NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Physical & Chemical Changes | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Which of the following is a physical change?
(a) Rusting of iron
(b) Combustion of magnesium ribbon
(c) Burning of candle
(d) Melting of wax
Ans: d
Explanation:
Rusting of iron, combustion and burning of the candle are chemical changes where produced cannot be converted into reactants.
Q.2. Which of the following is a chemical change?
(a) Twinkling of stars
(b) Cooking of vegetables
(c) Cutting of fruits
(d) Boiling of water
Ans: b
This process is a chemical change because:
- New substances are formed during cooking.
- The original properties of the vegetables change.
- Cooking involves a chemical reaction that alters the food.
Q.3. A chemical change may involve –
(a) change in colour only
(b) change in temperature only
(c) evolution of gas only
(d) any or all of the above
Ans: d
Explanation:
A chemical change may involve a change in colour, temperature, smell or evolution of gas, heat, etc.
Q.4. Which of the following is/are true when milk changes into curd?
- Its state is changed from liquid to semi-solid.
- It changes colour.
- It changes the taste.
- The change cannot be reversed.
Choose the correct option from below :
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) to (iv) are correct
Ans: c
Explanation:
When milk turn to turn it changes its shape to semisolid, its taste turn sour but its colour remains white hence the answer is c)
Q.5. A man painted his main gate made up of iron, to
- prevent it from rusting.
- protect it from the sun.
- make it look beautiful.
- make it dust-free.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) only (ii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans: d
- The man painted his iron gate primarily to prevent it from rusting.
- Painting creates a protective layer that blocks moisture and oxygen, which are essential for rust formation.
- This method is effective in maintaining the gate's appearance and durability.
Q.6. Iron pillar near the Qutub Minar in Delhi is famous for the following facts. Which of these facts is responsible for its long stability?
(a) It is more than 7 metres high.
(b) It weighs about 6000 kg.
(c) It was built more than 1600 years ago.
(d) It has not rusted after such a long period.
Ans: d
- The Iron pillar near the Qutub Minar is renowned for its remarkable rust resistance.
- It has remained unrusted for over 1600 years, showcasing advanced ancient metal technology.
- This durability is attributed to its unique composition and the environmental conditions it has endured.
Q.7. Galvanisation is a process used to prevent the rusting of which of the following?
(a) Iron
(b) Zinc
(c) Aluminium
(d) Copper
Ans: a
Explanation: Galvanization is a method used to protect iron from rusting by coating it with zinc. This process helps to:
- Prevent direct contact with oxygen and moisture.
- Reduce the rate of rust formation, especially in humid environments.
- Extend the lifespan of iron products, such as pipes and structures.
For example, iron pipes used in homes are often galvanisedto ensure they do not rust quickly.
Q.8. Paheli’s mother made a concentrated sugar syrup by dissolving sugar in hot water. On cooling, crystals of sugar got separated. This indicates a –
(a) a physical change that can be reversed.
(b) the chemical change that can be reversed.
(c) a physical change that cannot be reversed.
(d) the chemical change that cannot be reversed.
Ans: a
Explanation:
- The formation of sugar crystals from a concentrated sugar syrup indicates a physical change.
- This change is reversible, meaning sugar can be separated from the solution.
- When the syrup cools, the sugar comes out of the solution as crystals.
Q.9. Which of the following statement is incorrect for a chemical reaction?
(a) Heat may be given out but never absorbed.
(b) The sound may be produced.
(c) A colour change may take place.
(d) A gas may be evolved.
Ans: a
Explanation:
During chemical reaction heat may be absorbed or given out hence option a) is a wrong statement.
Q.10. Two drops of dilute sulphuric acid were added to 1 g of copper sulphate powder and a then a small amount of hot water was added to dissolve it (step I). On cooling, beautiful blue coloured crystals got separated (step II). Step I and Step II are:
(a) physical and chemical changes, respectively.
(b) chemical and physical changes, respectively.
(c) both physical change.
(d) both chemical change.
Ans: c
Explanation:
Dissolution of copper sulphate powder in water in the presence of sulphuric acid is a physical change. On cooling this hot solution, the crystals of copper sulphate are separated, this is also a physical change.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. State whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) When a candle burns, both physical and chemical changes take place.
(b) Anaerobic bacteria digest animal waste and produce biogas.
(c) Ships suffer a lot of damage though they are painted.
(d) Stretching of the rubber band is not a physical change.
Ans:
(a) True
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False- Stretching of the rubber band is a physical change
Q.2. Melting of wax is a change where a solid changes to a liquid state. Give one more such change which you observe in your surroundings.
Ans: Melting of ice is another example where solid turns to liquid.
