Water—The Essence of Life NCERT Solutions | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 4/5 |

|
| Page No. 6 |

|
| Page No. 7 |

|
| Page No. 9 |

|
| Page No. 10 |

|
| Page No. 13 |

|
| Page No. 15 |

|
| Page No. 17-18 |

|
| Page No. 19 |

|
| Page No. 20 |

|
Page No. 4/5
Discuss
Q. Do you think we can drink the water present in the oceans?
Answer: No, we cannot drink ocean water because it is salty. Drinking salty water can be harmful to our bodies as it does not quench thirst and can make us sick.
Q. What can ocean water be used for?
Answer: Ocean water can be used to extract salt in salt pans (for example, in Gujarat). It is also used for some industrial purposes and supports marine life and shipping.
Activity 1

Page No. 6
Activity 2
(a) Where do these water droplets come from?
They come from water vapours in the air, which cools down and condenses on the cold surface of the glass.
(b) What happens to ice cubes after some time?
The ice cubes melt and turn into water.
(c) If we heat water, what will happen to it?
If we heat water, it will turn into steam (water vapour).
Q. In the above activity, what forms of water do you see?
Answer: Solid Form - Ice
Liquid form -Water
Gaseous form- Vapours
Observing Changes

Page No. 7
Activity 3: Demonstrating the Water Cycle
- Take a transparent plastic bag.
- Use a marker to draw the sun, clouds, arrows, and trees on it.
- Fill one-third of the bag with coloured water and seal it shut.
- Place the bag in sunlight and observe changes inside over time.
- Notice evaporation, condensation, and precipitation happening inside the bag.
- This activity shows how the water cycle operates in nature.

Answer:
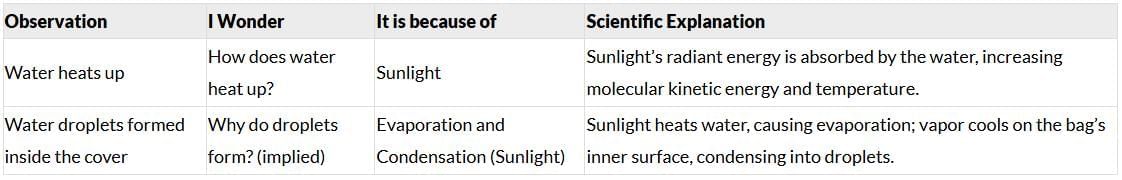
Other Observations can be:
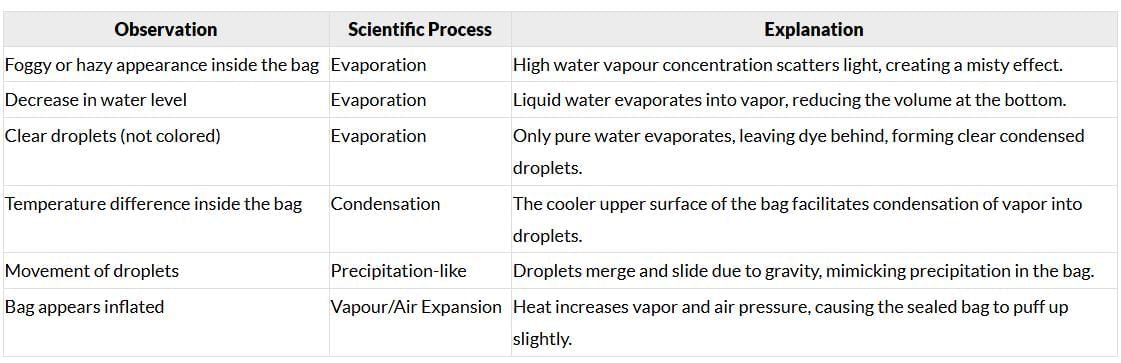
Page No. 9
Activity 4
- Take a transparent glass.
- Fill half of it with soil.
- Slowly pour water into the soil using a spoon.
- Observe what happens.

Answer:
- When you pour water onto the soil in the glass, it soaks down.
This shows how, in nature, rainwater soaks through soil and gets stored underground as groundwater, which can be drawn out by wells and handpumps.
Activity 5

