Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Maths Olympiad Class 6 > Mind Map: Symmetry
Mind Map: Symmetry | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
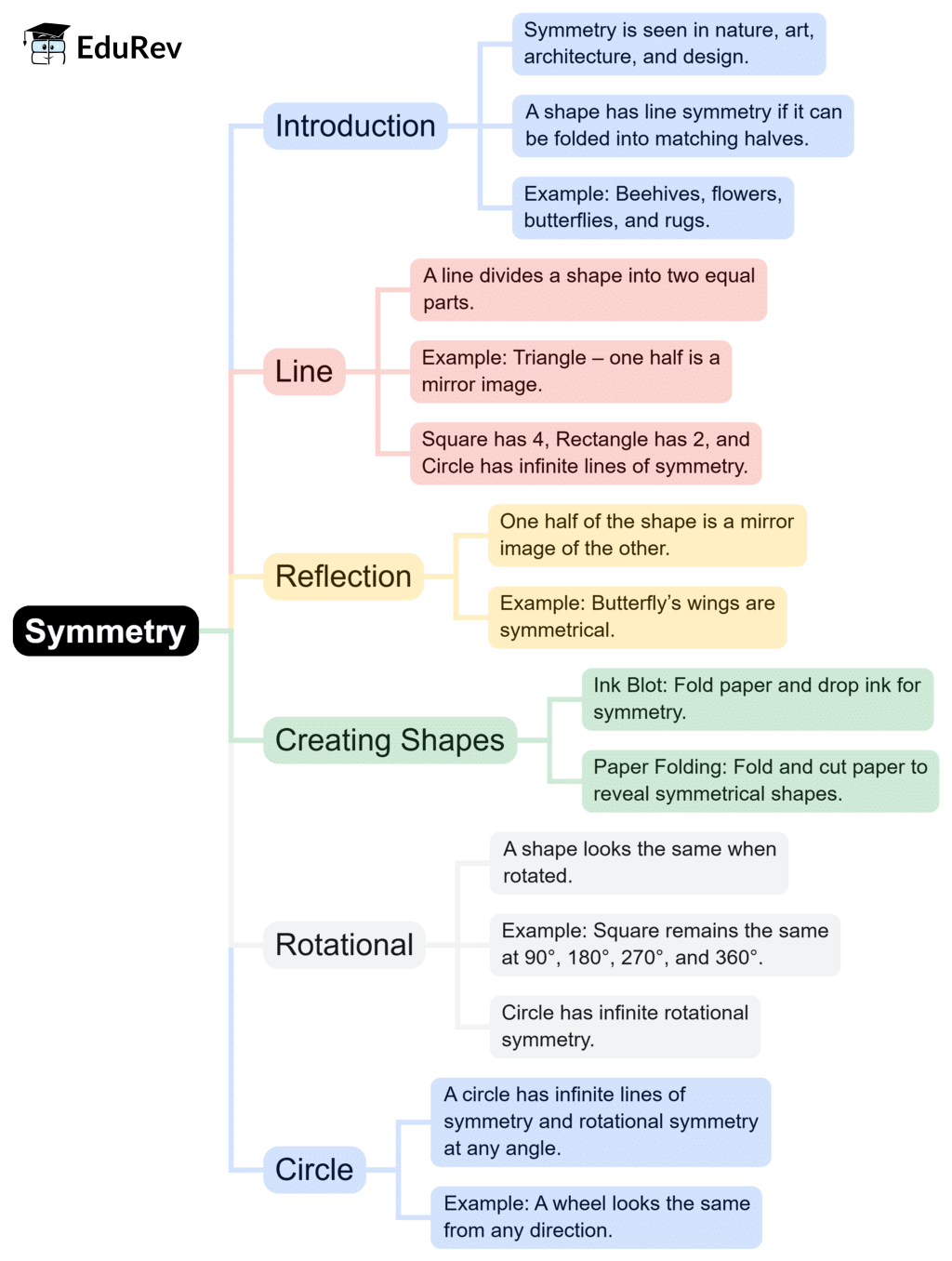
The document Mind Map: Symmetry | Maths Olympiad Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Maths Olympiad Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Symmetry - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is symmetry in geometry? |  |
Ans.Symmetry in geometry refers to a property where a shape or object can be divided into parts that are arranged in a balanced and proportional manner. When an object is symmetrical, one half is a mirror image of the other half. Symmetry can be found in various forms, including line symmetry (or reflectional symmetry), rotational symmetry, and translational symmetry.
| 2. How can we identify line symmetry in shapes? |  |
Ans.Line symmetry can be identified by drawing a line (called the line of symmetry) through a shape. If the two halves of the shape on either side of the line match perfectly, the shape has line symmetry. Common shapes that exhibit line symmetry include squares, rectangles, and circles.
| 3. What are some everyday examples of symmetry? |  |
Ans.Everyday examples of symmetry include the human face, butterflies, leaves, and architectural designs. For instance, a butterfly has wings that are mirror images of each other, and many buildings have symmetrical facades that create a pleasing appearance.
| 4. How do we find rotational symmetry in shapes? |  |
Ans.Rotational symmetry is found when a shape can be rotated around a central point and still look the same at certain angles. To find it, you can rotate the shape and check if it matches its original position. For example, a flower with five petals has rotational symmetry because it looks the same when rotated by 72 degrees.
| 5. Why is symmetry important in mathematics and art? |  |
Ans.Symmetry is important in mathematics because it helps in understanding shapes, patterns, and geometric properties. In art, symmetry contributes to aesthetic appeal and balance in designs. Artists often use symmetry to create visually pleasing compositions, drawing the viewer's attention and creating harmony in their work.
Related Searches





















