Class 7 Science Chapter 10 NCERT Based Activity - Life Processes in Plant
Activity 10.1: Let us test some explanations
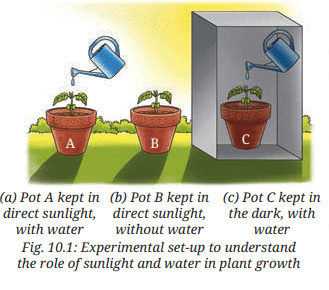
Objective: To understand the role of sunlight and water in plant growth.
Procedure:
- Take three earthen pots (A, B, C) of the same size filled with garden soil.
- Plant saplings of similar sizes (e.g., chilli or tomato) in each pot.
- Label the pots:
- Pot A: Direct sunlight, with water.
- Pot B: Direct sunlight, without water.
- Pot C: In the dark, with water.
- Count the initial number of leaves and record observations.
- Place Pot A in sunlight, keep soil moist daily. Place Pot B in sunlight, no water. Place Pot C in the dark, keep soil moist daily.
- Observe for two weeks, recording changes in height, number of leaves, leaf color, and other changes in Table 10.1.
 Table 10.1: Effect of sunlight and water on plant growth
Table 10.1: Effect of sunlight and water on plant growth
Ans: On Day 1, each sapling (e.g., chilli) has approximately 4 leaves, height of 10 cm, and green leaves. Table 10.1: Effect of sunlight and water on plant growth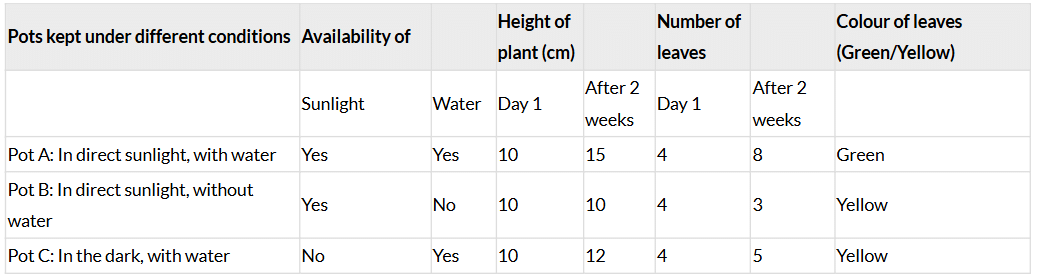
Differences observed:
- Pot A: Plant shows significant growth (height increased by 5 cm, 4 new leaves), leaves remain green, indicating healthy growth due to sunlight and water.
- Pot B: Plant shows no height increase, loses leaves (1 leaf dropped), leaves turn yellow, indicating wilting due to lack of water despite sunlight.
- Pot C: Plant shows minimal growth (height increased by 2 cm, 1 new leaf), leaves turn yellow, indicating poor growth due to lack of sunlight despite water.
- Maximum growth: Pot A has the plant with the maximum growth, as it received both sunlight and water, essential for photosynthesis and growth.
- Least growth: Pot B has the plant with the least growth, as it lacked water, causing wilting despite sunlight.
Activity 10.2: Let us check (demonstration activity)
Objective: To test for the presence of starch in leaves, indicating food production.
Procedure:
- Boil a leaf in water for 5 minutes to soften it.
- Dip the leaf in a test tube with alcohol and place the test tube in boiling water until the leaf becomes colorless (decolorization).
- Place the decolorized leaf on a plate.
- Add a few drops of diluted iodine solution to the leaf and wait a few minutes.
- Observe if the leaf turns blue-black, indicating starch presence.
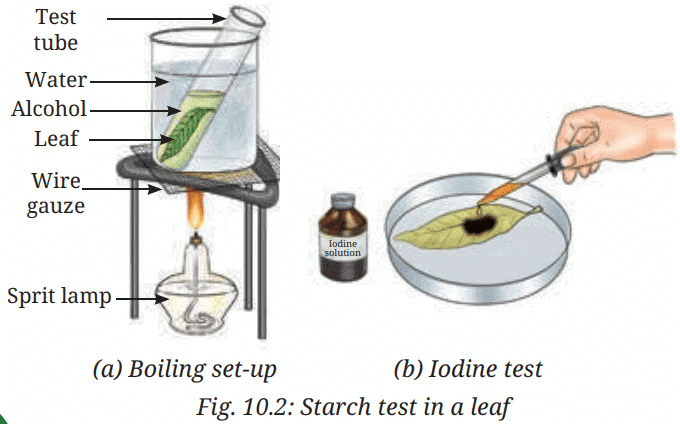
Caution: Alcohol is flammable; avoid direct heat sources.
