NCERT Solution: The Decision of the Panchayat | English Santoor Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Let us Think (Page 95) |

|
| Let us Learn (Page 96) |

|
| Let us Speak (Page 98) |

|
| Let us Write (Page 100) |

|
| Let us Listen (Page 101) |

|
| Let us do (Page 103) |

|
Let us Think (Page 95)
A. Answer the following questions
Q1: Why did the farmer buy the well?
Ans: The farmer bought the well to have a source of water for his fields.
Q2: Why did the farmer become upset?
Ans: The farmer became upset because his neighbour refused to let him take water from the well, claiming the water still belonged to him.
Q3: How did the Panchayat solve the problem?
Ans: The Panchayat solved the problem by reasoning that if the neighbour claimed the water was his, he must remove it from the farmer’s well, or it would belong to the farmer.
Q4: What was the final judgment given by the Panchayat?
Ans: The final judgment was that the neighbour must remove his water from the farmer’s well immediately, or the water would belong to the farmer. The neighbour also had to pay a fine and apologise.
a. “I sold only the well, not the water,”
b. “Remove the water or use it all up immediately,”.
c. “He is not letting me take the water.”
Ans:
– The neighbour said to the farmer.
– The village chief said to the neighbour
– The farmer said to the village chief.
Let us Learn (Page 96)
A. Match the words with their meanings
1-f
2-a
3-e
4-c
5-b
6-d
B. Fill in the blanks with the correct prepositions (in, at, by, after, before, under, with, to, for). A preposition can be used more than once.
1. The farmer went ................... the village chief to explain his problem.
2. The neighbour was standing ................... the well, blocking the way.
3. The villagers tried to reason ................... the cunning man.
4. The decision was made ................... careful consideration of both sides.
5. Their lived a farmer ................... the small village.
6. The Panchayat members listen to both sides ................... coming to a decision.