Q.3. What kind of change is shown by tearing of paper?
Ans: This is a physical change that cannot be reversed.
Short Answer Questions
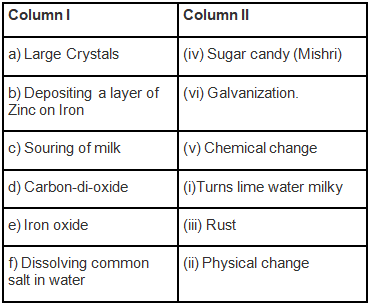
Q.1. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II.
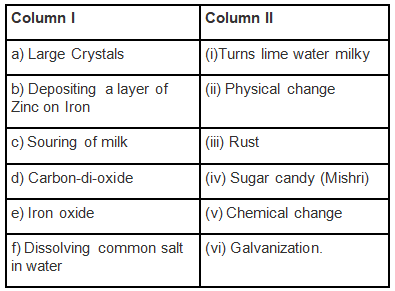
Ans:
Q.2. Fill in the blanks in the following statements using the words given in the box.
rusted, colourful, substance, chemical, physical, reversible, iron oxide, object
(a) Making sugar solution is a ____________ change.
(b) A physical change is generally____________.
(c) Grinding of wheat grain changes its size. It is a ____________ change.
(d) Iron benches kept in lawns and gardens get____________. It is a _________ change because a new _________ is formed.
Ans:
(a) Making sugar solution is a Physical change.
(b) A physical change is generally reversible.
(c) Grinding of wheat grain changes its size. It is a physical change.
(d) Iron benches kept in lawns and gardens get rusted. It is a chemical change because a new substance is formed.
Q.3. Classify the following processes into physical or chemical changes:
(i) The beating of aluminium metal to make aluminium foil.
(ii) Digestion of food.
(iii) Cutting of a log of wood into pieces.
(iv) Burning of crackers.
Ans:
i) Physical change
ii) Chemical change
iii) Physical change
iv) Chemical change
Q.4. Write word equations for two chemical reactions with the help of materials given in the box.
Air, copper sulphate, iron, vinegar, iron oxide, carbon dioxide, iron sulphate, copper, lime water, water
Ans:
(1) Iron + Air + Water _ Iron oxide
(2) Copper sulphate + Iron _ Iron sulphate + Copper
Q.5. Explain the following:
(a) Lime water turns milky on passing carbon dioxide gas into it.
(b) Bubbles are produced when acetic acid is added to a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Ans:
(a) White coloured insoluble calcium carbonate is formed.
(b) Carbon dioxide is evolved due to the chemical reaction between acetic acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Give two examples for each of the following cases:
(a) Physical changes are reversible.
(b) Physical changes are not reversible.
(c) Chemical changes.
Ans:
- Folding of paper, melting of ice
- Tearing of paper, breaking of glass
- Curdling of milk, cooking of food
Q.2. Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations:
(a) A change in colour is observed.
(b) Gas is evolved.
(c) Sound is produced.
Ans:
(a) The reaction between copper sulphate solution and iron metal.
(b) The reaction between baking soda and vinegar (carbon dioxide is evolved).
(c) Burning of crackers.
Q.3. If you leave a piece of iron in the open for a few days, it acquires a film of brownish substance, called rust.
(a) Do you think rust is different from iron?
(b) Can you change rust back into iron by some simple method?
(c) Do you think the formation of rust from iron is a chemical change?
(d) Give two other examples of a similar type of change
Ans:
a) Rust is iron oxide and it’s different from iron
b) Formation of rust is irreversible hence it cannot be reversed by any method.
c) When iron reacts with water and atmospheric oxygen iron oxide is formed which is called rust. This is a chemical change as a new compound is formed.
(d)
- The setting of curd from milk.
- Burning of magnesium ribbon to form magnesium oxide.
Q.4. A student took a solution of copper sulphate in a beaker and put a clean iron nail into it and left it for about an hour.
(a) What changes do you expect?
(b) Are these changes chemical in nature?
(c) Write a word equation for the chemical change, if any.
Ans:
(a)
- Colour of the solution in the beaker changes from blue to green.
- A brown coloured deposit is found on the surface of the iron nail.
b) These changes are chemical changes as the new substances are formed in the form of iron sulphate and copper.
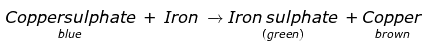
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Physical & Chemical Changes - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are physical changes? |  |
| 2. What are chemical changes? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? |  |
| 4. How can you distinguish between physical and chemical changes? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of physical and chemical changes? |  |





















