NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. The correct way of making a solution of acid in water is to
(a) add water to acid.
(b) add acid to water.
(c) mix acid and water simultaneously.
(d) add water to acid in a shallow container.
Ans: b
Explanation: If we try to add water to acid it will be an exothermic reaction that will produce a lot of heat which may lead to an explosion. Hence, water should not be added to acid to avoid any mishappening. While we dilute acid, it is always preferred that the acid is added to water rather than the water being added to the acid. As adding water to a concentrated acid releases a huge amount of heat, which can cause an explosion and acid burns on the skin, clothing, and other body parts. Due to this, adding acid to water is naturally safe, but adding water to acid is not safe.
Q.2. Products of a neutralisation reaction are always
(a) an acid and a base.
(b) an acid and a salt.
(c) salt and water.
(d) a salt and a base.
Ans: c
Explanation: The products of a neutralisation reaction are:
- Salt
- Water
In this process:
- When an acid reacts with a base, they neutralise each other.
- This reaction produces a new substance called salt.
- Heat is also released during the reaction.
For example:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) + Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) → Sodium chloride (NaCl) + Water (H2O)
Thus, the correct answer is (c) Salt and water.
Q.3. Turmeric is a natural indicator. On adding its paste to acid and base separately, which colours would be observed
(a) Yellow in both acid and base.
(b) Yellow in acid and red in the base.
(c) Pink in acid and yellow in the base.
(d) Red in acid and blue in the base.
Ans: b
Explanation: Turmeric paste is yellow in colour and it is acidic in nature hence it remains yellow in acid whereas it is converted to red due to neutralization by the base.
Q.4. Phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator and its colours in acidic and basic solutions, respectively are
(a) red and blue.
(b) blue and red.
(c) pink and colourless.
(d) colourless and pink
Ans: d
Explanation: Phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator that changes colour based on the acidity or basicity of a solution:
- In acidic solutions, it appears colourless.
- In basic solutions, it turns pink.
Q.5. When the soil is too basic, plants do not grow well in it. To improve its quality what must be added to the soil?
(a) Organic matter
(b) Quick lime
(c) Slaked lime
(d) Calamine solution
Ans: a
Explanation: Organic matter is added to basic soil to neutralize its base which improves its quality.
Q.6. ‘Litmus’, a natural dye is an extract of which of the following?
(a) China rose (Gudhal)
(b) Beetroot
(c) Lichen
(d) Blueberries (Jamun)
Ans: c
Q.7. A neutralisation reaction is a
(a) physical and reversible change.
(b) a physical change that cannot be reversed.
(c) chemical and reversible change.
(d) the chemical change that cannot be reversed.
Ans: d
Explanation:
- A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base.
- This reaction produces salt and water.
- It typically involves the release of heat, making it an exothermic process.
- The resulting salt can be acidic, basic, or neutral.
- Neutralization is generally considered a chemical change that cannot be reversed.
Q.8. A solution changes the colour of turmeric indicator from yellow to red. The solution is
(a) basic
(b) acidic
(c) neutral
(d) either neutral or acidic
Ans: a
Explanation: The turmeric indicator changes colour based on the acidity of a solution:
- In acidic solutions, turmeric turns red.
- This colour change indicates the solution's acidic nature.
Q.9. Which of the following set of substances contain acids?
(a) Grapes, lime water
(b) Vinegar, soap
(c) Curd, milk of magnesia
(d) Curd, vinegar
Ans: d
Explanation: Curd contains lactic acid and vinegar contains acetic acid.
Q.10. On adding phenolphthalein indicator to a colourless solution, no change is observed. What is the nature of this solution?
(a) Basic
(b) Either acidic or basic
(c) Either acidic or neutral
(d) Either basic or neutral
Ans: c
Explanation:
- The colour of phenolphthalein remains unchanged in both acidic and neutral solutions.
- This indicates that the solution is either acidic or neutral.
Q.11. Which of the following is an acid-base indicator?
(a) Vinegar
(b) Lime water
(c) Turmeric
(d) Baking soda
Ans: c
Explanation: Turmeric is a natural indicator that changes colour based on the acidity or basicity of a solution:
- Turns yellow in acidic solutions.
- Changes to red in basic solutions.
This property makes turmeric useful for identifying the nature of various substances.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Look at the given reaction.
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide (base) → Sodium chloride (salt) + Water
Sodium chloride formed in this reaction remains in solution form. Can we get solid sodium chloride from this solution? Suggest a method (if any).
Ans:
- Sodium chloride is soluble in water, resulting in a solution of sodium chloride. To obtain solid sodium chloride from this solution, we can use the following method:
- Evaporation: Heat the solution to evaporate the water, leaving behind solid sodium chloride.
Q.2. State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements
(a) All substances are either acidic or basic.
(b) A compound if acidic will turn all indicators red.
