NCERT Exemplar: Integrals | Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Verify the following :
Q.1. 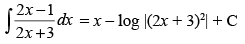
Ans.
L.H.S. =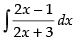
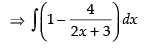 [Dividing the numerator by the denominator]
[Dividing the numerator by the denominator]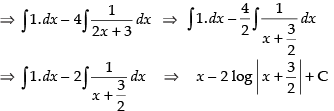
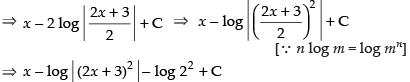
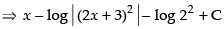
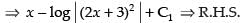 [where C1 = C – log 22]
[where C1 = C – log 22]
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Q.2. 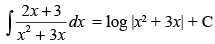
Ans.
L.H.S. =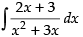
Put x2 + 3x = t
∴ (2x + 3) dx = dt
⇒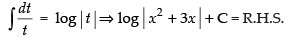
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence verified.
Evaluate the following:
Q.3.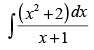
Ans.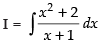
∴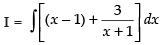
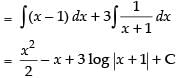
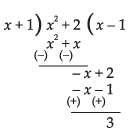
Hence, the required solution is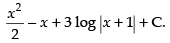
Q.4. 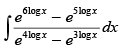
Ans.
Let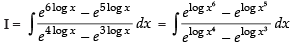
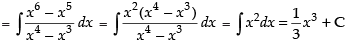
Hence, the required solution is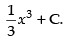
Q.5. 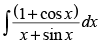
Ans.
Let 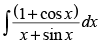
Put x + sin x = t ⇒ (1 + cos x) dx = dt
∴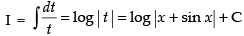
Hence, the required solution is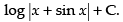
Q.6.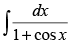
Ans.
Let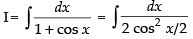
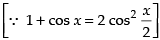
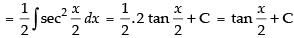
Hence, the required solution is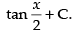
Q.7.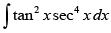
Ans.
Let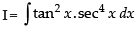
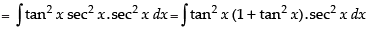
Put tan x = t, ∴ sec2 x dx = dt
∴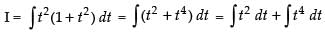
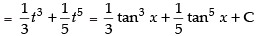
Hence, the required solution is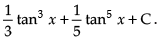
Q.8. 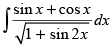
Ans.
Let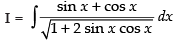
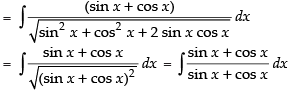
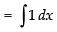
= x + C
Hence, the required solution is x + C.
Q.9.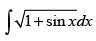
Ans.
Let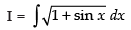
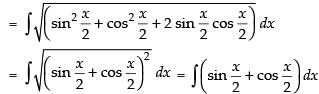
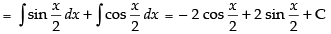
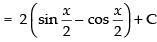
Hence, the required solution is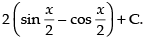
Q.10.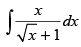
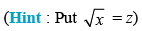
Ans.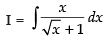
Put √x = t x = t2 ∵ dx = 2t . dt
∴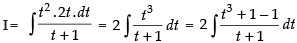
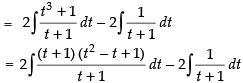
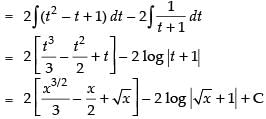
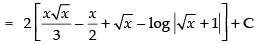
Hence,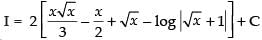
Q.11.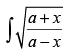
Ans.
Let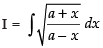
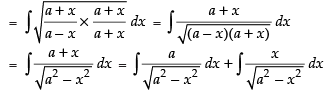
Let I = I1 + I2
Now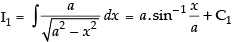
and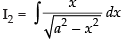
Put a2 – x2 = t ⇒ – 2x dx = dt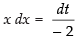
∴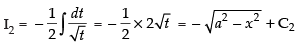
Since I = I1 + I2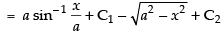
∴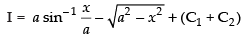
Hence,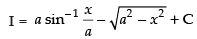 [C = C1 + C2]
[C = C1 + C2]
Alternate method: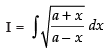
Put x = a cos 2θ
∴ dx = a (– 2 sin 2θ) dθ = – 2a sin 2θ dθ
∴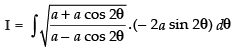
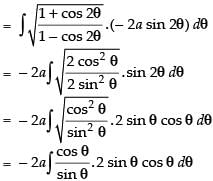
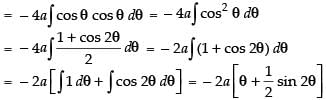
Now x = a cos 2θ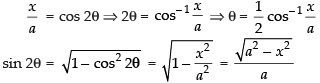
∴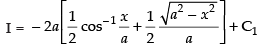
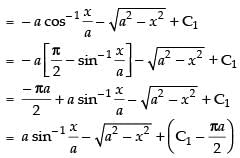
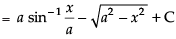
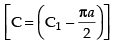
Hence,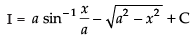
Q.12. 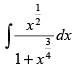 (Hint : Put x = z4)
(Hint : Put x = z4)
Ans.
