NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics - Introduction to Micro Economics
Q1: Discuss the central problems of an economy.
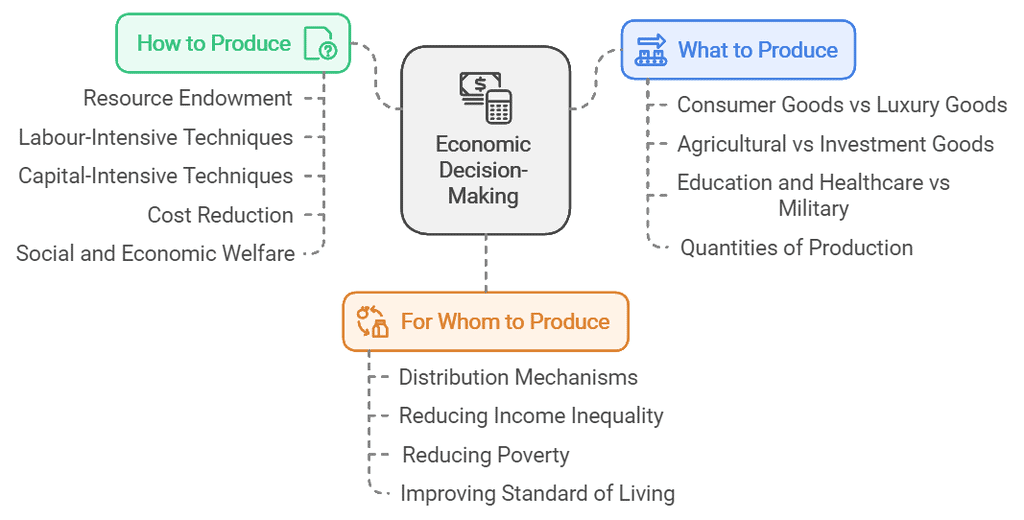
Ans: Every economy faces three central problems due to the scarcity of resources. This scarcity creates challenges in effectively using available resources to meet unlimited demands. The three central problems are:
- Allocation of scarce resources: Deciding how to distribute limited resources among various goods and services.
- Production choices: Determining which goods and services to produce and in what quantities.
- Distribution of goods: Figuring out how to share the produced goods and services among individuals in the economy.
(i) What to produce and in what quantities?
- The first challenge is determining which goods to produce and in what amounts.
- Every society experiences resource scarcity, necessitating the allocation of resources based on collective needs and wants. This creates a choice problem, requiring decisions between various products.
- Decisions include whether to produce consumer or luxury goods, agricultural or investment goods, and prioritizing sectors like education or military.
- After deciding what to produce, the next step is estimating the quantity of production.
(ii) How to produce?
- The second issue is determining how to utilize available resources for production.
- This decision is influenced by the nation’s resource endowment, determining whether to use labour-intensive or capital-intensive techniques.
- The chosen method should minimize production costs while enhancing social and economic welfare.
- For instance, in a country with high unemployment, opting for labour-intensive methods can help reduce joblessness.
(iii) For whom to produce?
- Finally, the distribution of produced goods and services (national income) must be addressed; that is, determining who receives what and how much.
- The economy must establish an effective distribution mechanism among different societal segments.
- The goal is to reduce income inequality, alleviate poverty, and enhance social welfare.
Q2: What do you mean by the production possibilities of an economy?
Ans: The Production possibilities of an economy imply the numerous alternative combinations of goods and services that a particular economy can produce with the given technology and by fully and efficiently employing the available resources thoroughly and efficiently. In other words, it refers to various feasible bundles of goods and services that can be produced together by efficiently utilizing the given technology and available resources.
Q3: What is a production possibility frontier?
Ans: The production possibility frontier (PPF) refers to a curve that shows various alternative combinations of two goods that can be produced with efficient utilization of the given resources and technology. It is also called the production possibility curve (PPC).
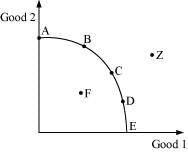 PPCAll the points lying on the PPC, that is, curve AE, are associated with different quantities of good 1 and good 2 produced by employing the available resources fully and in an efficient manner. Meanwhile, any point lying under the curve, like F, depicts inefficiency or underutilization of available resources. Meanwhile, any point lying outside the curve, like Z, depicts overutilization of the available endowment of resources and technology, making it non-feasible.
PPCAll the points lying on the PPC, that is, curve AE, are associated with different quantities of good 1 and good 2 produced by employing the available resources fully and in an efficient manner. Meanwhile, any point lying under the curve, like F, depicts inefficiency or underutilization of available resources. Meanwhile, any point lying outside the curve, like Z, depicts overutilization of the available endowment of resources and technology, making it non-feasible.
Q4: Discuss the subject matter of economics.
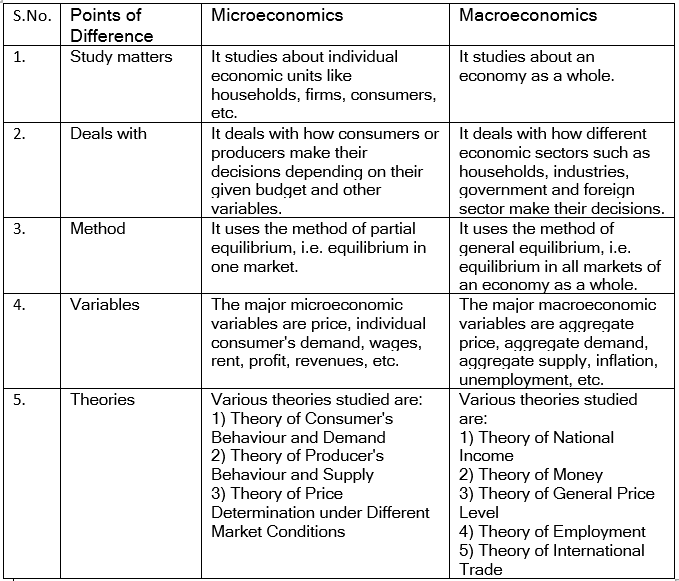
Ans: The subject matter of economics is subdivided into two core branches: microeconomics and macroeconomics. This division came into existence only after 1930, as per the suggestion by Ragnar Frisch. The domains of interest of these two branches of economics can be presented as follows:
(i) Microeconomics
- It is the study of individual economic units, i.e. the behaviour of consumers and firms. The study of how they utilize the given resources in the best possible manner to maximize their rational objectives falls under the domain of microeconomics.