Ans:
- Observation: If the leaf turns blue-black after adding iodine, it indicates the presence of starch.
- Reason for Decolorization: Decolorizing the leaf removes chlorophyll, making it easier to observe the color change caused by the iodine test.
- Inference: Leaves store food in the form of starch, which is produced during photosynthesis.
Activity 10.3: Let us check
Objective: To investigate the role of sunlight and chlorophyll in starch production.
Procedure: Take leaves with green and non-green patches from two similar potted plants:
- One kept in sunlight.
- One kept in the dark for 36 hours.
- Sketch the leaves to record green and non-green patches.
- Perform the iodine test (as in the previous activity) on both leaves.
- Record observations in Table 10.2.
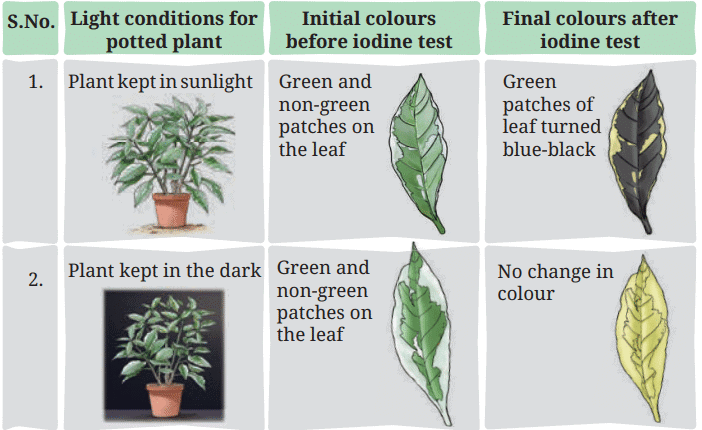
Ans: Table 10.2 (as provided in the document):
The green patches of the leaf from the plant in sunlight turn blue-black, indicating starch presence due to photosynthesis enabled by sunlight and chlorophyll. The leaf from the plant in the dark shows no colour change, indicating no starch production due to lack of sunlight. Non-green patches do not turn blue-black, suggesting insufficient chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Activity 10.4: Let us experiment (demonstration activity)
Objective: To test the role of carbon dioxide in starch production.
Procedure:
- Take a potted plant, keep it in the dark for 2-3 days to destarch.
- Select one leaf for the experiment.
- Pour caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) into a wide-mouthed bottle to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Insert half of the destarched leaf into the bottle through a split cork, leaving the other half outside.
- Place the setup in sunlight for a few hours.
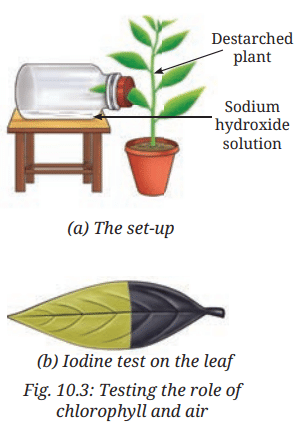
- Record availability of water, sunlight, chlorophyll, and carbon dioxide in Table 10.3.
- Remove the leaf and perform the iodine test.
- Record observations in Table 10.3.
Ans: Table 10.3: Role of air in the preparation of starch by plants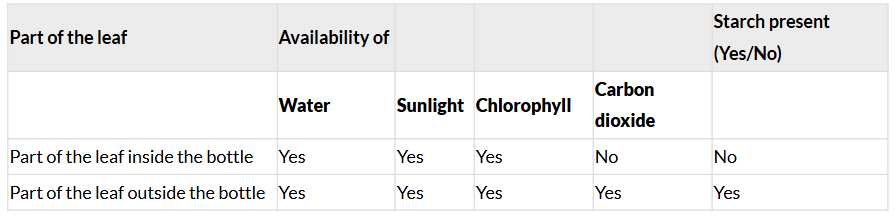
The part of the leaf outside the bottle turns blue-black after the iodine test, indicating starch presence due to the availability of water, sunlight, chlorophyll, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The part inside the bottle does not turn blue-black, indicating no starch production because caustic soda absorbed carbon dioxide, preventing photosynthesis.
Activity 10.5: Let us explore
Objective: To demonstrate that oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
Procedure: Compare two setups (A and B) in Fig. 10.4:
- Setup A: Placed in sunlight.
- Setup B: Placed in the dark.
- Observe if air bubbles emerge in the inverted test tube in Setup A.
- Collect sufficient gas in the test tube in Setup A.
- Place a thumb on the test tube’s mouth, remove it, and insert a lit matchstick.
- Observe the matchstick’s flame intensity.