Let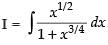
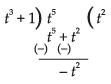
Put x = t4 ⇒ dx = 4t3 dt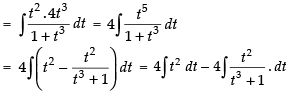
I = I1 – I2
Now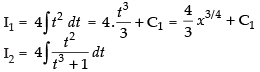
Put t3 + 1 = z ⇒ 3t2 dt = dz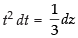
∴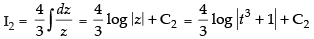
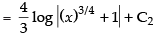
∴ I = I1 – I2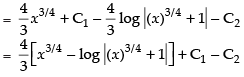
Hence,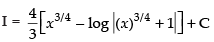 [∵ C = C1 - C2]
[∵ C = C1 - C2]
Q.13.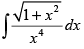
Ans.
Let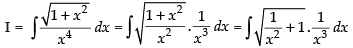
Put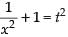
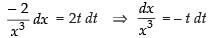
∴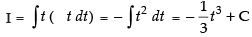
Hence,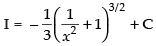
Q.14.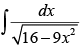
Ans.
Let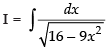
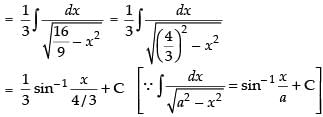
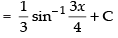
Hence,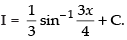
Q.15.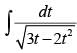
Ans.
Let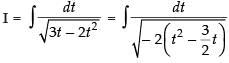
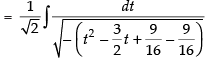 [Making perfect square]
[Making perfect square]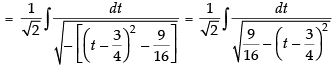
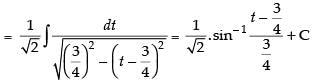
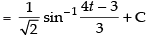
Hence,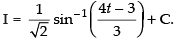
Q.16.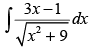
Ans.
Let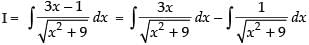
I = I1 – I2
Now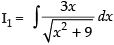
Put x2 + 9 = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt
x dx = dt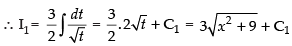
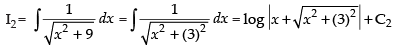
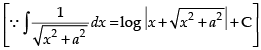
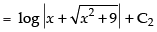
∴ I = I1 – I2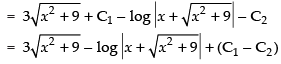
Hence,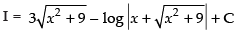
Q.17.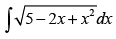
Ans.
Let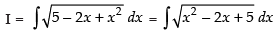
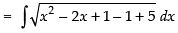 (Making perfect square)
(Making perfect square)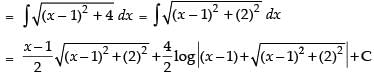
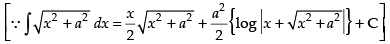
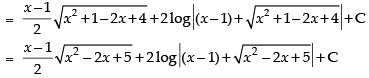
Hence,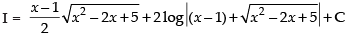
Q.18.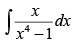
Ans.
Let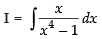
Put x2 = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx =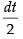
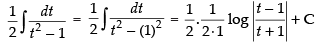
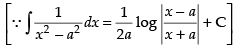
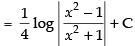
Hence,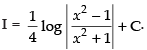
Q.19.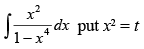
Ans.
Let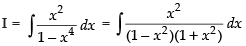
Put x2 = t for the purpose of partial fractions.
We get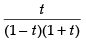
Resolving into partial fractions we put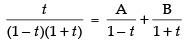
[where A and B are arbitrary constants]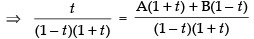
⇒ t = A + At + B – Bt
Comparing the like terms, we get A – B = 1 and A + B = 0
Solving the above equations, we have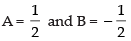
∴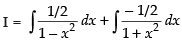 (Putting t = x2)
(Putting t = x2)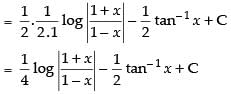
Hence,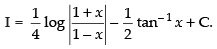
Q.20.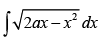
Ans.
Let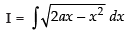
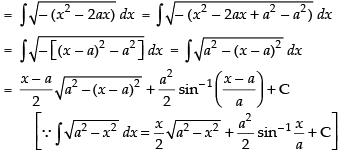
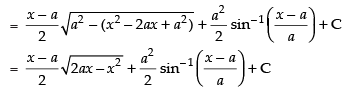
Hence,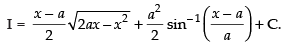
Q.21.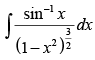
Ans.
Let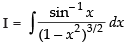
Put x = sin θ ⇒ dx = cos θ dθ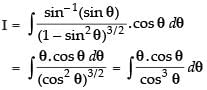
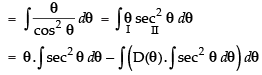
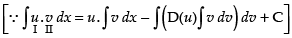
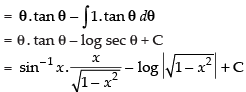
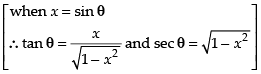
Hence,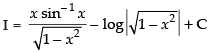
Q.22.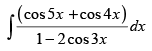
Ans.
