NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 3 - The Making of a Global World
Q1. Give two examples of different types of global exchanges which took place before the seventeenth century, choosing one example from Asia and one from the Americas.
Ans:
(i) Asia
- The Silk Routes are an example of vibrant pre-modem trade. These routes linked Asia with Europe and northern Africa and were used for trades in Chinese pottery and spices from India and Southeast Asia.
- Gold and silver came from Europe to Asia. Noodles are believed to reach Europe from China.
- Christian missionaries and Muslim preachers too travelled through these routes.
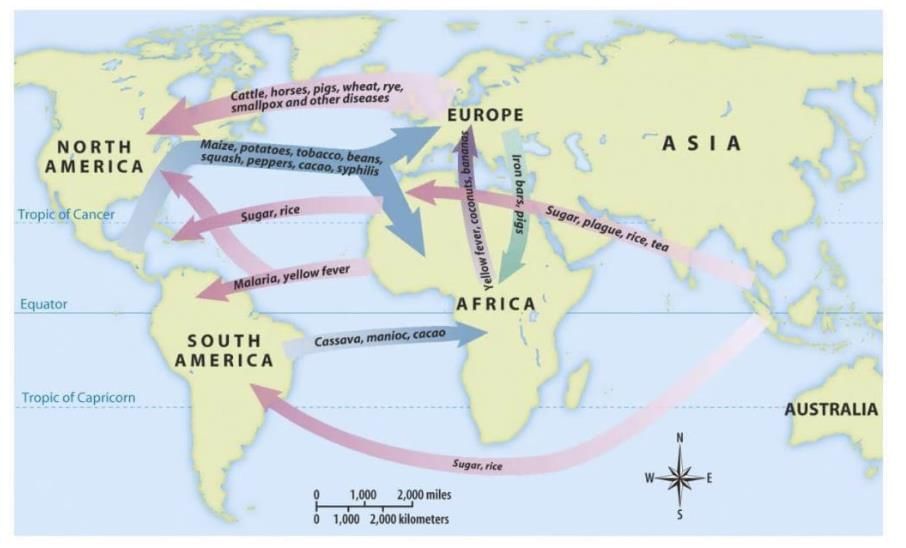
(ii) America
- America was rich in foods and minerals. Today’s common foods like potatoes, tomatoes, chillies, soya, maize, groundnuts, etc., came to Europe and then Asia from America after Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered this continent.
- Precious metals like silver from mines in Peru and Mexico enhanced Europe’s wealth and financed its trade with Asia.
- Thus, there was a global exchange before the seventeenth century
Q2. Explain how the global transfer of disease in the pre-modern world helped in the colonization of the Americas.
Ans:
- The global transfer of disease in the pre-modern world helped in the colonisation of the Americas because the native Americans had no immunity against the disease that came from Europe.
- Before the discovery of America, it had been cut off from the rest of the world for millions of years. So, they had no defense against the disease.
- In particular, Smallpox proved a deadly killer. It killed and decimated whole communities, paving the way for conquest.
Q3. Write a note to explain the effects of the following:
(a) The British government’s decision to abolish the Corn Laws.
Ans:
- The British government's decision to abolish the Corn Laws resulted in the inflow of cheaper food in Britain. British agriculture was unable to compete with imports. Vast areas of land were left uncultivated.
- Thousands of men and women, who were thrown out of work, migrated to towns and cities. This indirectly led to global agriculture and rapid urbanisation, a prerequisite of industrial growth.
(b) The coming of Rinderpest to Africa
Ans:
- Rinderpest (a fast-spreading disease of cattle plague) arrived in Africa in the late 1880s. Within two years, it spread in the whole continent reaching Cape Town within five years.
- Rinderpest had a terrifying impact on people’s livelihoods and the local economy. It killed about 90% of the cattle.
- Planters, mine owners and colonial governments became successful to strengthen their power and forcing Africans into the labour market.
(c) The death of men of working-age in Europe because of the World War.
