NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 11 > Mind Map: Motion in a Straight Line
Mind Map: Motion in a Straight Line | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
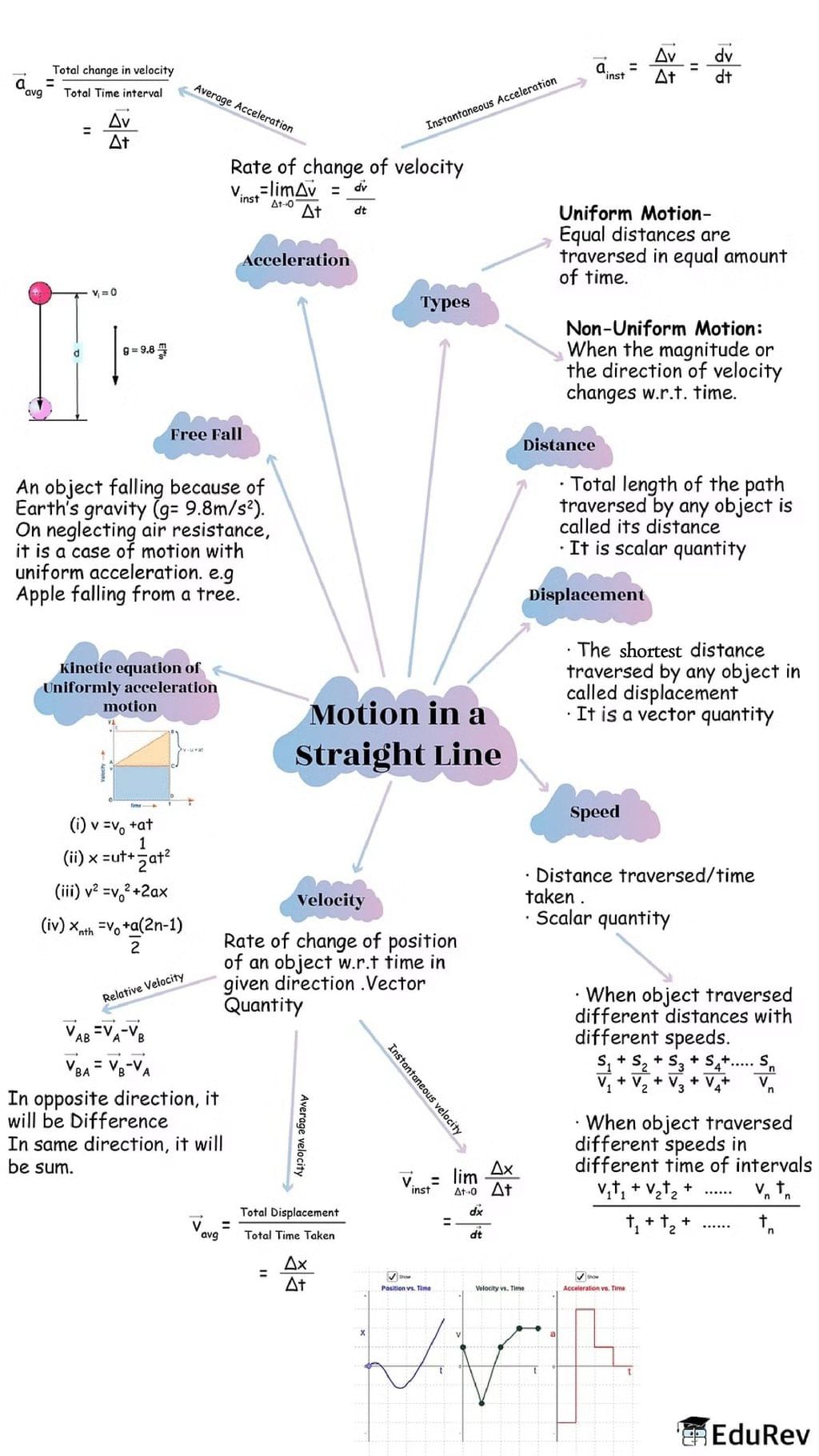
The document Mind Map: Motion in a Straight Line | Physics Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Motion in a Straight Line - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is motion in a straight line? |  |
Ans. Motion in a straight line refers to the movement of an object along a straight path. This type of motion can be described using parameters such as displacement, distance, speed, velocity, and acceleration. It is characterized by the object's position changing over time in a linear direction.
| 2. What are the key equations of motion for straight-line motion? |  |
Ans. The key equations of motion for straight-line motion are derived from the relationships between displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. The three main equations are:
1. \( v = u + at \)
2. \( s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2 \)
3. \( v^2 = u^2 + 2as \)
Here, \( u \) is the initial velocity, \( v \) is the final velocity, \( a \) is the acceleration, \( s \) is the displacement, and \( t \) is the time.
| 3. How do speed and velocity differ in straight-line motion? |  |
Ans. Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, regardless of its direction. It is calculated as the distance traveled divided by the time taken. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. Therefore, an object can have a constant speed while changing its velocity if it changes direction.
| 4. What factors affect the acceleration of an object moving in a straight line? |  |
Ans. The acceleration of an object moving in a straight line can be affected by several factors:
1. Net Force: According to Newton's second law, acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on an object and inversely proportional to its mass.
2. Mass: Heavier objects require more force to accelerate than lighter ones.
3. Friction: The presence of friction can reduce the acceleration of an object by opposing its motion.
| 5. How is displacement different from distance in straight-line motion? |  |
Ans. Displacement is a vector quantity that measures the shortest straight-line distance from an object's initial position to its final position, along with the direction. Distance, however, is a scalar quantity that measures the total length of the path traveled by the object, regardless of direction. Thus, displacement can be less than or equal to the distance traveled, but never greater.
Related Searches

