Let I =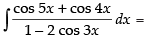
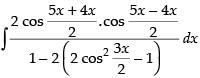
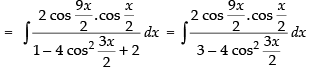
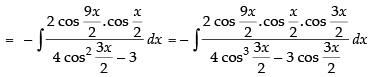
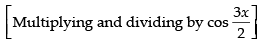
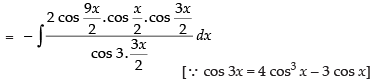
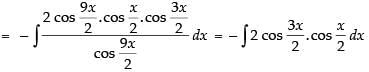
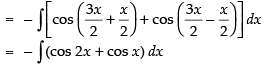
[∵ 2 cos A cos B = cos (A + B) + cos (A - B)]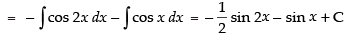
Hence,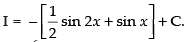
Q.23.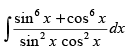
Ans.
Let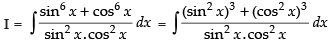
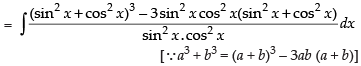
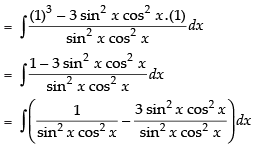
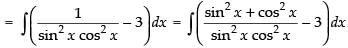
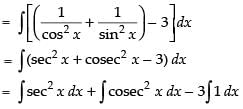
= tan x – cot x – 3x + C
Hence, I = tan x – cot x – 3x + C.
Q.24.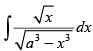
Ans.
Let I =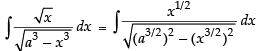
Put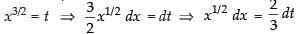
∴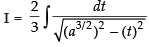
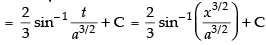
Hence,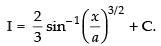
Q.25.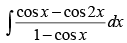
Ans.
Let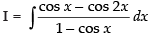
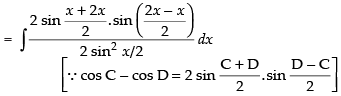
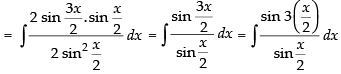
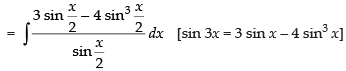
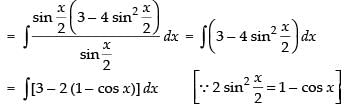
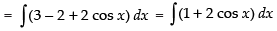
= x + 2 sin x + C
Hence, I = x + 2 sin x + C.
Q.26.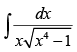 (Hint : Put x2 = sec θ)
(Hint : Put x2 = sec θ)
Ans.
Let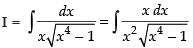
Put x2 = sec θ
∴ 2x dx = sec θ tan θ dθ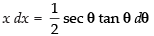
∴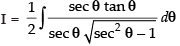
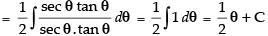
So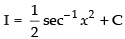
Hence,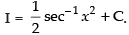
Evaluate the following as limit of sums:
Q.27.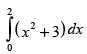
Ans.
Let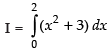
Using the formula,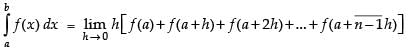
where h =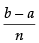
Here, a = 0 and b = 2
∴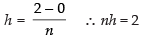
Here, f(x) = x2 + 3
f(0) = 0 + 3 = 3
f(0 + h) = (0 + h)2 + 3 = h2 + 3
f(0 + 2h) = (0 + 2h)2 + 3 = 4h2 + 3
..............................
..............................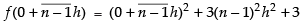
Now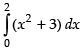
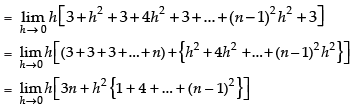
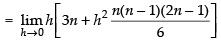
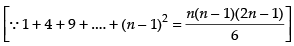
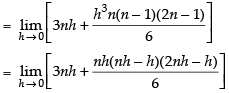
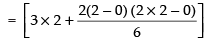
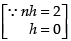
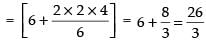
Hence,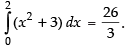
Q.28.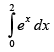
Ans.
Let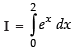
Here, a = 0 and b = 2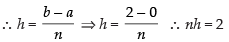
Here f(x) = ex
f(0) = e0 = 1
f(0 + h) = e0 + h = eh
f(0 + 2h) = e0 + 2h = e2h
................................
................................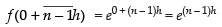
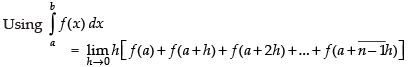
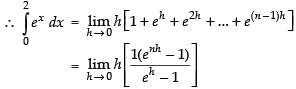
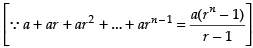
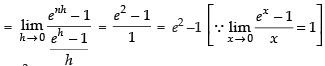
Hence, I = e2 –1.
Evaluate the following:
Q.29.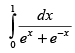
Ans.
Let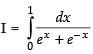
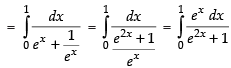
Put ex = t ⇒ ex dx = dt
Changing the limit, we have
When x = 0 ∴ t = e0 = 1
When x = 1 ∴ t = e1 = e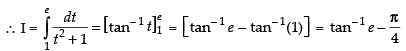
Hence,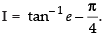
Q.30.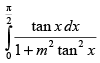
Ans.