Ans:
- World War-I was mainly fought in Europe between the years 1914 to 1918. Millions of soldiers were recruited from all over the world. The scale of death and destruction - 9 million dead and 20 million injured - was unthinkable. Most of the killed and injured were men of working age.
- In Europe, there was a reduction in the able-bodied workforce due to the deaths and injuries of the war. This led to the decline in the household incomes as the number of people reduced in the family.
- Due to this, the women stepped in to undertake the jobs that earlier only men were expected to do. It increased the role of women that led to a demand for their equal status in society. It made the feminist movement even stronger.
(d) The Great Depression on the Indian Economy
Ans:
- In the nineteenth century, colonial India had become an exporter of agricultural goods and an importer of manufactures. The impact of the Great Depression in India was felt, especially in the agricultural sector.
- It was evident that the Indian economy was closely becoming integrated into the global economy. India was a British colony and exported agricultural goods and imported manufactured goods.
- As international prices crashed so did the prices in India. The wheat prices in India fell by 50% between 1928 and 1934. The government did not decrease their taxes due to which peasants' indebtedness increased all across India.
(e) The decision of MNCs to relocate production to Asian countries.
Ans: The relocation of industry to the low-wage countries had the following impact:
- It provided a cheap source of labour for MNCs.
- It stimulated world trade and increased capital inflow in the Asian Countries.
- It brought about new technology and production methods to the Asian Countries.
- It produced greater employment opportunities for Asian countries.
Q4. Give two examples from history to show the impact of technology on food availability.
Ans: Examples of Technology Impacting Food Availability are:
(i) Improved Transportation Systems: Improved transportation systems helped the foods get delivered on time to the markets without any harm. Faster railways, lighter wagons and larger ships helped move food cheaply and quickly from faraway farms to final markets.
(ii) Refrigerated Ships: The development of refrigerated ships enabled the transport of perishable foods over long distances. Animals were slaughtered for food at the starting point -in America, Australia or New Zealand – and then transported to Europe as frozen meat. This reduced shipping costs and lowered meat prices in Europe.
Q5. What is meant by the Bretton Woods Agreement?
Ans:
- In order to preserve economic stability and full employment in the industrial world, the post-war international economic system was established.
- To execute the same, the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference was held in July 1944 at Bretton Woods in New Hampshire, USA. The Bretton Woods Conference established the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to deal with external surpluses and shortages of its member-nations.
- The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (popularly known as the World Bank) was set up for financial post-war reconstruction, and they started the financial operations in 1947.
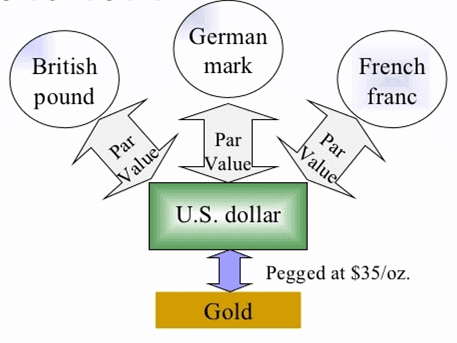 Bretton Woods System
Bretton Woods System - Under the agreement, currencies were pegged to the price of gold, and the US dollar was seen as a reserve currency linked to the price of gold. Decision-making authority was given to the Western industrial powers.
Q6. Imagine that you are an indentured Indian labourer in the Caribbean. Drawing from the details in this chapter, write a letter to your family describing your life and feelings.
Ans:
Dear Family,
I hope you all are fine there. I am working in the Caribbean as an indentured labourer. Through this letter, I want to tell you about my work life and hardships. I have been hired by the colonisers under a contract that included wrong information regarding the place of work, mode of travel and living and working conditions. The contractor uses harsh and abusive language for us. There is a lot of work at the plantations with a heavy workload and sometimes I have to finish all of it in just one day. The contractor cuts my wages if he is not satisfied with my work. I am living here a slave’s life. I know you will be very upset to know my situation but the governments here are thinking to introduce new laws to protect the labourers like us. So, I hope this situation will pass soon.
Your Loving,
ABC
Q7. Explain the three types of movements or flows within the international economic exchange. Find one example of each type of flow that involved India and Indians, and write a short account of it.
