JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Mind Map: Aromatic Hydrocarbons | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
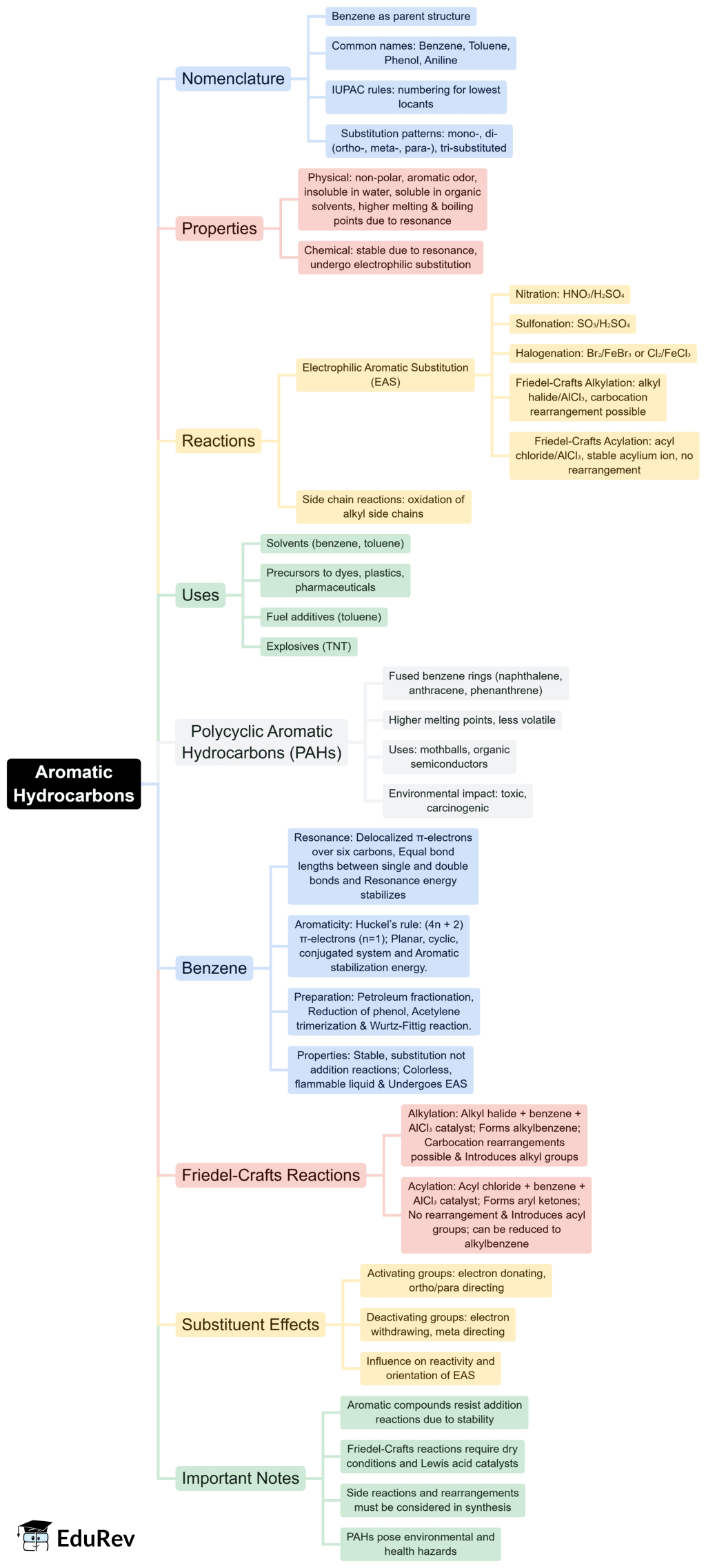
The document Mind Map: Aromatic Hydrocarbons | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Aromatic Hydrocarbons - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are aromatic hydrocarbons and how are they classified? |  |
Ans. Aromatic hydrocarbons, also known as arenes, are compounds that contain at least one aromatic ring, which is a stable ring structure with delocalized pi electrons. They can be classified into two main categories: monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which have a single aromatic ring (like benzene), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which have multiple fused aromatic rings (like naphthalene and anthracene).
| 2. What is the significance of resonance in aromatic hydrocarbons? |  |
Ans. Resonance in aromatic hydrocarbons is crucial because it explains their stability and unique chemical properties. The electrons in the pi bonds are delocalized over the entire ring structure, which lowers the overall energy of the molecule and makes them less reactive than aliphatic hydrocarbons. This delocalization results in equal bond lengths and strengths within the ring.
| 3. How do aromatic hydrocarbons react with electrophiles? |  |
Ans. Aromatic hydrocarbons react with electrophiles through a process called electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS). In this reaction, an electrophile attacks the aromatic ring, temporarily disrupting its aromaticity. The hydrogen atom is replaced by the electrophile, restoring the aromatic character of the compound. Common electrophiles include halogens, nitrating agents, and sulfonating agents.
| 4. What are some common examples of aromatic hydrocarbons used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Common examples of aromatic hydrocarbons include benzene, toluene, xylene, and naphthalene. These compounds are widely used in the production of plastics, dyes, detergents, and pharmaceuticals. For instance, benzene is used as a solvent and in the synthesis of various chemicals, while naphthalene is often found in mothballs and as a precursor to other chemical products.
| 5. What are the health and environmental concerns associated with aromatic hydrocarbons? |  |
Ans. Aromatic hydrocarbons, particularly benzene, are known to be carcinogenic and can pose serious health risks upon exposure. Prolonged inhalation or ingestion can lead to various health issues, including leukemia and other blood disorders. Environmentally, these compounds can contribute to air pollution and are persistent in the environment, necessitating careful management and regulation in industrial processes.
Related Searches





