- It is also the study of demand and supply and how their interaction determines the prices of various goods and services.
- Microeconomics helps in solving the three central problems of an economy. It is also called the Price theory, as it primarily focuses on how prices are determined both in commodity and factor markets.
(ii) Macroeconomics
- It is the study of how the economy as a whole operates. It focuses on the determination of aggregate measures, like aggregate demand, aggregate supply, and overall price level, and how they change over time.
- It is also known as the Theory of Income and Employment, as its main focus is on how income and employment levels are determined.
- Macroeconomics helps in understanding and solving problems like inflation, unemployment, Balance of Payments (BOP), disequilibrium, poverty, etc.
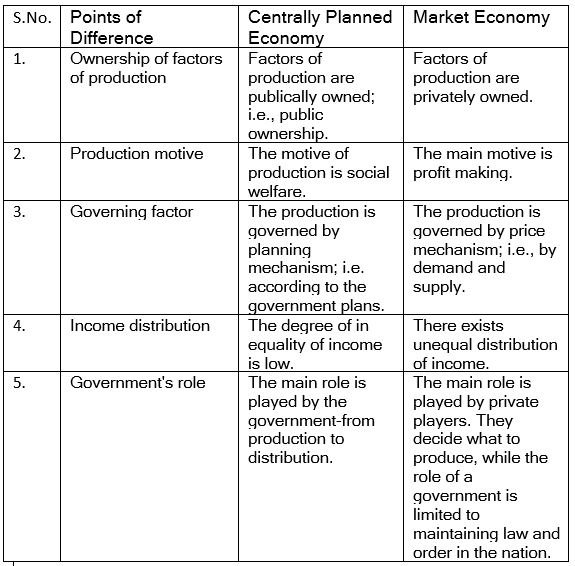
Q5: Distinguish between a centrally planned economy and a market economy.
Ans:
Ans:
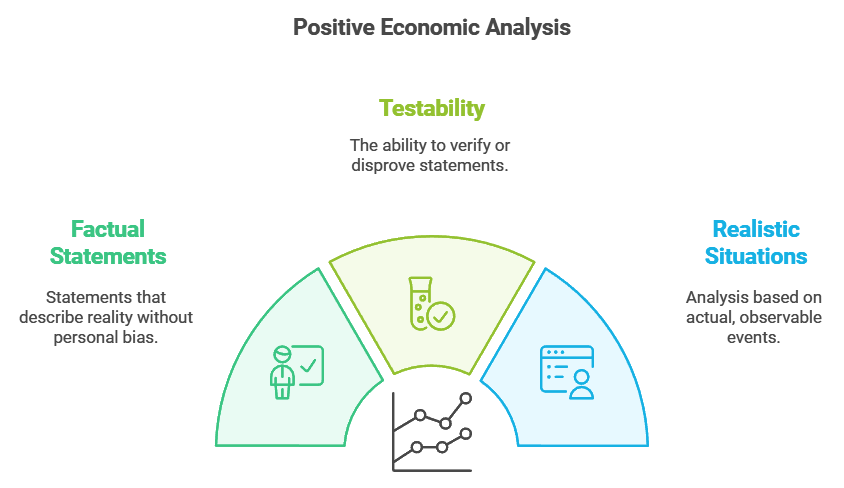
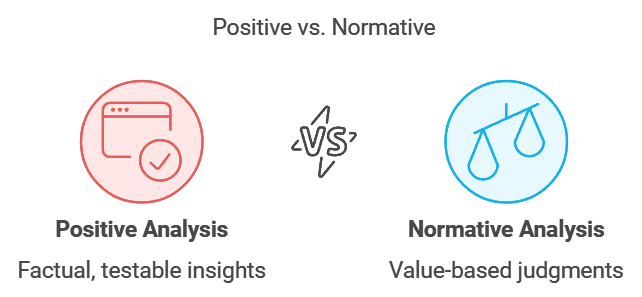
- Positive economic analysis looks at economic issues and how they are resolved using factual information.
- It focuses on what has happened, what is happening, and what could happen.
- These facts can be tested and are free from personal opinions.
- For instance, saying "it is raining outside" is something that can be verified.
Q7: What do you understand by normative economic analysis?
Ans: Normative economic analysis refers to the analysis in which we study whether a particular mechanism is desirable or not.
- In this analysis, we study what ought to be the desired situation or in what ways the economic problems should be solved.
- In other words, it is concerned with what should be and what should not be and what is desirable and what is not.
- In normative economic analysis, we come across normative statements that cannot be tested as they involve personal value judgments. It deals with idealistic situations and is based on ethics.
- An example of a normative statement could be, ‘Central government should not stop providing minimum support price to the farmers’.
Ans:
|
60 videos|287 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics - Introduction to Micro Economics
| 1. What is microeconomics? |  |
| 2. What are the basic principles of microeconomics? |  |
| 3. How does microeconomics differ from macroeconomics? |  |
| 4. What are the main goals of microeconomics? |  |
| 5. How does microeconomics impact everyday life? |  |

