Let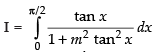
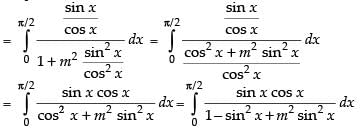
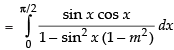
Put sin2 x = t
2 sin x cos x dx = dt
sin x cos x dx =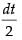
Changing the limits we get,
When x = 0 ∴ t = sin2 0 = 0; When x =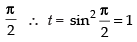
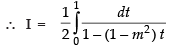
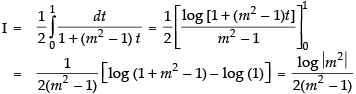
Hence,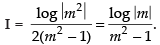
Q.31.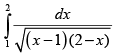
Ans.
Let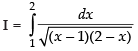
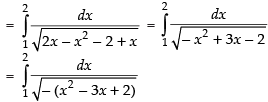
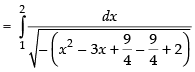 [Making perfect square]
[Making perfect square]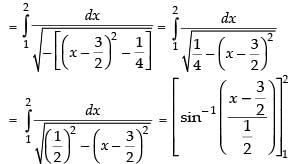
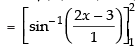 = sin– 1 (4 – 3) – sin– 1 (2 – 3)
= sin– 1 (4 – 3) – sin– 1 (2 – 3)
= sin– 1 (1) – sin– 1 (– 1) = sin– 1 (1) + sin– 1 (1)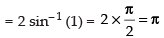
Hence, I = π.
Q.32.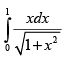
Ans.
Let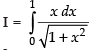
Put 1 + x2 = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx =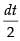
Changing the limits, we have
When x = 0 ∴ t = 1
When x = 1 ∴ t = 2
∴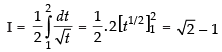
Hence, I = √2 -1 .
Q.33.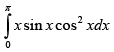
Ans.
Let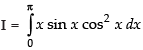 ...(i)
...(i)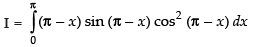
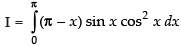 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii) we get,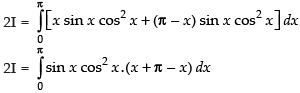
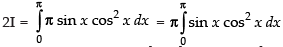
Put cos x = t ⇒ – sin x dx = dt ⇒ sin x dx = – dt
Changing the limits, we have
When x = 0, t = cos 0 = 1; When x = p, t = cos p = – 1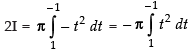
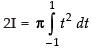
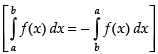
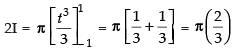
∴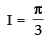
Q.34.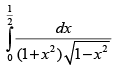 (Hint: let x = sinθ)
(Hint: let x = sinθ)
Ans.
Let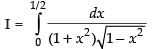
Put x = sin θ
∴ dx = cos θ dθ
Changing the limits, we get
When x = 0 ∴ sin θ = 0 ∴ θ = 0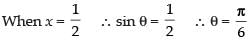
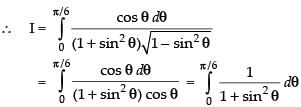
Now, dividing the numerator and denominator by cos2 θ, we get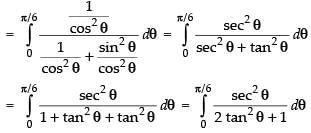
Put tan θ = t
∴ sec2 θ dθ = dt
Changing the limits, we get
When θ = 0 ∴ t = tan 0 = 0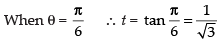
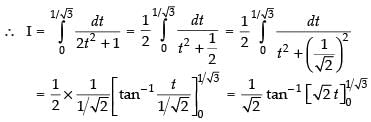
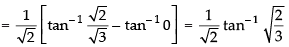
Long Answer (L.A.)
Q.35. 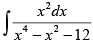
Ans.
Let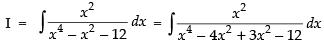
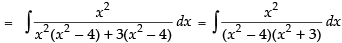
Put x2 = t for the purpose of partial fraction.
We get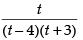
Let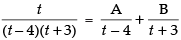
[where A and B are arbitrary constants]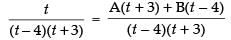
⇒ t = At + 3A + Bt – 4B
Comparing the like terms, we get
A + B = 1 and 3A – 4B = 0
⇒ 3A = 4B
∴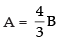
Now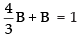
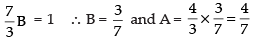
So,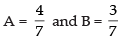
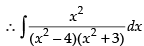
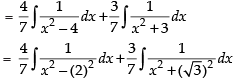
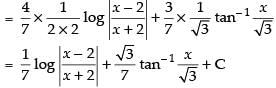
Hence,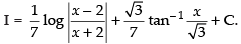
Q.36.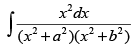
Ans.
Let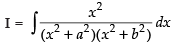
Put x2 = t for the purpose of partial fraction.
We get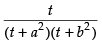
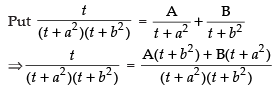
⇒ t = At + Ab2 + Bt + Ba2
Comparing the like terms, we get
A + B = 1 and Ab2 + Ba2 = 0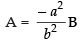
∴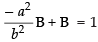
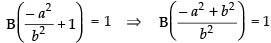
⇒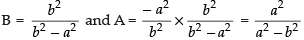
So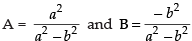
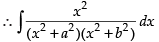
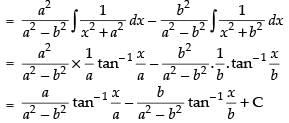
Hence,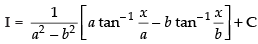
Q.37.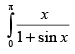
Ans.