Ans: The three types of movements or flows within the international economic exchange are:
(i) Flow of trade (trade in goods such as cloth or wheat): India was involved in trade relations since ancient times. It exported textiles and spices in return for gold and silver from Europe.
(ii) Flow of labour (the migration of people to new areas in search of work): In the nineteenth century, thousands of Indian labourers went to work on plantations, in mines, and in road and railway construction projects around the world. Indentured labourers were hired under contacts which promised their return to India after working for five years in the plantation. The living conditions were harsh and the labourers had very few legal rights.
(iii) Flow of capital (short-term and long-term loan to and from other nations): To finance the World War, Britain took high loans from the USA. Since India was under British rule, the impact of these loan debts was felt in India too. The British government increased taxes, interest rates, and lowered the prices of products it bought from the colony. This affected the Indian economy very strongly.
Q8. Explain the causes of the Great Depression.
Ans: There were various factors that led to the Great Depression: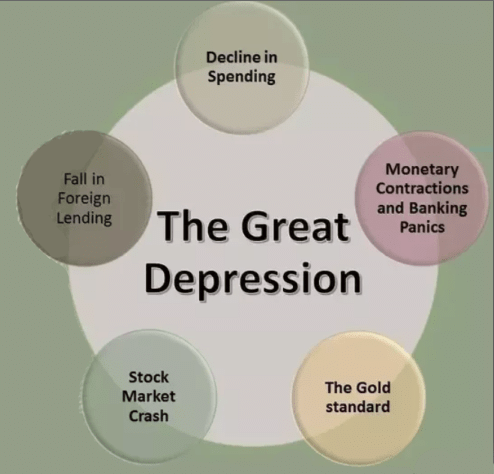
- The post-war global economy was weak during that time. The problem began with agricultural overproduction, which got worse by the falling of food grain prices. Due to the fall in prices, the agricultural incomes declined.
- Farmers began expanding their production and bringing, even more, produce to the markets to maintain their annual incomes. This worsened the glut in the market, pushing down prices even further.
- Prosperity in the USA during the 1920s created a cycle of higher employment and incomes. It led to a rise in consumption and demands. More investment and more employment created tendencies of speculations which led to the Great Depression of 1929 up to the mid-1930s.
- The stock market crashed in 1929. It created panic among investors and depositors who stopped investing and depositing. As a result, it created a cycle of depreciation.
- Most of the countries took loans from the US, but American overseas lenders were wary about the same. As they decreased the amount of loans, the countries which were economically dependent on the US loans faced an acute crisis.
- In Europe, it led to the failure of some major banks and the currencies collapsed. The USA import duties were doubled in order to protect its economy. All these factors played a major role in causing the Great Depression.
Q9. Explain what is referred to as the G-77 countries. In what ways can G-77 be seen as a reaction to the activities of the Bretton Woods twins?
Ans:
- G-77 countries is a group of developing countries that demanded a new International Economic Order (NIEO). By the NIEO they meant a system that would give them:
(i) Real control over their natural resources.
(ii) Fairer prices for raw materials.
(iii) Better access for their manufactured goods in the markets of the developed countries. - The Group of 77 (G77) at the United Nations is a coalition of 134 developing countries, designed to promote its members’ collective economic interests.
- The Bretton Woods twins i.e., the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have been established by the developed countries.
- These institutions were set up to meet the financial needs of the industrialised countries and had nothing to do with the economic growth of the former colonial countries and developing nations.
- G-77 was created entirely to cater to the needs of developing nations.
- Thus it was a reaction to the activities of the Bretton Woods system and to protect the interests of the developing countries.
|
66 videos|632 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 3 - The Making of a Global World
| 1. What is the significance of the global economy in the 19th century? |  |
| 2. How did the First World War impact global trade? |  |
| 3. What role did the Great Depression play in shaping the global economy? |  |
| 4. How has globalization transformed cultural exchanges? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by countries in a globalized world? |  |






















