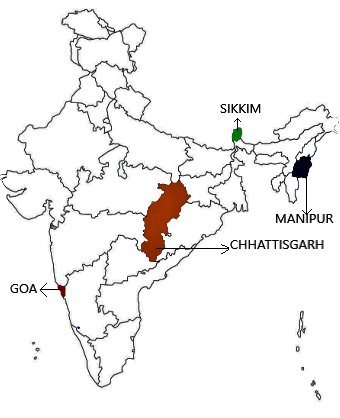
Q1. Locate the following States on a blank outline map of India:
Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh, and Goa.
Ans:
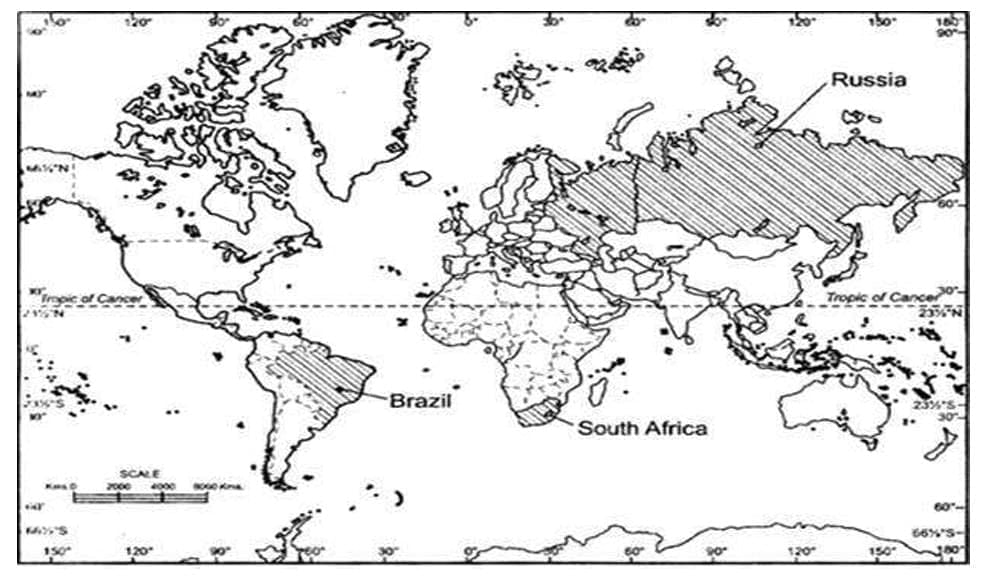
Q2: Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline map of the world.
Ans: Three federal countries other than India are:
Q3. Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Ans: (a) Similar feature: Distribution of powers:
(i) In both countries, power has been divided among the national government, state (provincial) governments, and local governments (community govt, in Belgium).
(ii) In Belgium, the community government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
(iii) In India, the legislative powers are divided as mentioned in the Union List, State List and Concurrent List. In addition to this, by the Act of 1992, the local governments have been granted more powers.
(b) Different features:
In Belgium, in addition to the Central and State governments, there is a third kind of government that is community government. This is elected by people belonging to one language community - Dutch, French and German-speaking, no matter where they live. This government deals with cultural, educational and language-related issues. In India, there is no such government.
In India, there is a three-tier government. The third government is the local government, i.e., Panchayats at the village level and Municipalities at the town level.
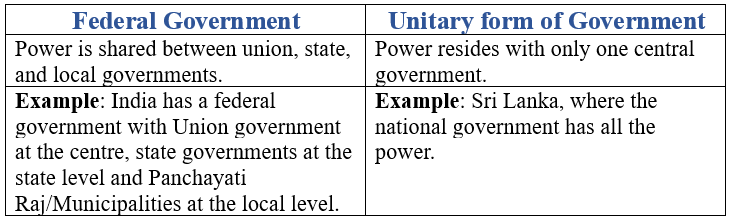
Q4. What is the main difference between a federal form of government and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
Ans:
 Q5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Q5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Ans: Two differences between the local government before and after the constitutional amendment in 1992 are as follows:
(i) Before 1992, elections to the local bodies were not held regularly. Since 1992, it has been constitutionally mandated to hold regular elections for local government bodies.
(ii) Before 1992, local bodies did not have any powers or resources of their own. After 1992, the state governments were required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies.
Q6. Fill in the blanks:
Since the United States is a (i) ______________ type of federation, all the Constituent States have equal powers and States are (ii)______________vis-a-vis the federal government. But India is a (iii) ______________ type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the (iv) __________ government has more powers.
Ans: (i) coining together
(ii) strong
(iii) holding together
(iv) central
Q7. Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India. Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Arman: Language-based States have divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consolidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Ans: Sangeeta’s position that the policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity is valid. To prevent a situation like Sri Lanka, where the language of the majority was promoted, the Central Government decided to continue using both English and Hindi for official purposes. Unlike Sri Lanka, where a single language is prioritized, our country gives equal status to all the major languages spoken across various regions.