Let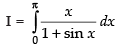 ...(i)
...(i)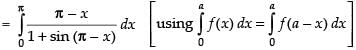
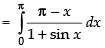 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get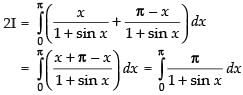
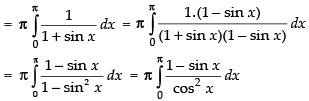
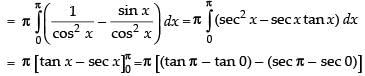
2I = π [0 - (- 1 - 1)] = π(2)
∴ I = π
Hence, I = π.
Q.38.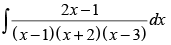
Ans.
Let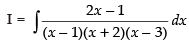
Resolving into partial fraction, we put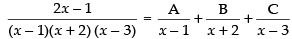
⇒ 2x – 1 = A(x + 2)(x – 3) + B(x – 1)(x – 3) + C(x – 1)(x + 2)
put x = 1, 1 = A(3)(– 2)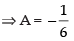
put x = – 2, – 5 = B(– 3)(– 5)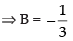
put x = 3, 5 = C(2)(5)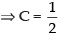
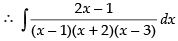
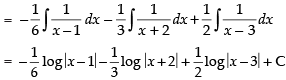
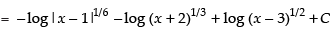
Hence,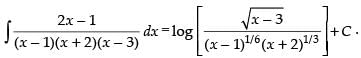
Q.39.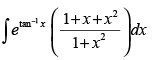
Ans.
Let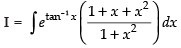
Put tan– 1x = t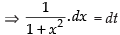
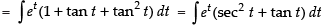
Here f(t) = tan t
∴ f ′(t) = sec2 t
= et . f(t) = et tan t = - + e tan-1 x .x + C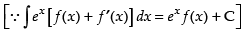
Hence, I = - + e tan-1 x .x + C.
Q.40.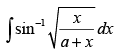 (Hint: Put x = a tan2θ)
(Hint: Put x = a tan2θ)
Ans.
Let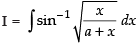
Put x = a tan2 θ
dx = 2a tan θ . sec2 θ . dθ
∴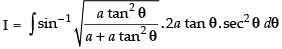
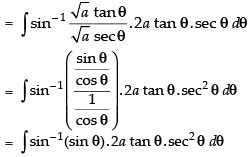
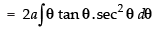
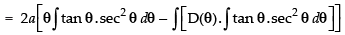
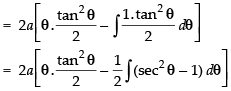
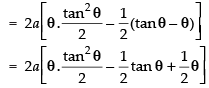
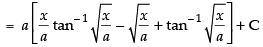
Hence,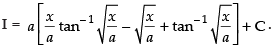
Q.41.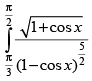
Ans.
Let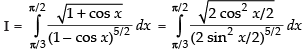
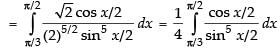
Put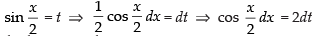
Changing the limits, we have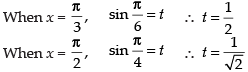
∴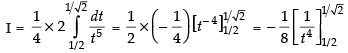
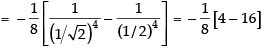
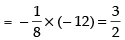
Hence,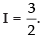
Q.42.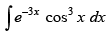
Ans.
Let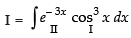
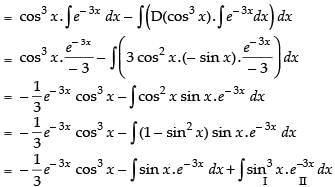
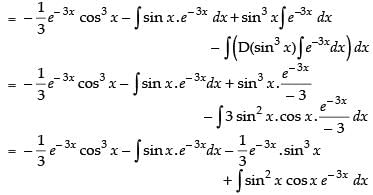
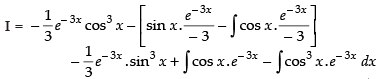
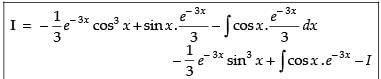
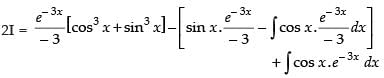
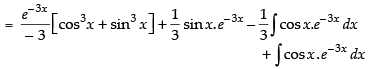
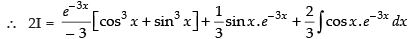
Now, put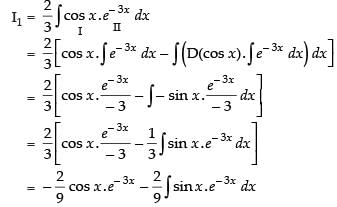
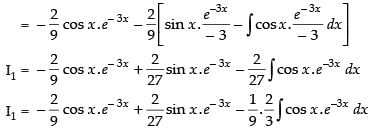
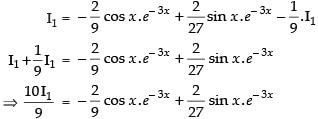
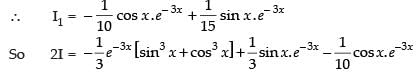
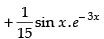
∴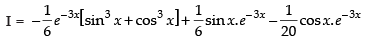
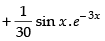
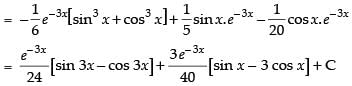
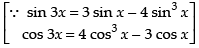
Hence,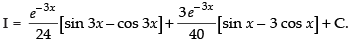
Q.43.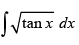 (Hint: Put tanx = t2)
(Hint: Put tanx = t2)
Ans.