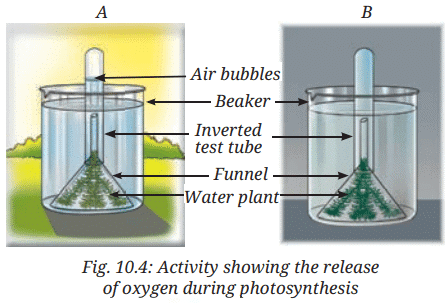
Ans: In set-up A (placed in sunlight), air bubbles emerge in the inverted test tube, indicating gas production. In set-up B (placed in the dark), no bubbles are observed, as no gas is produced. The gas in set-up A is oxygen, confirmed by the lit matchstick producing an intense flame when inserted into the test tube, indicating oxygen release during photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight.
Activity 10.6: Let us examine (demonstration activity)
Objective: To observe stomata on leaves for gas exchange.
Procedure:
- Collect a leaf (e.g., rhoeo, money plant).
- Place it in a beaker with water.
- Peel a thin layer from the lower leaf surface.
- Place the peel in a watch glass with water.
- Transfer the peel to a microscope slide with a drop of water.
- Add a drop of ink to the peel.
- Cover with a coverslip and observe under a microscope.
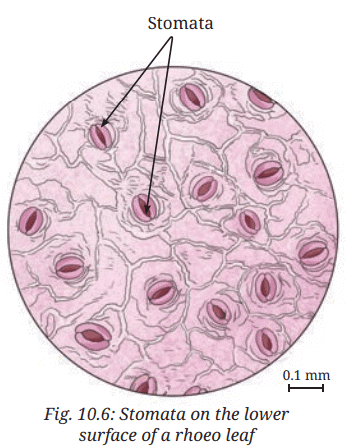
Ans: Under the microscope, tiny pores are observed on the leaf peel, as shown in Fig. 10.6. These pores are stomata, which facilitate the exchange of gases (carbon dioxide and oxygen) during photosynthesis and respiration.
Activity 10.7: Let us experiment
Objective: To study water transport in plants.
Procedure: Take two glass tumblers, fill with water, and add red ink to one.
Place twigs of similar tender plants (e.g., white sadabahar) in each tumbler:
- One in plain water.
- One in colored water.
- Observe after one day for color changes in the twigs or flowers.
- Examine the cut end of the twig for colored water uptake.
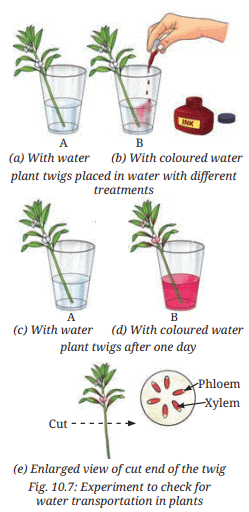
Ans: After one day, the twig in coloured water (Fig. 10.7d) shows red coloration in the stem and white flowers, indicating that water (with red ink) is transported from the roots to the stem and flowers. The twig in plain water (Fig. 10.7c) shows no colour change. The cut end of the twig (Fig. 10.7e) reveals red-stained xylem vessels, confirming that xylem transports water and minerals upward in the plant.
Activity 10.8: Let us find out (demonstration activity)
Objective: To demonstrate that plants respire and produce carbon dioxide.
Procedure:
- Soak moong bean seeds overnight.
- Place wet cotton in a conical flask and add soaked seeds.
- Cover the flask with a cork having two holes, fitted with tubes A and B.
- Leave undisturbed for 24 hours in the dark.
- Fill two test tubes with lime water; connect one to the flask via a tube.
- Compare both test tubes for color changes.
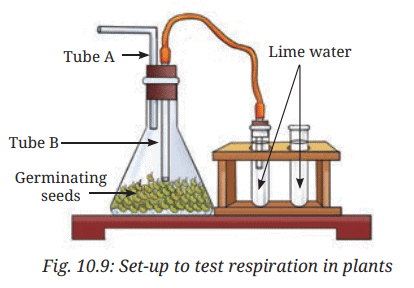
Ans: The lime water in the test tube connected to the flask (containing moong bean seeds) turns milky, while the lime water in the other test tube (exposed to normal air) does not. The milky appearance in the connected test tube is due to carbon dioxide produced by the respiring seeds reacting with lime water. This confirms that seeds respire, releasing carbon dioxide, unlike the control test tube with minimal atmospheric carbon dioxide.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 10 NCERT Based Activity - Life Processes in Plant
| 1. What are the main life processes in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is the role of transpiration in plants? |  |
| 4. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 5. Why is respiration important for plants? |  |
