7. The villagers gathered the Panchayat................... the banyan tree.
8. The neighbour was punished ................... his dishonesty.
9. The chief listened carefully ................... both the farmer and the neighbour.
10. The villagers agreed to meet ................... a later time to discuss the issue.
11. The farmer decided to buy a well ...................buying his third field.
Ans: 1. The farmer went to the village chief to explain his problem.
2. The neighbour was standing by the well, blocking the way.
3. The villagers tried to reason with the cunning man.
4. The decision was made after careful consideration of both sides.
5. The farmer lived in the small village.
6. The Panchayat members listened to both sides before coming to a decision.
7. The villagers gathered under the Panchayat by the banyan tree.
8. The neighbour was punished for his dishonesty.
9. The chief listened carefully to both the farmer and the neighbour.
10. The villagers agreed to meet at a later time to discuss the issue.
11. The farmer decided to buy a well after buying his third field.
C. Rearrange the events in the correct order
 Ans:
Ans:
Let us Speak (Page 98)
Look at the Pictures below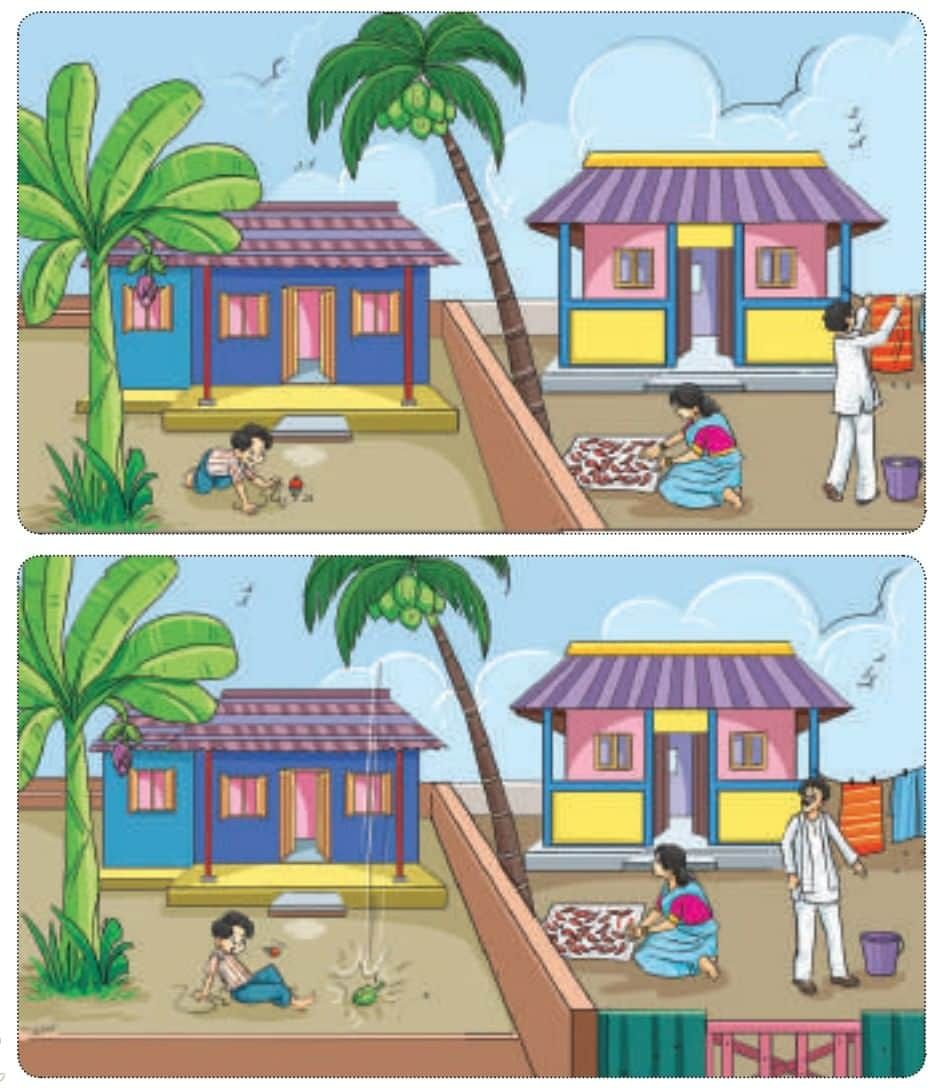
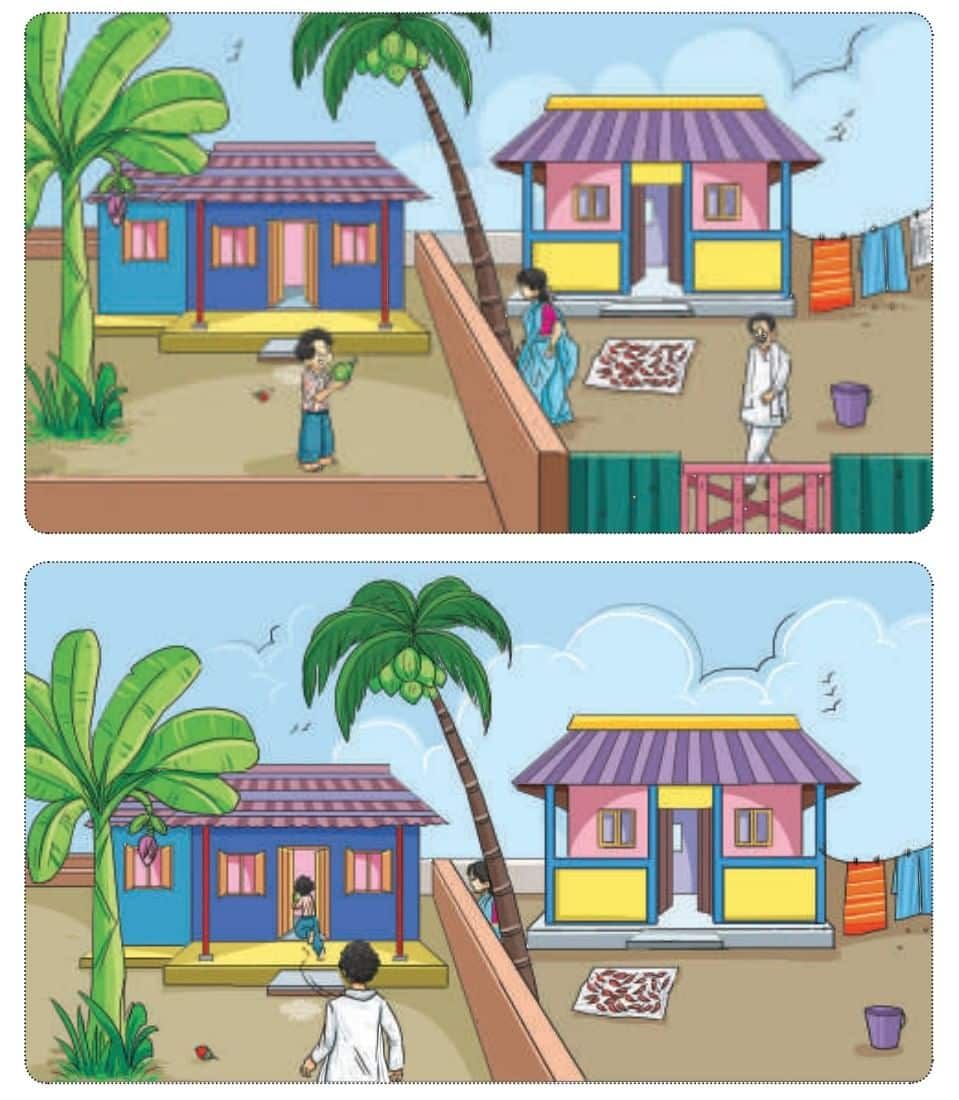
Let us Write (Page 100)
A. Imagine you are the farmer. Write a letter to your friend about the incident and the decision of the Panchayat. You may begin as follows:
My dear friend,
Something happened last week which I want to tell you. I wanted to buy a well ...
My dear friend,
Something happened last week, which I want to tell you. I wanted to buy a well for my fields, so I bought one from my neighbor. But the next day, he stopped me from taking water, saying he only sold the well, not the water! I was upset and went to the village chief. The Panchayat met under the banyan tree and heard both sides. They decided that if the water was his, he must remove it from my well, or it belongs to me. The neighbor apologized and paid a fine. I’m so relieved!
Yours,
The Farmer
B. Read the Following


