Mnemonics: The World of Metals and Non-metals | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Properties of Metals |

|
| 2. Distinguishing Properties of Metals and Non-Metals |

|
| 3. Rusting Conditions: |

|
| 4. Preventing Rust: Galvanisation |

|
| 5. Uses of Non-Metal |

|
1. Properties of Metals
Mnemonic: Hi, do cows like Sheep?
- Hi - Hard
- Do – Ductile
- Cow – Conductors (good) of heat and electricity
- Like – Lustrous
- Sheep – Sonorous: Can make ringing sounds
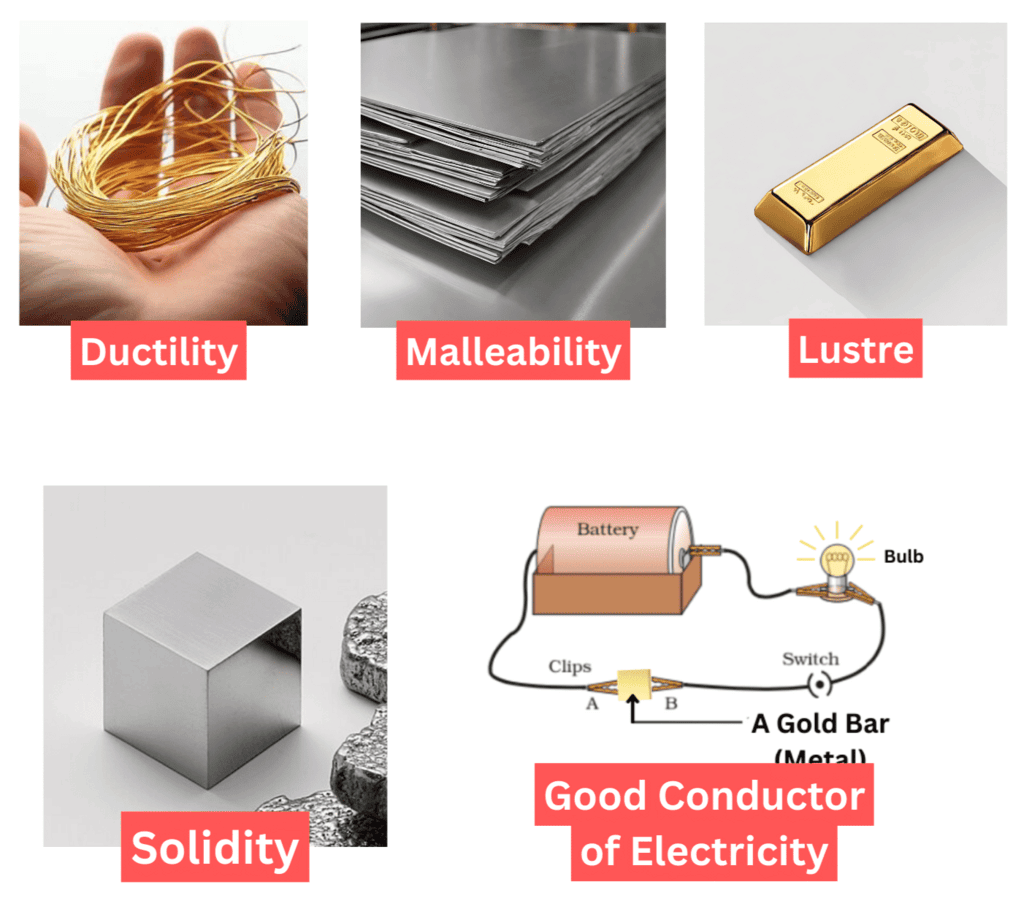
Mnemonic Explanation: This sentence helps recall the key characteristics of metals: they are shiny, hard, ductile, conduct heat and electricity, have metallic lustre, and are sonorous.
2. Distinguishing Properties of Metals and Non-Metals
(i) Malleability vs Brittleness
Mnemonic: Metal Bends, Non-metal Breaks
- Metal → Bends into sheets (Malleable)
- Non-metal → Breaks into pieces (Brittle)
Mnemonic Explanation: This short phrase distinguishes how metals and non-metals behave when hammered. Metals are malleable; non-metals are brittle.
(ii) Sonority
Mnemonic: Metal Bells Sing, Wood Just Thuds
- Metal Bells Sing → Metals are sonorous
- Wood Just Thuds → Non-metals are not sonorous
Mnemonic Explanation: Highlights how metals ring when struck, while non-metals don’t.
(iii) Heat Conduction
Mnemonic: Metal Spoon Burns, Wooden Spoon Can't
- Metal Spoon Burns – Good conductor of heat
- Wooden Spoon Can't– Poor conductor (remains cool)
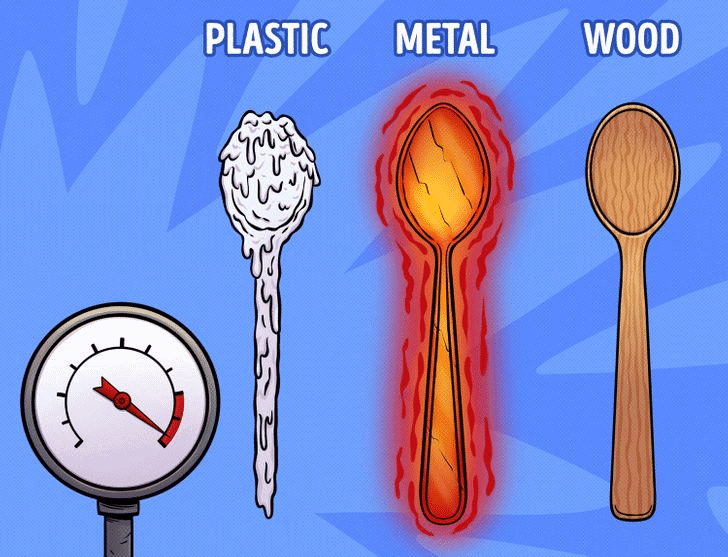
Mnemonic Explanation: Helps remember that metals conduct heat, non-metals like wood do not.
(iv) Acidic or Basic Oxides
Mnemonic: Metal Base, Non-metal Acid – MBA
Easy recall because “MBA” is a popular degree → memory anchor.
- Metal → Base (e.g., Magnesium oxide is basic)
- Non-metal → Acid (e.g., Sulfur dioxide forms acid)
Mnemonic Explanation: Helps identify the nature of oxides based on whether they come from metals or non-metals.
3. Rusting Conditions:
Mnemonic: "RAW → Rust needs Air + Water."
Mnemonic Explanation: This mnemonic simplifies the conditions required for rusting:
- R = Rust: Rusting specifically occurs in iron and steel, forming reddish-brown flakes.
- A = Air (Oxygen): Oxygen from the air is essential for the rusting reaction.
- W = Water (Moisture): Water provides the medium for oxygen to react with iron.
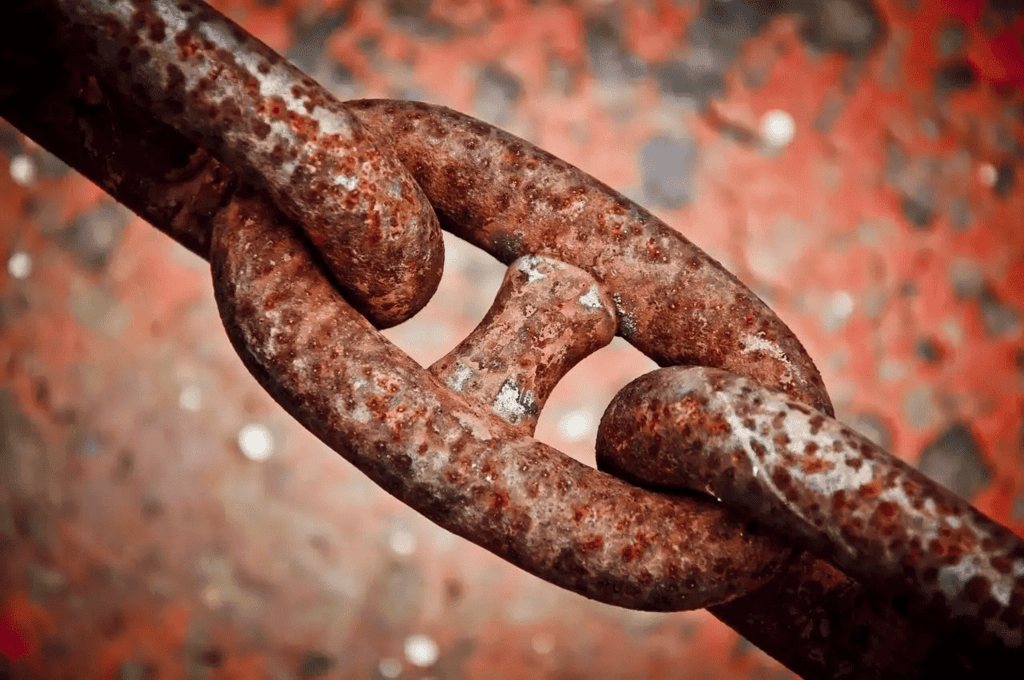