Let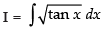
Put tan x = t2
sec2 x dx = 2t dt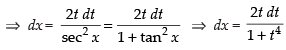
∴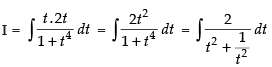
[Dividing the numerator and denominator by t2]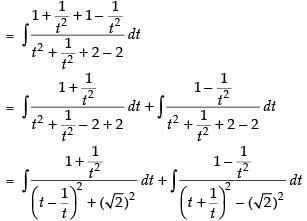
Put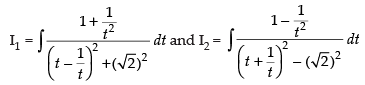
∴ I = I1 + I2 ...(i)
Now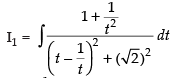
Put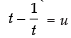
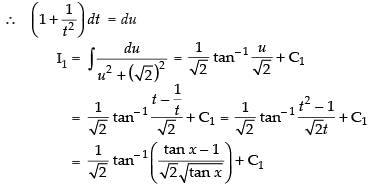
Now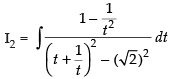
Put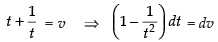

So I = I1 + I2
⇒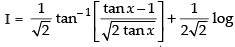
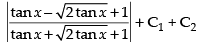
Hence,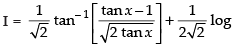
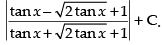
Q.44.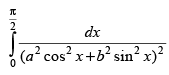
Ans.
Let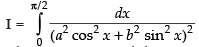
Dividing the numerator and denominator by cos4 x, we have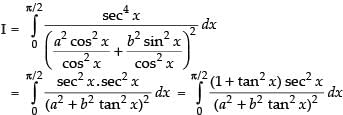
Put tan x = t ⇒ sec2 x dx = dt
Changing the limits, we get
When x = 0, t = tan 0 = 0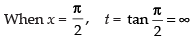
∴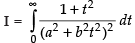
Put t 2 = u only for the purpose of partial fraction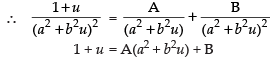
Comparing the coefficients of like terms, we get
a2A + B = 1 and b2A = 1
Now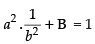
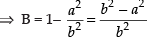
∴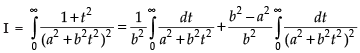
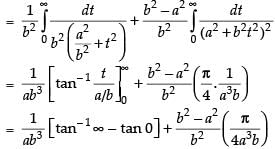
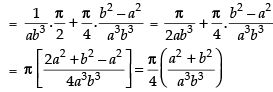
Hence, I =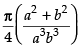
Q.45.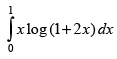
Ans.
Let I =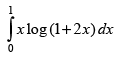
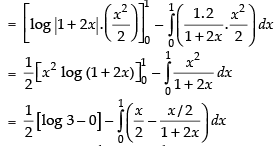
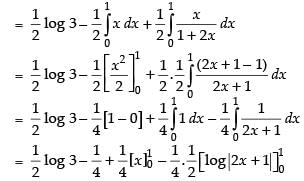
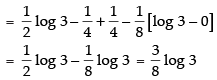
Hence,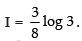
Q.46.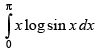
Ans.
Let I =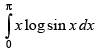
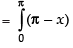 log sin (π - x) dx
log sin (π - x) dx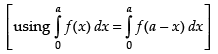
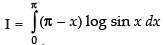 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get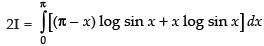
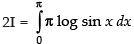
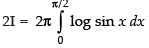
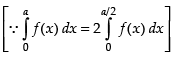
∴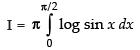 ...(iii)
...(iii)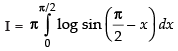
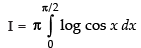 ...(iv)
...(iv)
On adding (iii) and (iv), we get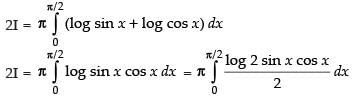
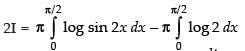
Put 2x = t ⇒ 2 dx = dt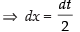
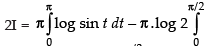 dx [Changing the limit]
dx [Changing the limit]
2I = I -π . log 2 [ x]0π/2 [from eqn. (iii)]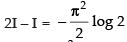
So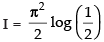
Q.47.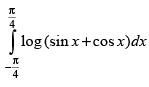
Ans.
