Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Mind Map: Nationalism in India
Mind Map: Nationalism in India | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
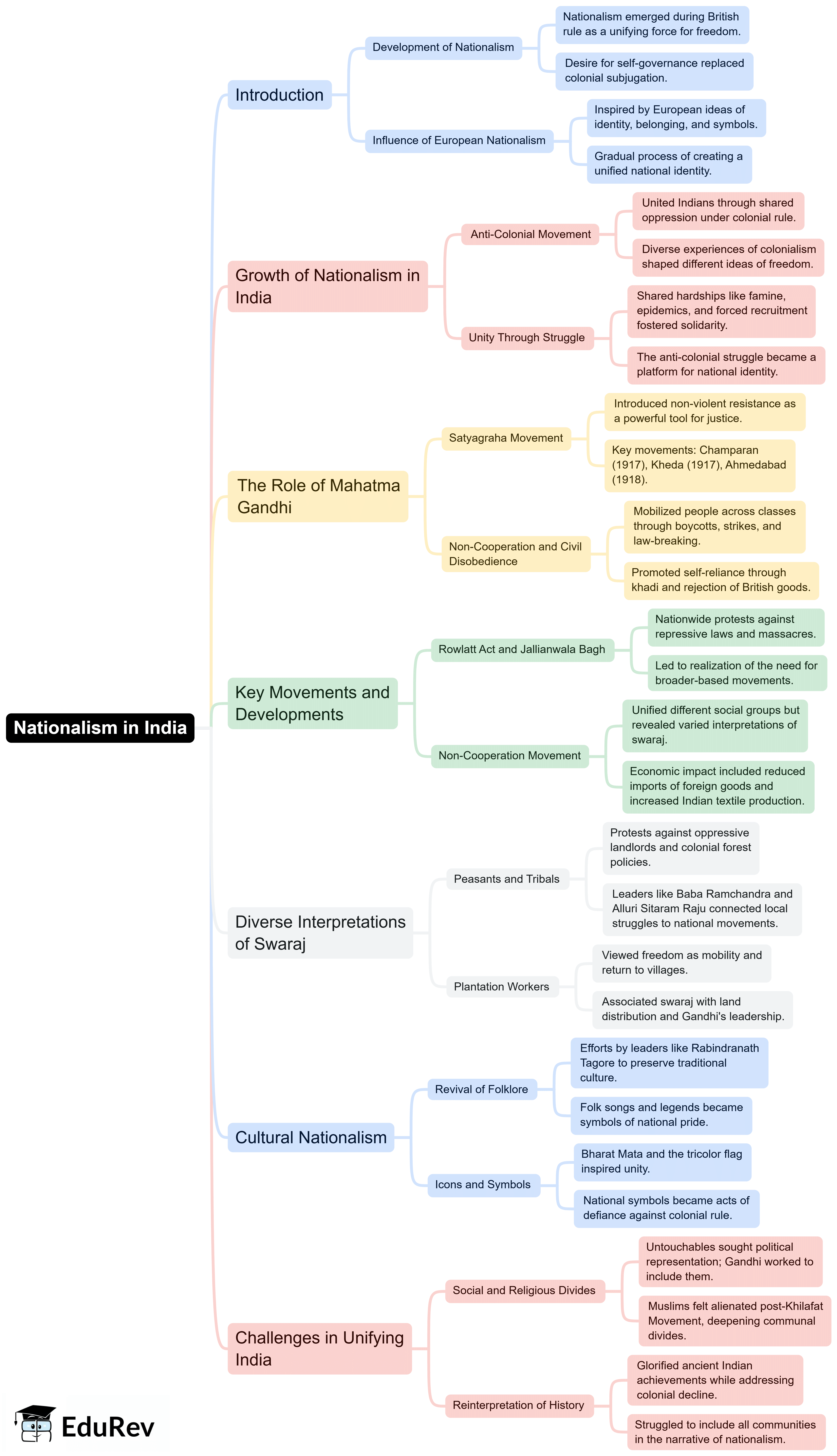
The document Mind Map: Nationalism in India | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Nationalism in India - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What were the main causes of nationalism in India during the British colonial period? |  |
Ans. The main causes of nationalism in India during the British colonial period included economic exploitation, social reforms, the influence of Western education, the impact of the First World War, and the growth of political consciousness among Indians. The British policies led to widespread poverty and discontent, while the Western ideals of liberty and equality inspired leaders and the masses to seek self-rule and assert their identity.
| 2. How did the Indian National Congress contribute to the nationalist movement? |  |
Ans. The Indian National Congress (INC) played a pivotal role in the nationalist movement by providing a platform for political dialogue and mobilizing public opinion against British rule. Established in 1885, the INC united various Indian communities and advocated for greater political rights, eventually leading to mass movements like the Non-Cooperation Movement and the Quit India Movement, which galvanized the public for independence.
| 3. What role did prominent leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru play in Indian nationalism? |  |
Ans. Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru were central figures in the Indian nationalist movement. Gandhi introduced non-violent resistance and civil disobedience as effective strategies against British rule, emphasizing mass participation. Nehru, as a leader of the INC, advocated for a secular and democratic vision for India. Their combined efforts helped to unify diverse groups under the common goal of independence.
| 4. What impact did World War II have on the Indian nationalist movement? |  |
Ans. World War II significantly impacted the Indian nationalist movement by intensifying the demand for independence. The British decision to involve India in the war without consulting Indian leaders led to widespread resentment. This situation catalyzed the Quit India Movement in 1942, where Indians called for an end to British rule, further straining British resources and commitment to maintaining control over India.
| 5. How did the concept of nationalism in India differ from that in Europe? |  |
Ans. Nationalism in India differed from that in Europe primarily in its focus on anti-colonial struggle rather than ethnic or cultural homogeneity. Indian nationalism was characterized by a broader coalition of diverse religious and cultural groups uniting against colonial oppression, rather than a singular national identity based on ethnicity. This inclusiveness aimed at achieving independence while promoting unity among India's varied populations.
Related Searches






















