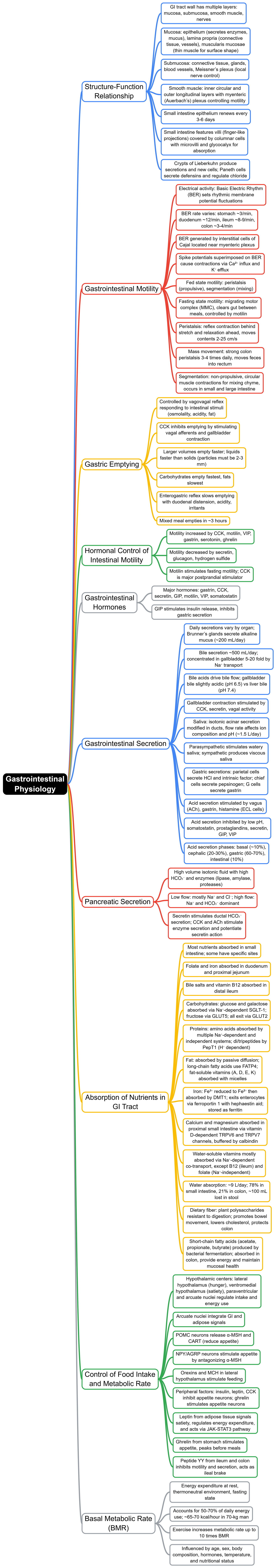
The document Mind Map: Gastrointestinal Physiology | Physiology - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Physiology.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Gastrointestinal Physiology - Physiology - NEET PG
| 1. What are the main functions of the gastrointestinal (GI) system? |  |
Ans. The main functions of the gastrointestinal system include digestion, which is the breakdown of food into smaller components; absorption, where nutrients and water are taken into the bloodstream; secretion of digestive enzymes and hormones; and motility, which is the movement of food through the digestive tract. Additionally, the GI system plays a role in immune function and the maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance.
| 2. How does the process of digestion occur in the stomach? |  |
Ans. Digestion in the stomach involves both mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanically, the stomach churns food into a semi-liquid substance called chyme. Chemically, gastric glands secrete gastric juice containing hydrochloric acid (HCl) and pepsinogen. HCl creates an acidic environment that activates pepsinogen to pepsin, an enzyme that begins the digestion of proteins. This mixture aids in breaking down food further before it moves to the small intestine for nutrient absorption.
| 3. What is the role of the small intestine in nutrient absorption? |  |
Ans. The small intestine is primarily responsible for the absorption of nutrients. It is divided into three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach and bile from the liver, which emulsifies fats. The jejunum and ileum have specialized structures, such as villi and microvilli, that increase the surface area for absorption. Nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed into the bloodstream through these structures.
| 4. What factors can influence gastrointestinal motility? |  |
Ans. Gastrointestinal motility can be influenced by several factors, including neural control (enteric nervous system and autonomic nervous system), hormonal signals (such as gastrin and cholecystokinin), and the presence of food in the stomach and intestines. Physical factors like the composition of the diet (fiber content) and medical conditions (like diabetes) can also affect motility. Stress and certain medications may further alter the motility patterns of the GI tract.
| 5. What is the significance of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal physiology? |  |
Ans. The gut microbiota consists of trillions of microorganisms living in the gastrointestinal tract and plays a crucial role in gastrointestinal physiology. It aids in the digestion of complex carbohydrates, synthesizes certain vitamins (like vitamin K and some B vitamins), and contributes to the immune response by preventing pathogenic infections. A balanced gut microbiota is essential for maintaining gut health, and imbalances may lead to conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
Related Searches