Let I =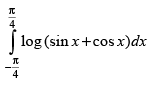 ...(i)
...(i)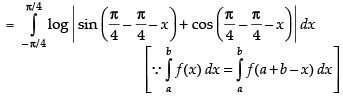
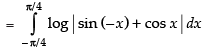
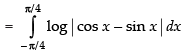 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get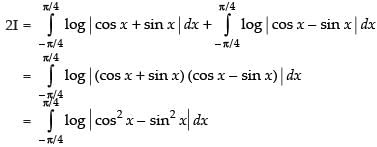
∴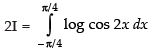
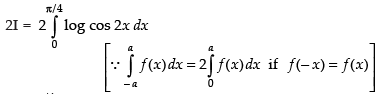
∴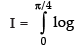 cos 2x dx
cos 2x dx
Put 2x = t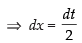
Changing the limits we get
When x = 0 ∴ t = 0; When x =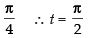
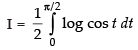 ...(iii)
...(iii)
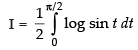 ...(iv)
...(iv)
On adding (iii) and (iv), we get,
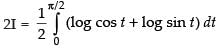
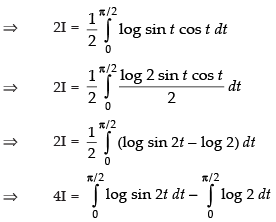
Put 2t = u ⇒ 2 dt = du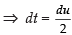
∴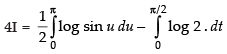
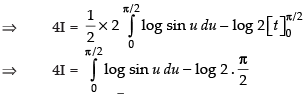
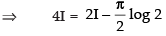 [From eq. (ii)]
[From eq. (ii)]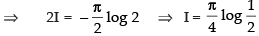
Hence,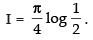
Objective Type Questions
Q.48.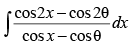 is equal to
is equal to
(a) 2(sinx + xcosθ) + C
(b) 2(sinx – xcosθ) + C
(c) 2(sinx + 2xcosθ) + C
(d) 2(sinx – 2x cosθ) + C
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Let I =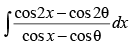
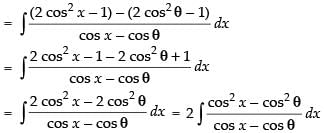
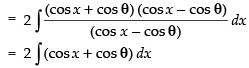
∴ I = 2(sin x +cos θ .x)+ C.
Hence, correct option is (a).
Q.49.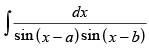 is equal to
is equal to
(a) sin (b – a) log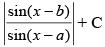
(b) cosec (b – a) log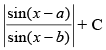
(c) cosec (b – a) log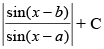
(d) sin (b – a) log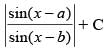
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Let I =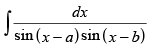
Multiplying and dividing by sin (b – a) we get,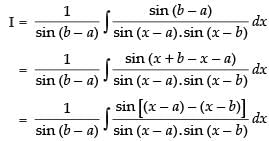
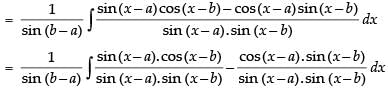
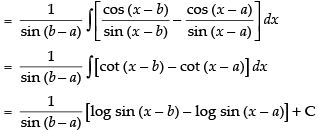
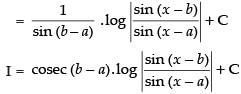
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.50.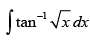 is equal to
is equal to
(a) (x + 1) tan –1 √x – √x + C
(b) x tan –1 √x – √x + C
(c) √x – x tan –1 √x + C
(d) √x – ( x + 1) tan –1 √x + C
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Let I =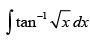
Put √x = tan θ ⇒ x = tan2 θ ⇒ dx = 2 tan θ sec2 θ dθ
∴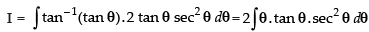
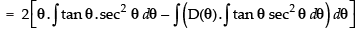
Let us take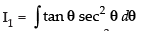
Put tan θ = t ⇒ sec2 θ dθ = dt
∴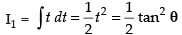
∴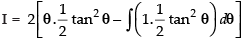
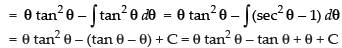
∴ I = tan - 1 √x .x - √x+ tan-1 √x + C =
( x + 1) tan - 1 √x -√x+ C
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.51.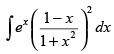 is equal to
is equal to
(a)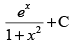
(b)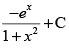
(c)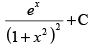
(d)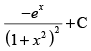
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Let I =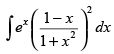
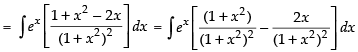
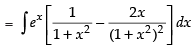
Here f(x) =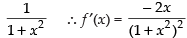
Using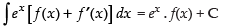
∴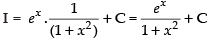
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.52.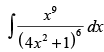 is equal to
is equal to
(a)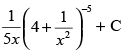
(b)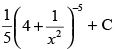
(c)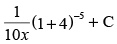
(d)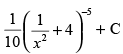
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Let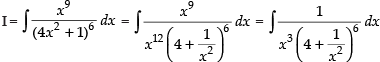
Put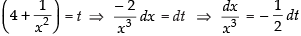
∴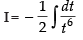
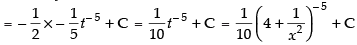
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.53. If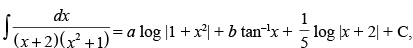 then
then
(a)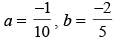
(b)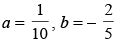
(c)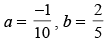
(d)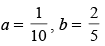
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Let I =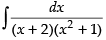
Put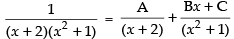
1 = A(x2 + 1) + (x + 2) (Bx + C)
1 = Ax2 + A + Bx2 + Cx + 2Bx + 2C
1 = (A + B)x2 + (C + 2B)x + (A + 2C)
Comparing the like terms, we have
A + B = 0 ...(i)
2B + C = 0 ...(ii)
A + 2C = 1 ...(iii)
Subtracting (i) from (iii) we get
2C – B = 1 ∴ B = 2C – 1
Putting the value of B in eqn. (ii) we have
2(2C – 1) + C = 0 ⇒ 4C – 2 + C = 0
