NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 5 - Democratic Rights
Q1. Which of the following is not an instance of an exercise of a fundamental right?
(a) Workers from Bihar go to the Punjab to work on the farms
(b) Christian missions set up a chain of missionary schools
(c) Men and women government employees get the same salary
(d) Parents’ property is inherited by their children
Ans: (d) Parents’ property is inherited by their children
Inheritance of property is governed by civil law and is not an instance of the exercise of a fundamental right. The other options involve fundamental rights such as the right to freedom of movement, religion, and equality.
Q2. Which of the following freedoms is not available to an Indian citizen?
(a) Freedom to criticise the government
(b) Freedom to participate in armed revolution
(c) Freedom to start a movement to change the government
(d) Freedom to oppose the central values of the Constitution
Ans: (b) Freedom to participate in armed revolution
Indian citizens do not have the freedom to participate in an armed revolution, as it is against the law. While citizens are free to criticize the government and start movements for change, they must do so peacefully and within the framework of the Constitution. Opposing the central values of the Constitution is also not permissible.
Q3. Which of the following rights is available under the Indian Constitution?
(a) Right to work
(b) Right to adequate livelihood
(c) Right to protect one’s culture
(d) Right to privacy
Ans: (c) Right to protect one’s culture
Under the Indian Constitution, citizens have the right to preserve their language, script, and culture (Articles 29 and 30). This is a fundamental right under the Cultural and Educational Rights section.
Q4. Name the Fundamental Right under which each of the following rights falls:
(a) Freedom to propagate one’s religion
(b) Right to life
(c) Abolition of untouchability
(d) Ban on bonded labour
Ans:
(a) Right to Freedom of Religion
(b) Right to Freedom
(c) Right to Equality
(d) Right against Exploitation
Q5. Which of these statements about the relationship between democracy and rights is more valid? Give reasons for your preference.
(a) Every country that is a democracy gives rights to its citizens.
(b) Every country that gives rights to its citizens is a democracy.
(c) Giving rights is good, but it is not necessary for a democracy.
Ans: (a) Every country that is a democracy gives rights to its citizens.
Reasons:
(i) Rights are necessary for the very existence of democracy.
(ii) In a democracy, every citizen has the right to vote.
Q6. Are there restrictions on the right to freedom justified? Give reasons for your answer.
(a) Indian citizens need permission to visit some border areas of the country for reasons of security.
(b) Outsiders are not allowed to buy property in some areas to protect the interest of the local population.
(c) The government bans the publication of a book that can go against the ruling party in the next elections.
Ans:
(a) It is justified. The security of the country is the first duty of a government, and this cause can stop the people from visiting the border areas.
(b) This action is also justified. The local population may not be financially strong to protect its interests. Outsiders can take away their rights in their own area, so such a step of the government is correct.
(c) Not justified. The publication of a book can only be banned if it disturbs the peace and hurts the sentiments of a section of people, and not on the grounds of protecting the ruling party’s prospects in the next election.
Q7. Manoj went to a college to apply for admission into an MBA course. The clerk refused to take his application and said “You, the son of a sweeper, wish to be a manager! Has anyone done this job in your community? Go to the municipality office and apply for a sweeper’s position”. Which of Manoj’s fundamental rights are being violated in this instance? Spell these out in a letter from Manoj to the district collector.
Ans:
To,
The District Collector,
Address___________
Date_______________
Subject- Violation of a Fundamental Right
Respected Sir/Ma’am,
I had applied for an MBA course In order to fulfill my dream to become a Manager. But the Clerk in the office rejected my application and passed discriminatory comments. He made this decision on the basis of class bias. This is a clear violation of my Right to Freedom and equality. I am free to choose the profession I want to practice and nobody should discriminate against me on the basis of my class or caste. I request that you look into the matter and take the necessary action.
Thank You Sir/Ma’am.
