Mirror Formula & Magnification | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Magnification
 Power of a Mirror
Power of a Mirror
The power of a mirror is defined as
Convex Mirrors
Give erect, virtual and diminished image.In convex mirror, the field of view is increased as compared to plane mirror.
It is used as rear-view mirror in vehicles.
Concave Mirrors
Give enlarged, erect and virtual image, so these are used by dentists for examining teeth. Due to their converging property concave mirrors are also used as reflectors in automobiles head lights and search lights.
A real image can be taken on a screen, but a virtual image cannot be taken on a screen.
As focal length of a spherical mirror depends only on the radius of mirror and is independent of wavelength of light and refractive index of medium so the focal length of a spherical mirror in air or water and for red or blue light is same.
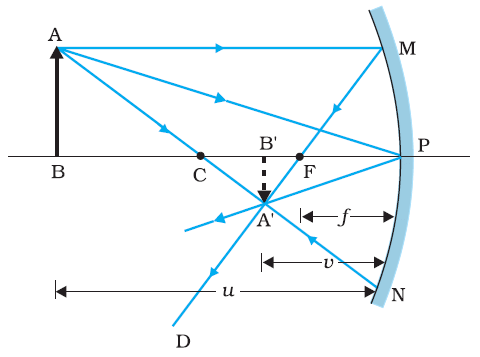
Mirror Formula
The relation between the distance of the object from the pole of the spherical mirror (u), the distance of the image from the pole of the spherical mirror (v) and its focal length (f) is given by the mathematical formula :
It must be remembered that focal length (f) of a spherical mirror is half the radius of curvature (R).
Thus, (i) R = 2f, (ii) f =
Important Points in using the Mirror Formula
(i) Put the correct signs of known variables according to the sign convention.
(ii) Do not put the sign of an unknown variable. The sign will be automatically appeared during calculations.
(iii) If the calculated sign turns out to be positive, then the variable calculated is behind the mirror. However, if calculated sign turns out to be negative, then variable is to be in front of the mirror.
Linear Magnification Produced by Spherical Mirrors
The ratio between the height of the image produced by the spherical mirror to the height of the object is called the linear magnification.
where m = magnification
hi = height of the image
ho = height of the object
Linear Magnification when the Image is Real
As we normally take the object above the principal axis, therefore, h0 is always positive. The real image is always inverted and is formed below the principal axis.
Therefore, hi is always negative. Thus, Linear magnification for real images = is always negative.
Linear Magnification when the Image is Virtual
In case of virtual image. it is erect and formed above the principal axis. Thus, h0 and hi are both positive.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is equal to the ratio of the distance of the image from the pole of the mirror (v) to the distance of the object from the pole of the mirror (u) with a minus sign.
Linear magnification,
Thus Linear magnification, =
Important Points in using Magnification Formula
(i) Put the correct signs of known variables according to the sign convention.
(ii) If 'm' is known, take the sign for virtual image positive and for real image negative.
(iii) Do not put the sign of unknown variables. The sign will automatically come up during calculations.
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Mirror Formula & Magnification - Science Class 10
| 1. What is magnification? |  |
| 2. What is the mirror formula? |  |
| 3. What is the linear magnification produced by spherical mirrors? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between convex and concave mirrors? |  |
| 5. How is the power of a mirror calculated? |  |






















