Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Legal Studies for Class 12 > Mind Map: Human Rights in India
Mind Map: Human Rights in India | Legal Studies for Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
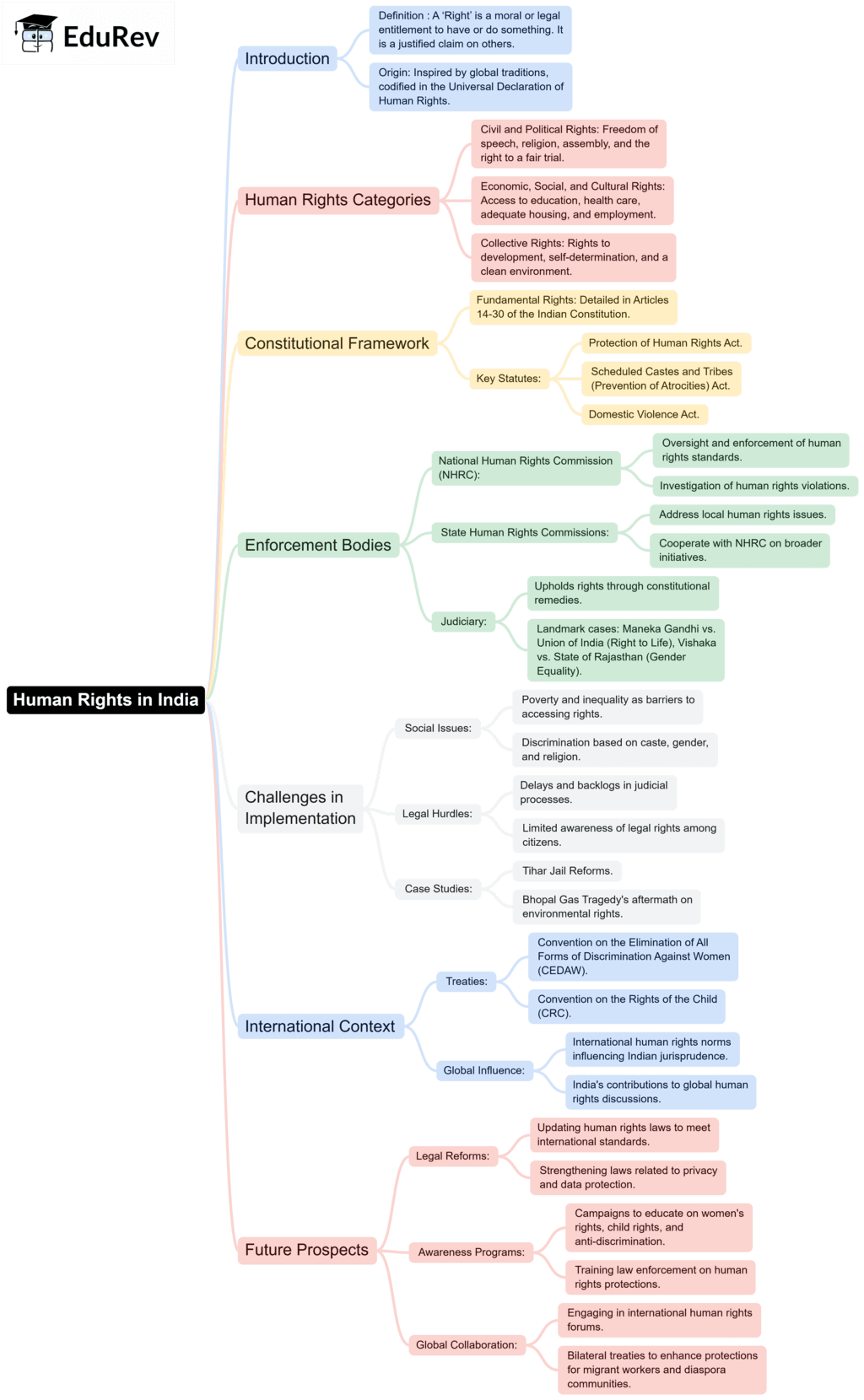
The document Mind Map: Human Rights in India | Legal Studies for Class 12 - Humanities/Arts is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Legal Studies for Class 12.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
98 videos|69 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Human Rights in India - Legal Studies for Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the fundamental human rights guaranteed by the Constitution of India? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India guarantees several fundamental human rights under Part III, which include the right to equality (Article 14-18), the right to freedom (Article 19-22), the right against exploitation (Article 23-24), the right to freedom of religion (Article 25-28), cultural and educational rights (Article 29-30), and the right to constitutional remedies (Article 32). These rights are essential for the protection of individual freedoms and the promotion of social justice.
| 2. How does the Indian judiciary protect human rights? |  |
Ans. The Indian judiciary plays a crucial role in protecting human rights through various mechanisms. It interprets the Constitution to uphold fundamental rights, evaluates the legality of government actions, and provides a platform for individuals to seek justice through public interest litigation (PIL). The Supreme Court and High Courts have established important precedents that expand the scope of human rights, ensuring they are accessible to all citizens.
| 3. What are some major human rights issues faced in India today? |  |
Ans. India faces several human rights issues, including caste-based discrimination, gender inequality, communal violence, police brutality, and the treatment of marginalized communities. Issues such as child labor, human trafficking, and the rights of indigenous peoples also remain significant concerns, prompting ongoing activism and governmental response to address these challenges.
| 4. What role do non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play in promoting human rights in India? |  |
Ans. NGOs play a vital role in promoting human rights in India by raising awareness, conducting research, and advocating for policy changes. They provide legal aid to victims of human rights violations, engage in grassroots mobilization, and work to empower marginalized communities. NGOs also monitor human rights practices and hold the government accountable, contributing to a more informed and active civil society.
| 5. How does India comply with international human rights standards? |  |
Ans. India is a signatory to several international human rights treaties, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR). The country is obligated to align its domestic laws with international standards, and it periodically reports to international bodies on its human rights practices. However, challenges remain in fully implementing these standards due to various socio-political factors.
Related Searches




