(c) Lime water turns red litmus blue.
(d) Common salt dissolved in water turns blue litmus red.
(e) Phenolphthalein is a natural indicator.
(f) Calamine can be used to treat ant’s sting.
(g) Lemon water is basic in nature.
Ans:
(a) False - Substances can be acidic, basic, or neutral.
(b) False - Acids do not turn all indicators red.
(c) True
(d) False - The colour of the litmus paper will not change.
(e) False - Phenolphthalein is a man-made indicator.
(f) True
(g) False - Lemon water is acidic in nature.
Q.3. Paheli is suffering from indigestion due to acidity. Is it advisable to give her orange juice in this situation and why?
Ans: No, orange juice is not recommended for indigestion caused by acidity.
- It is acidic in nature.
- Consuming acidic foods can worsen symptoms.
- It may irritate the stomach lining further.
Instead, consider alternatives like water or herbal teas.
Short Answer Questions
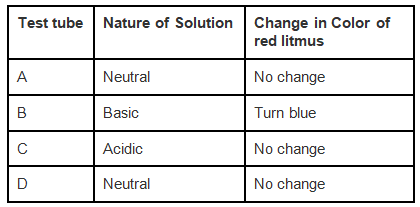
Q.1. Look at Figure which shows solutions taken in test tubes A, B, C and D. What colour is expected when a piece of red litmus paper is dropped in each test tube? Nature of the solutions is given in the table for your help.
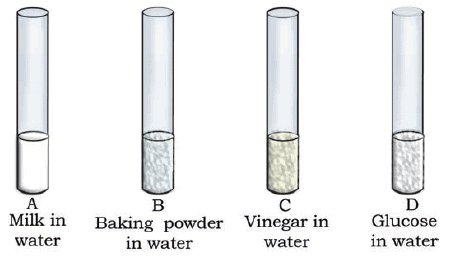
Ans:
Q.2. While playing in a park, a child was stung by a wasp. Some elders suggested applying the paste of baking soda and other lemon juice as the remedy. Which remedy do you think is appropriate and why?
Ans: Wasp stings inject an acidic substance into the body. To treat this, it is advisable to use baking soda because it is a base that can neutralise the acid.
Here are the key points:
- The sting causes pain and redness due to the acidic liquid.
- Applying baking soda helps to relieve these symptoms.
- Adding lemon juice may worsen the pain and redness.
Therefore, baking soda is the appropriate remedy for a wasp sting.
Q.3. Form a sentence using the following words – baking soda, ant bite, moist, effect, neutralised, rubbing.
Ans: The effect of an ant bite can be neutralised by rubbing moist baking soda.
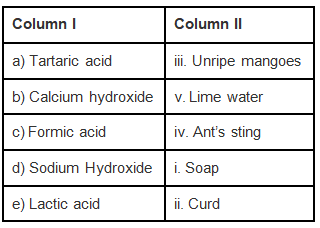
Q.4. Match the substances in Column I with those in Column II.
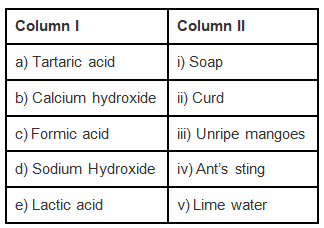
Ans:
Q.5. Fill the blanks in the following sentences
(a) Lemon juice and vinegar taste ___________ because they contain ___________.
(b) Turmeric and litmus are _________ acid-base indicators.
(c) Phenolphthalein gives _________ colour with lime water.
(d) When an acidic solution is mixed with a basic solution, they _________ each other forming _________ and water.
Ans:
(a) Lemon juice and vinegar taste sour because they contain acids.
(b) Turmeric and litmus are natural acid-base indicators.
(c) Phenolphthalein gives pink colour with lime water.
(d) When an acidic solution is mixed with a basic solution, they neutralize each other forming salt
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Boojho, Paheli and their friend Golu were provided with a test tube each containing China rose solution which was pink in colour. Boojho added two drops of solution ‘A’ in his test tube and got a dark pink colour. Paheli added 2 drops of solution ‘B’ to her test tube and got green colour. Golu added 2 drops of solution ‘C’ but could not get any change in colour. Suggest the possible cause for the variation in their results.
Ans: Since solution A turns China rose colour to dark pink hence Solution A is an acidic solution. solution B turns China rose colour to green colour hence Solution B is a basic solution. Since Solution C did not change the colour of china rose Solution it is a neutral solution.
Q.2. Fill in the crossword given as Figure with the help of the clues provided.
