Morphology of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Flowering Plants |

|
| Venation |

|
| What is Inflorescence? |

|
| Types of Inflorescence |

|
| Special Type of Inflorescence |

|
Flowering Plants
Flowering plants are the most diverse group of land plants with 300,000 known species. These are also known as angiosperms and produce seed-bearing fruits. It is believed that the flowering plant evolved from gymnosperms during the Triassic period and the first flowering plant emerged 140 million years ago.
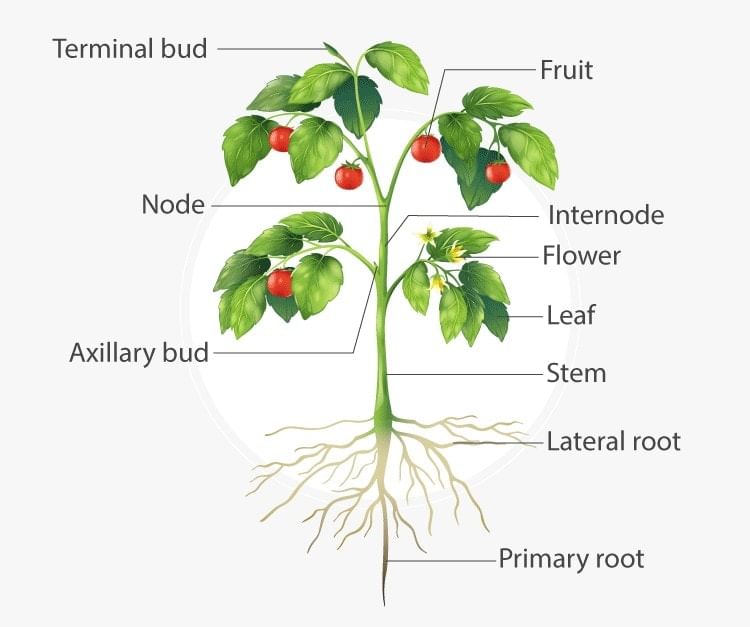 Structure of Plant
Structure of Plant
Flowers are the reproductive organs of the flowering plants and the most important feature that distinguishes them from other seed plants. These have led to the speciation of angiosperms that helps them to adapt to diverse ecological niches.The flowering plants reproduce by the process of pollination. In this, the pollen grains transfer from the anther of the male flowers to the stigma of the female flower where fertilization occurs and seed is formed.
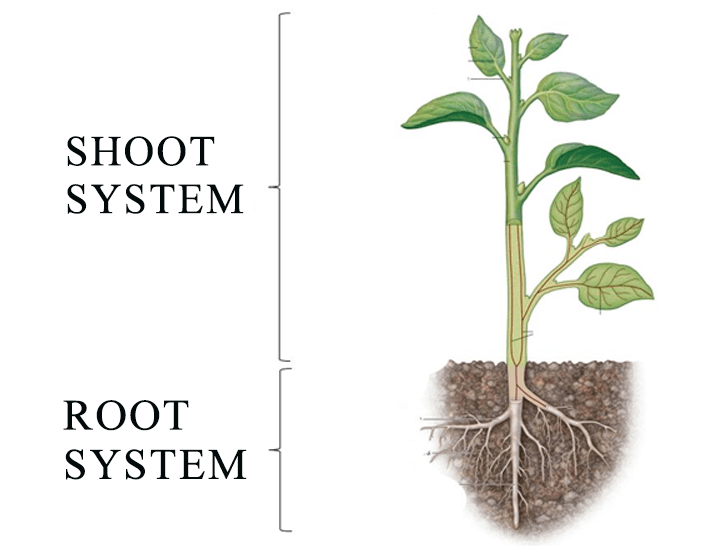
When we look into the morphology of flowering plants, a plant has two systems root system and shoot system. The underground part is called the root while the one above is named the shoot.
