NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 - The Indian Constitution
Q1: Why does a democratic country need a Constitution?
Ans: A democratic country need a Constitution because:
- It lays out the important guidelines that govern decision making within the various societies of the country.
- It lays down the ideals that form the basis of the kind of country that its citizens aspire to live in.
- It serves as asset of rules and principles as the basis by which the country has to be governed.
- It provides rules to safeguard the interests of minorities and prevent any kind of domination by the majority on minorities.
- It lays down rules that guard against the misuse of power by any politician leader.
- It also provides rights to its citizens and protects their freedom.
 Consititution of India
Consititution of India
Q2: Look at the wordings of the two documents given below. The first column is from the 1990 Nepal Constitution. The second column is from the more recent Constitution of Nepal.
1990 Constitution of Nepal Part 7: Executive | 2015 Constitution of Nepal Part 7: Federal Executive |
Article 35: Executive Power: The executive power of the Kingdom of Nepal shall be vested in His Majesty and the Council of Ministers. | Article 75: Executive Power: The Executive Power of Nepal shall, pursuant to this Constitution and law, be vested in the Council of Ministers. |
What is the difference in who exercises ‘Executive Power’ in the above two Constitutions of Nepal
Ans: In Article 35 of the 1990 Constitution of Nepal, the powers to rule the country, to set rules and to manage the country are all vested in the King of the country and the Ministers appointed under him.
However, Article 75 of the 2015 Constitution of Nepal states that the rules, governance and management of the country will be based on the laws mentioned in the Constitution of the country under the supervision of the Ministers.
Q3: What would happen if there were no restrictions on the power of elected representatives?
Ans: If there are no restrictions on the power of the elected representatives the leaders might misuse the powers given to them. The Constitution provides safeguards against this misuse of power by our political leaders.
Q4: In each of the following situations, identify the minority. Write one reason why you think it is important to respect the views of the minority in each of these situations.
(a) In a school with 30 teachers, 20 of them are male.
(b) In a city, 5 percent of the population are Buddhists.
(c) In a factory mess for all employees, 80 percent are vegetarians.
(d) In a class of 50 students, 40 belong to more well-off families.
Ans:
(a) Female teachers are in minority. The female teachers must be allowed space to voice their opinion so that their efforts at teaching are not hindered by their minority status.
(b) Buddhists are in minority. Every individual has the right to follow the religion of his/her choice. People of other faiths must respect the religion other than their own.
(c) Non-vegetarians are in minority. Food choice is personal wish so he/she should have the freedom to eat what he/she wants.
(d) Under privileged are in minority. Citizens can not be discriminated by their birth so their views have to be respected.
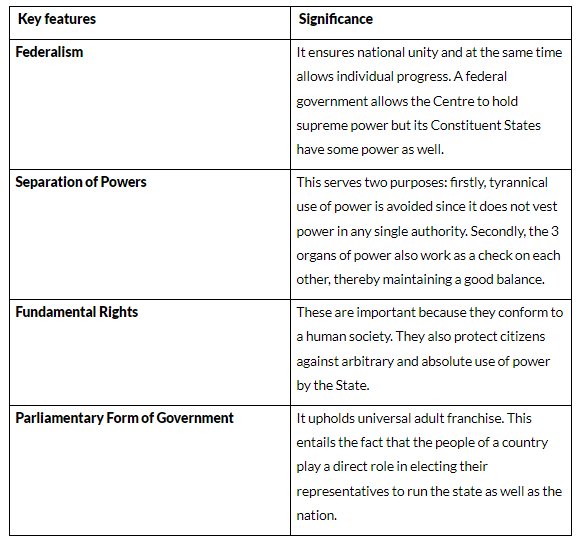
Q5: The column on the left lists some of the key features of the Indian Constitution. In the other column write two sentences, in your own words, on why you think this feature is important:
| Key Feature | Significance |
| Federalism Separation of Powers Fundamental Rights Parliamentary Form of Government |
Ans:
Q6: Write down the names of the Indian States, which share borders with the following neighbouring nations:
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal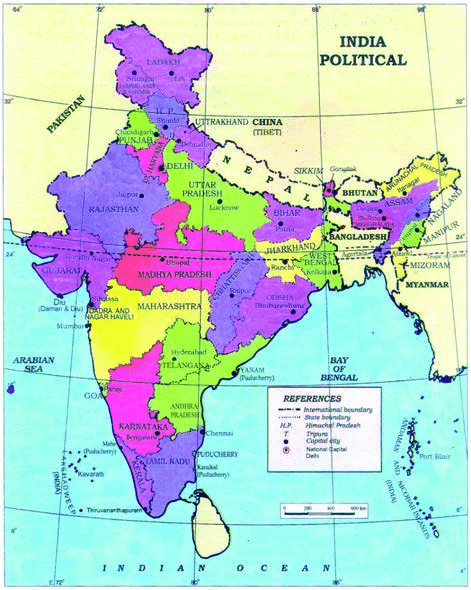 Ans:
Ans:
(a) States which share borders with Bangladesh are:
- West Bengal
- Assam
- Meghalaya
- Tripura
- Mizoram
(b) States which share borders with Bhutan are:
- Sikkim
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- West Bengal
(c) States which share borders with Nepal are:
- Uttarakhand
- Sikkim
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- West Bengal
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 - The Indian Constitution
| 1. What is the significance of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. How was the Indian Constitution drafted? |  |
| 3. What are the fundamental rights provided by the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How can the Indian Constitution be amended? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the judiciary in upholding the Indian Constitution? |  |






