With Regards,
Manoj
Q8. When Madhurima went to the property registration office, the Registrar told her. "You can’t write your name as Madhurima Banerjee d/o Α. K. Banerjee. You are married, so you must give your husband’s name. Your husband’s surname is Rao. So your name should be changed to Madhurima Rao." She did not agree. She said "If my husband’s name has not changed after marriage, why should mine?" In your opinion who is right in this dispute? And why?
Ans: Madhurima Banerjee is right. It is her freedom to choose the surname she wants. It cannot be obligated by others to force her to change her surname. The property registration officer has no legal right to ask her to change her name nor the authority to deny her work. She can forward a complaint to the Court on the violation of her rights.
Q9. Thousands of tribals and other forest dwellers gathered at Piparia in Hoshangabad district in Madhya Pradesh to protest against their proposed displacement from the Satpura National Park, Bori Wildlife Sanctuary and Panchmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary. They argue that such a displacement is an attack on their livelihood and beliefs. Government claims that their displacement is essential for the development of the area and for protection of wildlife. Write a petition on behalf of the forest dwellers to the NHRC, a response from the government and a report of the NHRC on this matter.
Ans: (a)
Letter from the Tribals to NHRC
To,
The Chairman,
National Human Rights Commission,
Delhi, India
Date:_____________
Subject: Displacement of Tribals
Respected Sir/Ma’am,
I want to draw your attention to plight of forest dwellers in Satpura National Park, Bori Wildlife Sanctuary and Panchmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary. The government wants to displace these people. The proposal of the government is a violation of the human rights of the forest dwellers. It is asking away their right to livelihood and to follow their beliefs. There has been no alternative suggestion by the government with regard to the future of the forest dwellers. We urge you to please look into the matter and provide the much-required help to these people.
Thank You Sir/Ma’am.
Regards,
Rohan or [Your Name]
Piparia, Hoshangabad
District, Madhya Pradesh or [Your Address]
(b) Response from the Government
- The government had given a warning to the people two years ago.
- There has been an alarming rise in poaching, cutting of trees and killing of wildlife.
- Environmental pollution has also increased.
- It is the government’s duty to protect the endangered species.
- The government has offered compensation and promised rehabilitation in alternative places.
- Offered jobs to the men.
(c) NHRC’s Report
- Both sides have a point
- The Tribals have tradition, practice and decades of residence behind them. It is their world and life.
- Sudden uprooting will leave them emotionally disturbed, turn them into vagabonds and force them into jobs or occupations that they have never followed.
- The government is right in its concern for wildlife. It is its duty to save certain species from becoming extinct. Poachers are having a field day, and every day the environment is threatened.
Q10. Draw a web interconnecting different rights discussed in this chapter. For example right to freedom of movement is connected to the freedom of occupation. One reason for this is that freedom of movement enables a person to go to place of work within one’s village or city or to another village, city or state. Similarly this right can be used for pilgrimage, connected with freedom to follow one’s religion. Draw a circle for each right and mark arrows that show connection between or among different rights. For each arrow, give an example that shows the linkage.
Ans: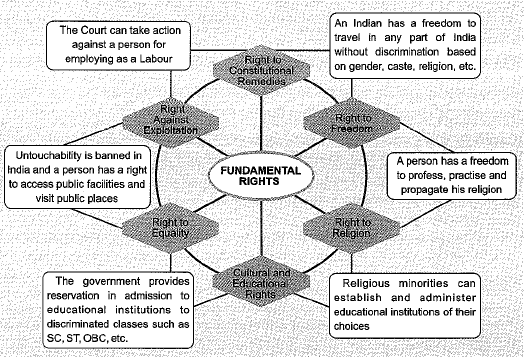
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 5 - Democratic Rights
| 1. What are democratic rights and why are they important? |  |
| 2. How do democratic rights differ from fundamental rights? |  |
| 3. What role does the Constitution play in safeguarding democratic rights? |  |
| 4. Can democratic rights be restricted? Under what circumstances? |  |
| 5. How can citizens protect their democratic rights? |  |

