Root System
The root is a brown, nongreen and underground part of a plant. Root with their branches is collectively called a root system. There are three types of the root system:
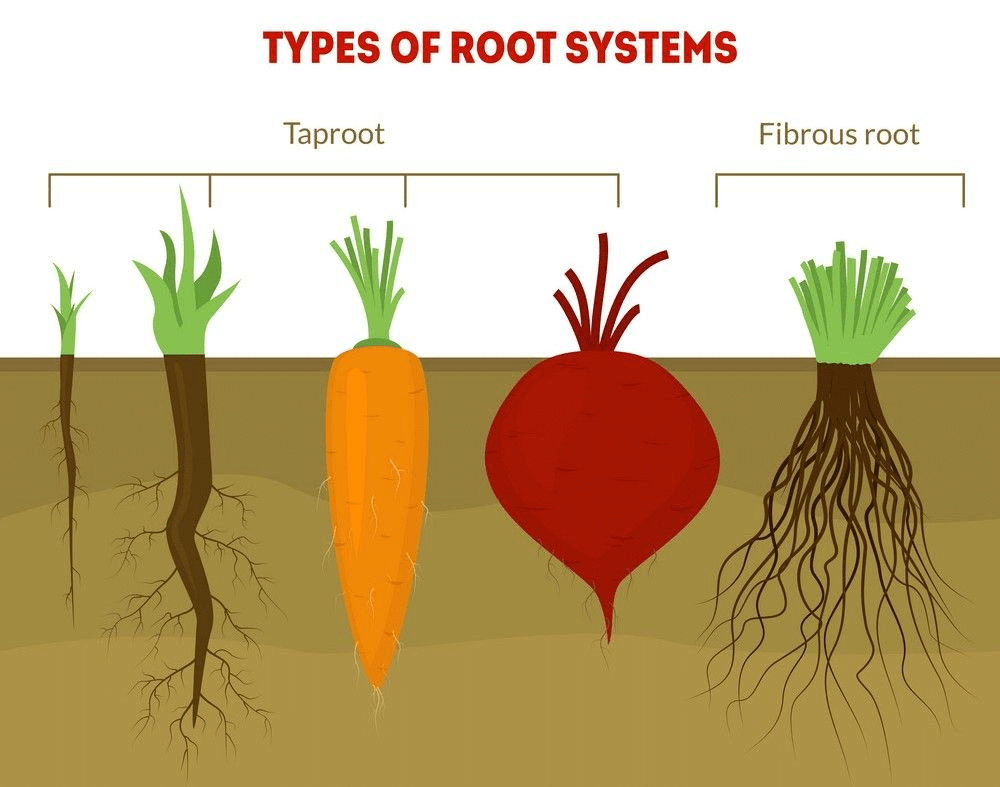
Taproot System
- The taproot is mainly found in dicotyledonous plants. It develops from the radicle of the germinating seed, along with its primary roots and branches, giving rise to the taproot system. Mustard seeds, mangoes, grams and banyan are a few examples of dicotyledonous plants with taproot system.
The Fibrous root System
- The fibrous root is mainly found in ferns and in all monocotyledonous plants. This root develops from thin, moderately branching roots or primary roots, growing from the stem. The fibrous root system usually does not penetrate deep into the soil, therefore, on full maturity, these roots look like a mat or a carpet on the floor. Wheat, paddy, grass, carrots, onion, grass are a few examples of monocotyledonous plants with the fibrous root system.
The Adventitious root System
- The roots which originate from any part of the plant body other than the radicle is called the adventitious root system. This root system is mainly found in all monocotyledonous plants. In plants, the adventitious root system is used for various purposes, like mechanical support, vegetative propagation, etc. Banyan tree, maize, oak trees, horsetails are a few examples of monocotyledonous plants with the adventitious root system.
Functions of Root
General functions of a root include:
- Storage.
- Anchorage.
- Absorption of water and minerals.
Regions of Root
The three regions of a root are-
- The Root Cap.
- The region of maturation.
- The region of Elongation.
Shoot System
Another essential part of the plant is its stem. It is the ascending part of the plant axis which bears branches, leaves, flowers, fruits and helps in the conduction of water and minerals. It is the aerial part of the plant, developed from the plumule of an embryo or the germinating seeds. Young stems are usually green in colour and subsequently becomes woody and brown. The stem is modified into certain structures according to the function they perform.