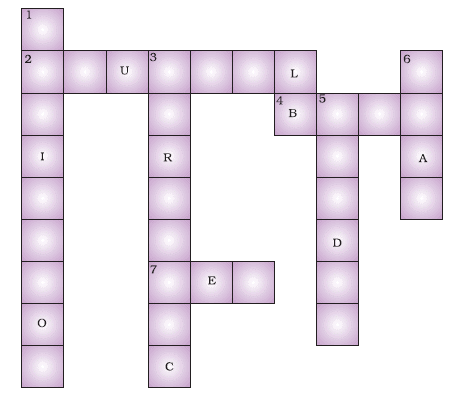
Across
(2) The solution which does not change the colour of either red or blue litmus.
(4) Phenolphthalein gives pink colour in this type of solution.
(7) Colour of blue litmus in lemon juice.
Down
(1) It is used to test whether a substance is acidic or basic.
(3) It is a natural indicator and gives a pink colour in a basic solution.
(5) Nature of ant’s sting.
(6) It is responsible for the increase in temperature during a neutralisation reaction.
Ans:
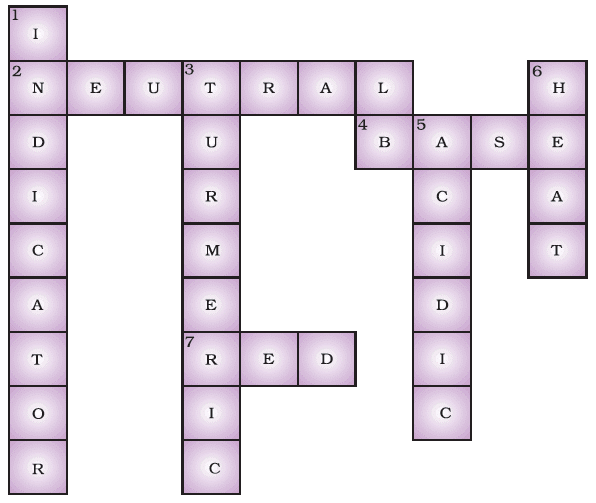
Q.3. A farmer was unhappy because of his low crop yield. He discussed the problem with an agricultural scientist and realised that the soil of his field was either too acidic or too basic. What remedy would you suggest the farmer to neutralise the soil?
Ans: If the soil is too acidic, it is treated with bases such as quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide). If the soil is too basic, organic matter is added to it. Organic matter releases acids which neutralise the basic nature of the soil.
Q.4. You are provided with four test tubes containing sugar solution, baking soda solution, tamarind solution, salt solution. Write down activity to find nature (acidic/basic/neutral) of each solution.
Ans: Add blue litmus solution and then red litmus solution for the test tubes containing sugar solution, baking soda solution, tamarind solution, salt solution. One can observe the colour changes to find the nature of each of them. It is as follows.
- Sugar and salt solution is neutral as there is no colour change
- Baking soda turns red litmus to blue and it is a basic solution.
- Tamarind solution turns blue litmus to red and it is acidic in nature
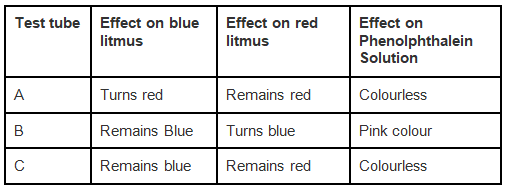
Q.5. You are provided with three test tubes A, B and C as shown in Figure with different liquids. What will you observe when you put
(a) a piece of blue litmus paper in each test tube.
(b) a piece of red litmus paper in each test tube.
(c) a few drops of phenolphthalein solution to each test tube.
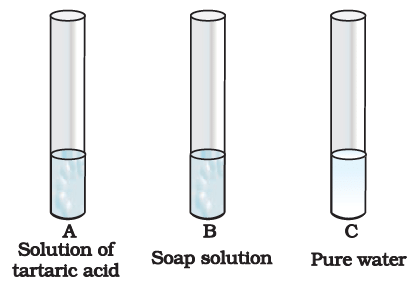
Ans:
Q.6. Paheli observed that most of the fish in the pond of her village were gradually dying. She also observed that the waste of a factory in their village is flowing into the pond which probably caused the fish to die.
(a) Explain why the fish were dying.
(b) If the factory waste is acidic in nature, how can it be neutralised?
Ans:
a) As Factory waste is disposed of in the river it can kill the fish as factory waste may contain acids, bases and other toxic compounds.
b) If the factory waste is acidic in nature, it can be neutralised by adding basic substances.
Q.7. Explain two neutralisation reactions related to a daily life situation.
Ans:
a) Acidity
Acidity is caused in the stomach as indigestion releases a lot of acids. This can be controlled by taking antacids like milk of magnesia.
(b) Ant’s sting
Ant’s sting releases formic acid in the skin. It can be neutralised by rubbing baking soda or putting calamine lotion.
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 2. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |
| 3. What is the pH scale? |  |
| 4. How is the pH of a solution determined? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |





