5C = 2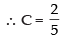
∴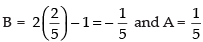
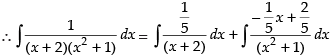
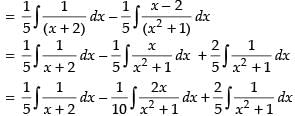
∴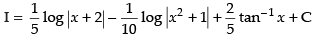
Putting the given value of I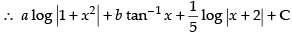
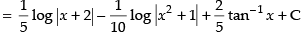
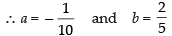
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.54.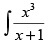 is equal to
is equal to
(a)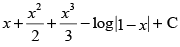
(b)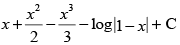
(c)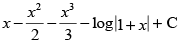
(d)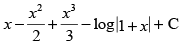
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Let I =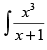
∴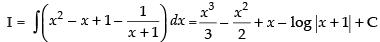
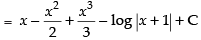
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.55.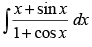 is equal to
is equal to
(a) log 1 + cos x + C
(b) log x + sin x + C
(c)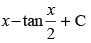
(d)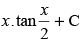
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Let I =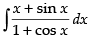
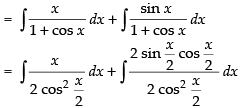
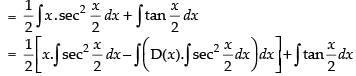
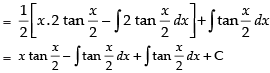
∴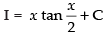
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.56. If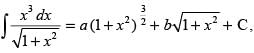 then
then
(a)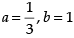
(b)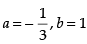
(c)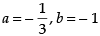
(d)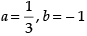
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Let I =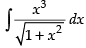
Put 1 + x2 = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx =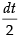
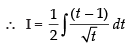
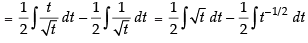
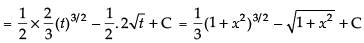
But I = a(1 + x2 )3/2 +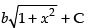
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.57.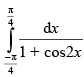 is equal to
is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Let I =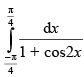
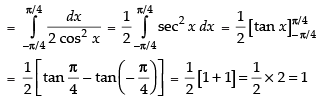
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.58.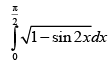 is equal to
is equal to
(a) 2√2
(b) 2( √2 + 1)
(c) 2
(d) 2( √2 - 1)
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Let I =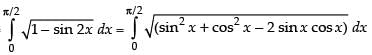
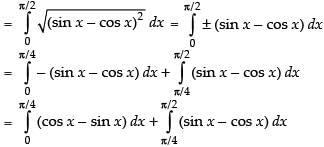
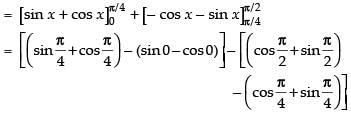
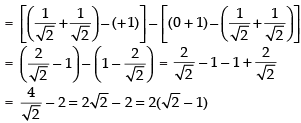
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.59.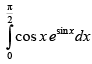 is equal to _______.
is equal to _______.
Ans.
Let I =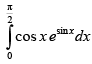
Put sin x = t ⇒ cos x dx = dt
When x = 0 then t = sin 0 = 0; When x =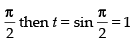
∴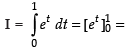
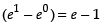
Hence, I = e – 1.
Q.60.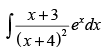 = ________.
= ________.
Ans.
Let I =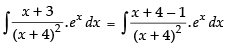
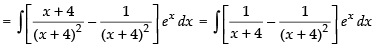
Put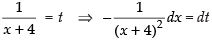
Let f(x) =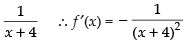
Using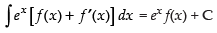
∴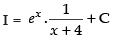
Hence,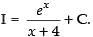
Fill in the blanks
Q.61. If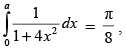 then a = ________.
then a = ________.
Ans.
Given that: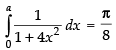
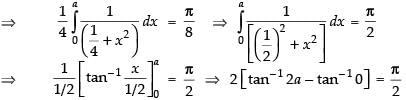
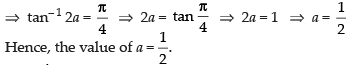
Q.62.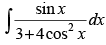 = ________.
= ________.
Ans.
Let I =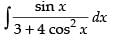
Put cos x = t
∴ – sin x dx = dt ⇒ sin x dx = – dt
∴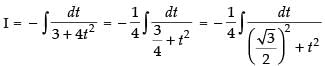
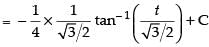
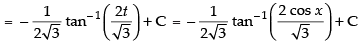
Hence,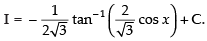
Q.63. The value of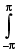 sin3x cos2x dx is _______.
sin3x cos2x dx is _______.
Ans.
Let I =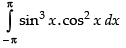
Let f(x) = sin3 x cos2 x f(– x)
= sin3(– x).cos2 (– x) = – sin3 x cos2 x = – f(x)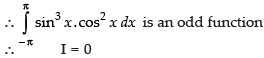
|
172 videos|487 docs|154 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Integrals - Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the concept of integration? |  |
| 2. How can integrals be used to find the area under a curve? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of integration? |  |
| 4. How can integrals be applied in physics and engineering? |  |
| 5. What is the fundamental theorem of calculus? |  |
