Characteristics of Stem
Some of the important characteristics of the stem are:
- The stem develops from the plumule and epicotyl of the embryo.
- The stem is erect and grows away from the soil towards the light.
- There is a terminal bud at the apex of the stem.
- In angiosperms, the shoot is differentiated into nodes and internodes.
- Young stems are green and photosynthetic.
- Multicellular hair is present.
- The stem and branches of mature plants bear fruits and flowers.
Different forms of Stem
The stem is modified into the following different forms:
- Suckers.
- Runners.
- Climbers.
- Tubers.
- Rhizome.
- Tendrils.
- Thorns.
- Cladode.
Leaves
The leaf is a laterally borne structure and usually flattened. It is the main photosynthetic part of the plants. It absorbs light and helps in the exchange of gases through the stomata. The main parts of the leaf include the leaf base, petiole, and lamina. They grow at the node and bear a bud at the axil. The arrangement of veins and veinlets in a leaf is called venation. The leaves are green because of the presence of the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and have a tiny pore or opening called stomata, where the gaseous exchange takes place. Leaves can be further classified into simple and compound leaf, which are based on the pattern of a leaf blade. There are other types of leaves and are classified based on their shapes, arrangements of leaves, and Venation.
Characteristics of Leaves
- The leaf arises from the node.
- It is exogenous in origin.
- It has a bud at its axis.
- The growth of the leaf is limited.
- The leaves do not bear an apical bud.
Modifications of Leaves
Leaves are modified according to the functions they perform. The different structural forms of leaves include:
- Leaf Tendrils.
- Spines.
- Storage Leaves.
- Insect-catching leaves.
Functions of Leaves
Some of the important functions performed by leaves are:
- Photosynthesis.
- Transpiration.
- Storage.
- Guttation.
- Defence.
Understanding the different types of venations is important as it helps in plant identification and classification. Additionally, venation plays a role in understanding the adaptations of plants to their environment, as the pattern of veins affects the distribution of resources within the leaf.
Venation
The arrangement of veins and veinlets in lamina or leaf blade of a leaf. It plays a crucial role in the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars within the leaf.
It is of two types.
1. Reticulate
- In this type of venation many veins are divided into various branches (veinlets) and form a net-like structure.
- Many smaller veins called veinlets arise from larger veins, creating an web like network.
- It is found in dicots.
- *Exception – Calophyllum (It has parallel venation)
2. Parallel
- In this type of venation, all veins run parallel to each other, and they do not form network.
- They extend from the base of the leaf to the tip, maintaining a consistent distance between each other.
- It is found in monocots.
- Exception(*) – Smilax (It has reticulate venation)
[Question: 810405]
Types of Leaf
leaves are one of the most important plant organs involved in photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration.
There are two types of Leaves
1. Simple Leaf
- Simple leaves are those that have only one lamina and are connected to the main stem by a petiole. The petiole is a slender stalk that joins the leaf blade to the main stem or branch of the plant. It acts as a support structure, allowing the leaf to be positioned optimally for light absorption during photosynthesis.
- It is characterized by having only one leaf blade or lamina, which is not divided into smaller leaflets.
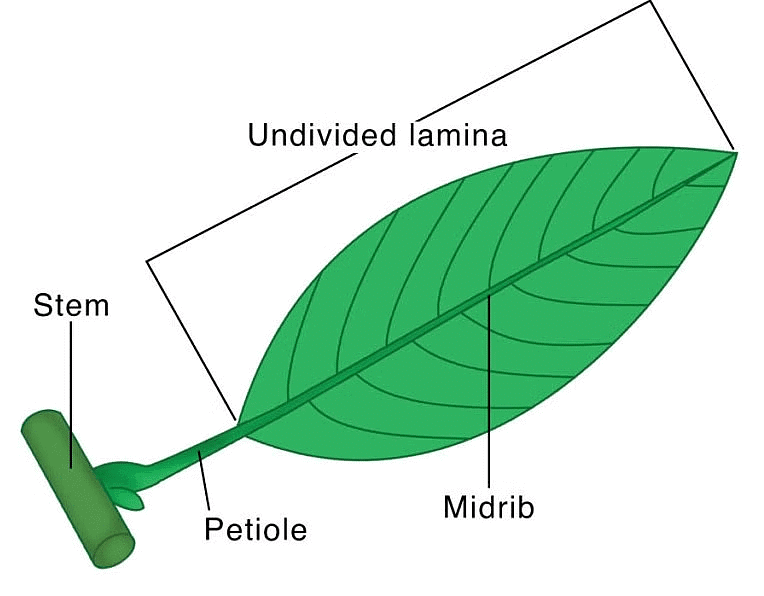
- The lamina of a simple leaf never gets divided into smaller leaflets.