Make sentences using the new words in your notebook.
1. Use + less = useless.
Sentence: The broken tool was useless for farming.
2. Hope + less = hopeless.
Sentence: The farmer felt hopeless when he couldn’t get water.
3. Care + less = careless.
Sentence: Being careless with water wastes it.
4. Fear + less = fearless.
Sentence: The fearless farmer spoke to the Panchayat confidently.
5. Help + less = helpless.
Sentence: Without the Panchayat, the farmer felt helpless.
Let us Listen (Page 101)
Listen to your teacher read out this passage and answer the questions by choosing the correct option.
1. Where was Sri Ramakrishna Paramahamsa born?
Ans: b. A small village in West Bengal.
2. Who was the curious boy that became Sri Ramakrishna’s student?
Ans: b. Swami Vivekananda (Naren)
3. What kind of life did Sri Ramakrishna live?
Ans: b. A simple and loving life.
4. What did Sri Ramakrishna compare religions to?
Ans: c. Rivers flowing to the ocean
5. What did Sri Ramakrishna teach Naren?
Ans: d. To find peace
Let us do (Page 103)
A. Read the passage carefully and answer the following questions.
1. Where can you find neem trees?
Ans: Neem trees can be found near houses, schools, or beside roads.
2. Why do you think ‘neem’ is called a magic tree?
Ans: Neem is called a magic tree because almost every part is used for medicine.
3. What happens when dry neem leaves are burnt?
Ans: When dry neem leaves are burnt, mosquitoes disappear.
4. Why do people put neem leaves in clothes and rice containers?
Ans: People put neem leaves in clothes and rice containers to keep insects and pests away.
5. How are neem twigs used?
Ans: Neem twigs are used as a toothbrush to clean teeth.
6. Find the meaning of the word ‘disappear’ from the following options:
Ans: b. Vanish
7. Find the word in the passage which means ‘a short stick’:
Ans: c. Twig

Ans:
- Sun: In the top image, the sun has rays, while in the bottom image it does not.
- Tulsi Pot Design: The tulsi pot has a white border near the base in the top image, missing in the bottom.
- Tulsi Plant: The tulsi plant has more leaves in the top image and fewer in the bottom.
- Chappals: Blue slippers are outside in the top image; yellow slippers are in the bottom image.
- Border of Saree (Bottom): The woman’s saree border has pink and green designs in the top image, plain blue in the bottom.
- Pallu Border: The border of the saree pallu in the top image has pink design; in the bottom image, it is plain blue with pink at the edge.
- Bindi: The woman wears a red bindi in the top image; it's missing in the bottom.
- Background Wall Design: The wall behind the tulsi pot has a green strip in the top image, which is missing in the bottom.
- Mud Pot Design (Top of Tulsi): The yellow part has a different wave design in both images.
- Fan Handle: The design in the circular hand-fan is different in color and style.
- Window Design: The window above the woman is open with bars in the top image; it has a blue glass pane in the bottom image.
|
44 videos|451 docs|63 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution: The Decision of the Panchayat - English Santoor Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the role of the Panchayat in decision-making within a community? |  |
| 2. How does the Panchayat ensure fairness in its decisions? |  |
| 3. What are some common issues that Panchayats typically address in a village? |  |
| 4. In what ways can villagers participate in the Panchayat's activities? |  |
| 5. What challenges do Panchayats face in their functioning? |  |