It reminds us that rusting requires both air and water (moist air), and iron won’t rust in dry air or water alone.
4. Preventing Rust: Galvanisation
Mnemonic: Paint Oil Zinc (POZ)
Mnemonic Explanation: This mnemonic covers methods to prevent iron from rusting:
- Paint: Painting iron surfaces creates a barrier against air and moisture.
- Oil: Applying oil or grease forms a protective layer to block moisture and air.
- Zinc: Galvanisation involves coating iron with zinc to prevent rusting.
This concise mnemonic helps recall practical ways to protect iron objects like tools or bridges.
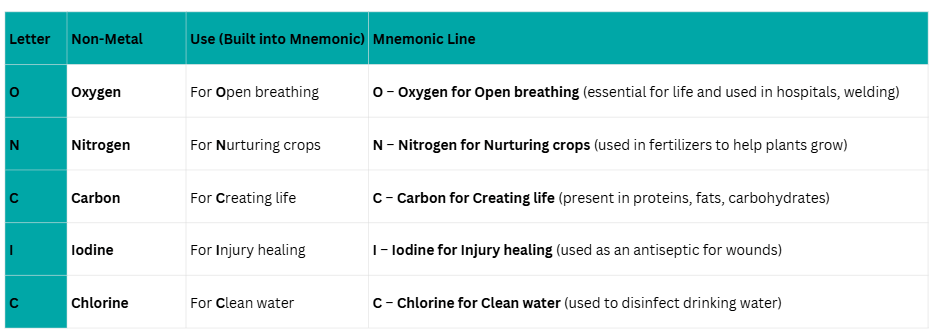
5. Uses of Non-Metal
Mnemonic: ONCIC
Mnemonic Explanation: With these, you can relate the first letter of each non-metal with the same letter function.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: The World of Metals and Non-metals - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the common properties of metals? |  |
| 2. How can we distinguish between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What conditions are necessary for rusting to occur? |  |
| 4. How can rusting be prevented? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of non-metals? |  |