Examples: Maples, Oregano, Banana, Guava, Mango, Black Cherry.
2. Compound Leaf
- A compound leaf is composed of multiple leaflets attached to the midvein, having their own stalks.
- Each leaflet of a compound leaf remains attached to the main stem by a short stem-like structure called the rachis.
- Each leaflet is similar to a small leaf, but they are not individually connected to the stem.
- Examples: Neem, Clover, Rose, Hickory, Walnut, Pecan.
There are two types of compound leaves

a) Pinnately Compound
- Number of leaflets are present on a common axis called rachis.
- In pinnately compound leaves, multiple leaflets are arranged along a central stalk called the rachis.
- The arrangement of leaflets resembles the shape of a feather or a pinnate structure, hence the name "pinnately compound.
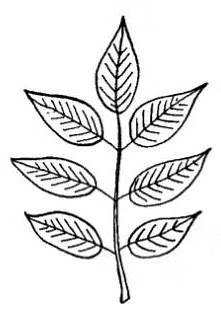 Example - Neem, Rose plants, Walnut trees, and Pecan trees.
Example - Neem, Rose plants, Walnut trees, and Pecan trees.
b) Palmately Compound
- The leaflets are attached at a common axis at the tip of petiole.
- The arrangement resemble the shape of an open palm or hand, hence the name "palmately compound.
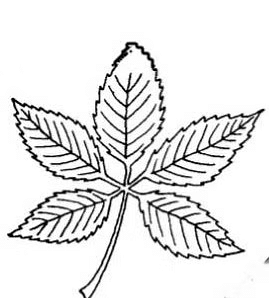 PalmatelyExample - Silk Cotton
PalmatelyExample - Silk Cotton
[Question: 810406]
Modifications of Leaves
When leaf is modified in a different structure to perform functions other than photosynthesis is called modification of leaf.
- Leaf tendril: In this, whole leaf is modified into a wire-like structure helping leaves to climb which is called leaf tendril
Example: Lathyrus aphaca (wild pea) - Leaf spine - Leaves or any part of leaflet are modified into pointed spine for defense function.
Example: Opuntia , Aloe, Argemone . - Leaf scale - In this leaves become thin, dry and form a membrane or paper-like structure and serve to protect axillary buds or store food and water as in onion.
Example: Ficus and Tamarix , Ruscus. - Leaf pitcher - Leaves of some plants are modified to pitcher shape.
Example: Nepenthes, Dishidia.
Note: Dionaea (Venus flytrap) is insectivorous plant and they also have modified leaves.
[Question: 810407]
What is Inflorescence?
The arrangement of flower on floral axis is called inflorescence.
A flower is a significant part of a plant tailored for reproduction. In addition, it is an essential part of the bouquet, decorations, celebrations, garden, rituals, etc. Among different parts of a plant, the flower is the most attractive part due to its beauty and fragrance.
Let’s learn more about inflorescence and different types of inflorescence.