This inclusive policy has not only minimized conflicts between different linguistic groups but also streamlined administration. It has facilitated greater participation in government activities by people from diverse linguistic backgrounds, contributing to a more unified and cooperative national environment.
Q8. The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(а) National government gives some powers to the provincial government.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Ans: (d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
We know that, federal government is that form of government in which the government is formed of three branches: legislative, executive, and judiciary, and hence the governmental power is divided between these different levels of government. Therefore, option (d) is correct.
Q9. A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below:
A. Defence
B. Police
C. Agriculture
D. Education
E. Banking
F. Forests
G. Communications
H. Trade
I. Marriages

Ans: (i) Union List: Defence, Banking and Communications.
(ii) State List: Police, Agriculture and Trade.
(iii) Concurrent List: Education, Forests and Marriages.
Q10. Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
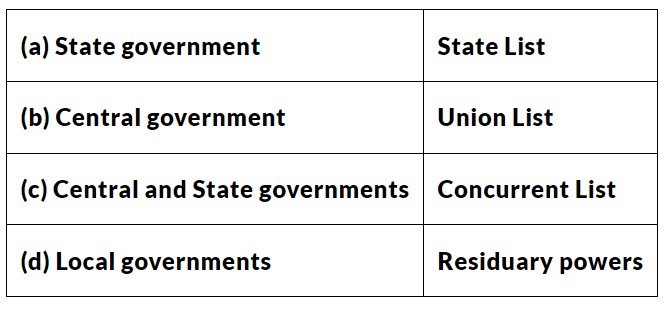
Ans: (d) Local governments — Residuary powers.
The residuary powers of legislation are vested in Parliament, not the States. The Constitution places national matters in the Union List, state-specific issues in the State List, and shared concerns in the Concurrent List.
Q11. Match List I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
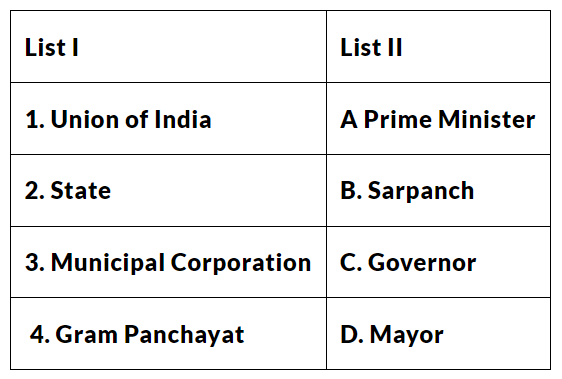
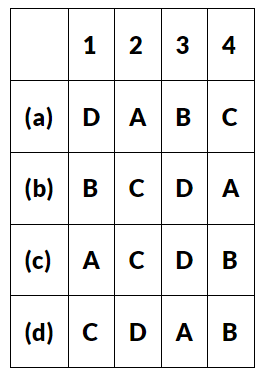
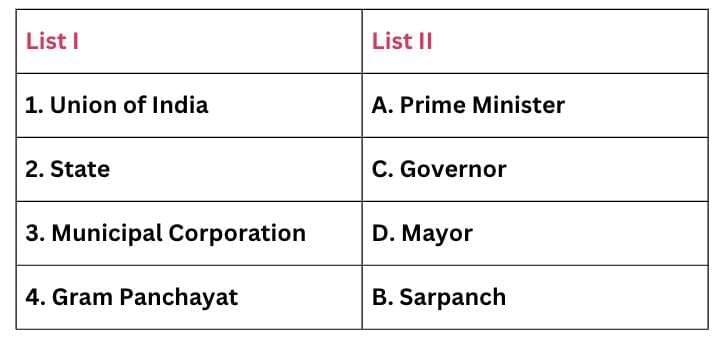
Ans: (c) A-1, C-2, D-3, B-4.
Q12. Consider the following statements:
A. In a federation, the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly demarcated.
B. India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
C. Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
D. India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, C and D
(c) A and B only
(d) B and C only
Ans: (c) A and B only.
Statement A: Correct. In a federation, the powers of the federal and provincial (or state) governments are clearly defined in the constitution.
Statement B: Correct. India is a federation because the Constitution specifies the powers of the Union and State Governments, and they have exclusive jurisdiction over their respective subjects.
Statement C: Incorrect. Sri Lanka is not a federation; it is a unitary state despite being divided into provinces.
Statement D: Incorrect. India remains a federation despite some powers being devolved to local government bodies; this devolution does not negate its federal nature.
Thus, the correct statements are A and B only.



 Q5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Q5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.





