 Types of Inflorescence
Types of Inflorescence
 |
Download the notes
Morphology of Flowering Plants
|
Download as PDF |
[Question: 875679]
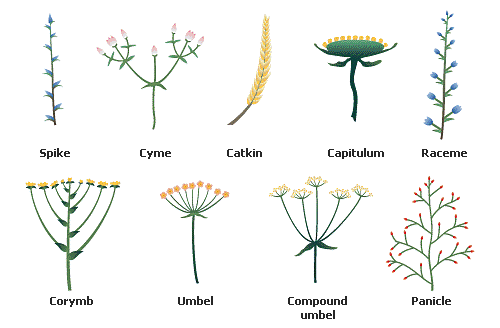
Types of Inflorescence
In a plant, flowers may grow either as a single flower or as a group. The inflorescence is defined as the arrangement of a cluster of flowers on a floral axis. The inflorescence is of two types, they are: Racemose and Cymose.
Racemose
In this type of inflorescence the main axis continues to grow and does not terminate in a flower and give off flowers laterally in acropetal manner (Where old flowers are arranged lower side and young flowers are upper side).
This is of following different types :
1. Raceme - When peduncle or (main axis) is elongated and flowers are pedicellate. Eg. Radish, Mustard
When peduncle is branched and each branch bear pedicelated flowers like racemose and are arranged in acropetal manner known as compound raceme or panicle Eg. Gulmohar, Neem.
2. Spike - In it peduncle is elongated but flowers are sessile. Eg.Achyranthes.
When peduncle is branched and each branch bear spike, like infloresence then the small branch having flower is called spikelet and this arrangement is called as spike of spikelet. Eg. in the members of grass family (Gramineae) wheat
3. Catkin/Amentum - In it peduncle is thin, long and weak, and flowers are sessile and unisexual Eg. Mulberry, Betula, Oak.
4. Spadix - In it peduncle is thick, long and fleshy and have small sessile and unisexual flowers covered with one or more green or colourfull bracts.Eg.Colocasia, Maize, Aroids, Palms, Grain of maize is fruit long filamentous threads protruding at the end of a young cob of maize are styles.
5. Corymb - In it peduncle is short and all flowers are present at same level because the lower flower has much long pedicel than the upper one. eg. Candytuft (Iberis amara) If in this type of inflorescence peduncle is branched, then each branch has flower cluster, then this type of inflorescence is called compound corymb. egPyrus terminalis
6. Umbel - An inflorescence in which the flower stalks are of more or less equal in length, arise from the same point, At the base of flowers stalk, there is whorl of bracts forming the involucre. eg.Centella.
If in this type of inflorescence, peduncle is branched then each branch has flower cluster then this type of inflorescence is called compound umbel. eg.coriander, Foeniculum, cuminum.
7. Capitulum/Racemose head (Anthodium) - In it the growth of peduncle is retarded and it become broad, flattened concave or convex. On it small flowers are found. These flowers are called floret.
If all the flower of capitulum are same, then it is called homogamous. If the younger flower are present towards centre and older towards the periphery, than it is known centripetal order. The flowers which are present in centre called disc floret and flowers at periphery are called as ray floret and arrangement of this type is called heterogamous. In this type of inflorescence florets may be unisexual, bisexual and sterile. This inflorescence is surrounded by one or more involucre. It is most advanced type of inflorescence, because all flowers are pollinated at same time. Eg. Sunflower, Zinnia, Marigold.
[Question: 875682]
Cymose
In this type of inflorescence, the peduncle terminate in a flower. In it the older flowers are present at upper portion and young buds are arranged towards base. This arrangement is called basipetal succession.
It is of following types –
1. Uniparous cyme/Monochasial cyme - The peduncle ending in a flower producing lateral branch at a time ending in a flower. It is two types –
(a) Helicoid cyme - When all lateral branches developed on the same side on peduncle then it is called helical cyme.
Eg. Heliotropism, Saraca.
(b) Scorpioid cyme - In this type the lateral branch develops on one side and the other branch will develop opposite to first one, i.e. they lie alternate to each other. Eg.Begonia, Vine.
2. Dichasial or biparous cyme - In this type peduncle ends in a flower, from the basal part of peduncle two lateral branches arise which also end in a flower now this same arrangement occur on these lateral branches.
Eg. Bougainvillea, Jasmine, Teak, Mirabilis.
3. Multiparous cyme/Polychasial - In this type peduncle ends in a flower and from the base of it many lateral branches arise, which also terminated in flower, this arrangement now also occur on these lateral branches Eg. Calotropis (madar), Nerium, Asclepias, Some species of croton and Euphorbia.
Special Type of Inflorescence
1. Cyathium - The bracts or the involucre become fused to form a cup-shaped structure on the margin of it secretory glands are found. In the central part of cup-shaped structure a female flowers is found, which mature earlier. Due to the growth of pedicel this come out from the cup-shaped structure. Female flowers are surrounded by small male flowers. These are also found on Pedicel. The male flower, which lie toward centre mature earlier than the flowers which are towards periphery.
This inflorescence is found in Euphorbiaceae family like Euphorbia, Poinsettia, Pedilanthus.
2. Verticillaster- This type inflorescence is found in Labiatae/Lamiaceae family. In this type of inflorescence leaves are arranged in opposite manner on stem. From the axil of each leaf inflorescence develops. From the main axil, lateral axil arises, on which flowers are found. Now from these branches lateral branches developed also. On these branches flowers are found also. In this inflorescence each dichasial chyme changes into monochasial (scorpioid) cyme. Eg. Salvia, Ocimum, Coleus
3. Hypanthodium - In it peduncle is modified in narrow cup like structure. At the base of cup female flowers develop while towards mouth male flower develops. All three types of flowers are present in this inflorescence. Eg. Banyan, Peepal,Ficus species
4. Mixed inflorescence – Sometimes flowers are arranged in both racemose and cymose manner on same peduncle called mixed inflorescence.
(i) Mixed spadix – Banana
(ii) Cymose raceme or thyrsus – Grapes
Flowers
The flowers are the reproductive part of the plant. The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is called inflorescence, which has two major parts called racemose which let the main axis continue to grow and cymose which terminates the main axis in a flow.
The flower consists of four different whorls:
- Calyx, the outermost.
- Corolla, composed of petals.
- Androecium, composed of stamens.
- Gynoecium, composed of one or more carpels.
The reproduction in plants occurs by the process of pollination. It is the process of transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same or different plants.
Functions of Flowers
The flower performs the following important functions:
- They help in the process of reproduction.
- They produce diaspores without fertilization.
- The gametophytes develop inside the flower.
- The flowers attract insects and birds which then act as a medium to transfer the pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of some other flower.
- The ovary of the flower develops into a fruit that contains seed.
Fruits
The fruit is the characteristic feature of flowering plants, which is a ripened or mature ovary and the seed is what the ovules develop into after fertilization. The fruit that develops without fertilization is known as parthenocarpic.
Types of Fruits
There are three different types of fruits and are classified mainly based on their mode of development.
- Simple— Developed from the monocarpellary ovary or multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Examples of simple fruits.
- Aggregate–Developed from the multicarpellary apocarpous ovary. Examples of aggregate fruits.
- Composite–These are false fruits, developed from the entire inflorescence rather than from single flower. Examples of composite fruits include blackberries, Raspberries strawberries, etc.
The Seed
A seed is a basic part of a plant, which is found enclosed within the fruit. It is made up of a seed coat and an embryo. During the development of the fruit, the wall of the ovary becomes the pericarp. In some plants, the ovary wall dries out completely, while in some it remains fleshy.
Types of Seeds
Based on the number of cotyledons, seeds are further classified into two types- dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous seeds.
- Monocotyledonous— The embryo consists of an embryo axis and has only one cotyledon. The monocotyledonous is also known as monocot seeds. Grains including rice, millet, wheat and other plants like onions, corn, ginger banana, palm tree, are examples of monocot seeds.
- Dicotyledonous— The embryo consists of an embryo axis and has two cotyledons. The dicotyledons are also known as dicots or dicot seeds. Legumes including beans, lentils, pea, peanuts, and tomato are examples of dicot seeds.
|
180 videos|367 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Morphology of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the purpose of inflorescence in flowering plants? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of inflorescence? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of venation in flowering plants? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a special type of inflorescence? |  |
| 5. How does the morphology of flowering plants contribute to their reproductive success? |  |


