Explanation: The green lawn is the surface that allows rainwater to seep into the ground and helps recharge groundwater. Concrete roads and paved areas do not let water seep in.
Page No. 10
Activity 6
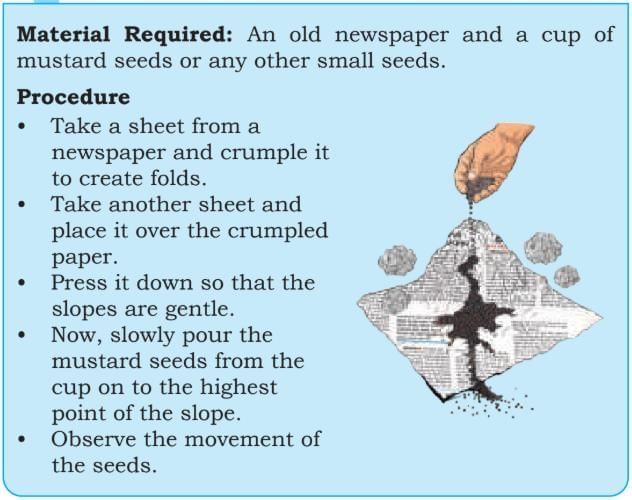
1. What did you observe about the mustard seeds?
Answer: The mustard seeds roll down according to the slope of the paper (like water flows downhill).
2. Are they moving in a straight line, or do they spread out in different directions?
Answer: They do not move in a straight line but spread out in different directions.
3. Are they collecting in some areas? Do they gather like water gathers in lakes, rivers and so on?
Answer: The seeds gather in places where there are dips or valleys, just like water collects in lakes, ponds, or river basins.
Discuss
Q. Based on Activity 6 with mustard seeds, discuss how some rivers flow towards the Arabian Sea while some flow towards the Bay of Bengal.
Answer: 
- The flow of rivers is influenced by the shape of the land and its slope.
- Rivers that begin in the western regions, such as the Narmada, move towards the Arabian Sea.
- Rivers that start in the north and east, like the Ganga and Godavari, flow towards the Bay of Bengal.
- The path of water is determined by various landforms such as mountains, valleys, and slopes.
- Each river chooses the route with the lowest slope and eventually flows into seas or marshes.
- An example is the Luni, which does not reach the sea but instead ends in the marshes of the Rann of Kutch.
Page No. 13
Activity 7
Follow the Flow!
In the map, you can see the rivers flowing in different directions. Some flow into the Bay of Bengal and some into the Arabian Sea.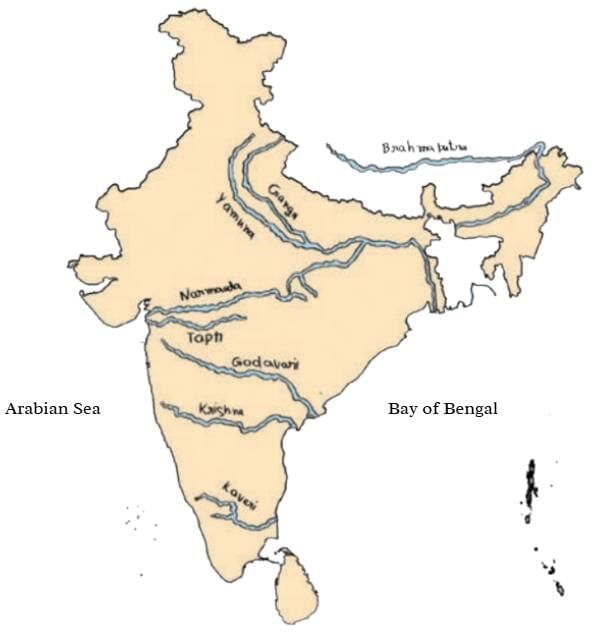
Observe and fill in the table.
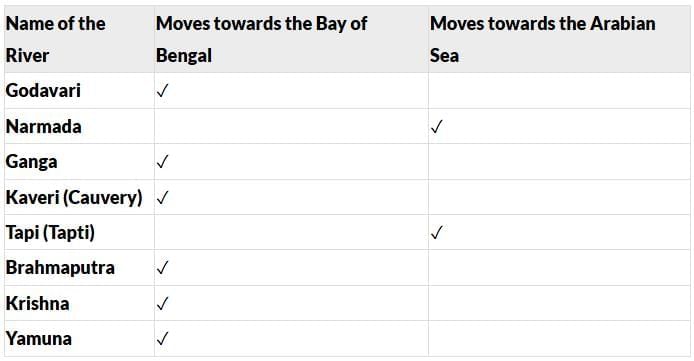
Page No. 15
Q. Discuss the characteristics of animals on land and animals in water.
Answer:

Page No. 17-18
Activity 8
Visit a local water body like a pond, lake or aquarium with your teacher or parents, and observe life in and around the water body.
1. Based on your observations, complete the following table.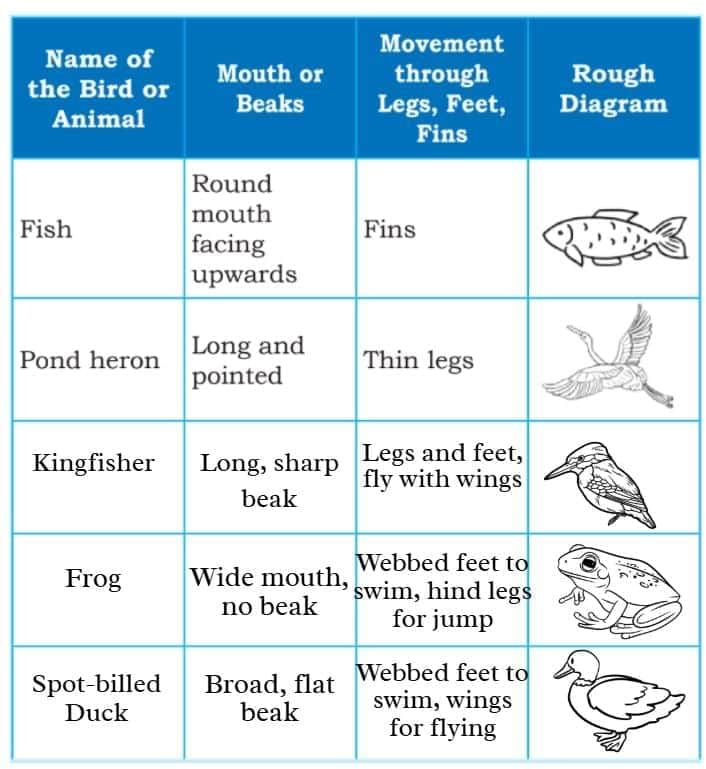
2. Draw the plants that you saw during the visit and label them with their local name.
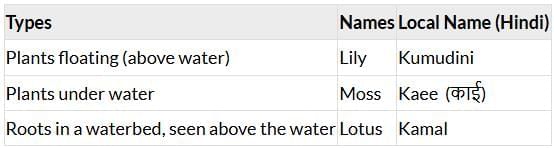
Activity 9
2. Colour the paper with a wax crayon. Now, put a drop of water on it. Do you observe any change?

Answer: Observation.
- On plain paper, water soaks in and spreads out.
- On wax crayon paper, the water forms a bead and rolls off, as the surface is waterproof.
- This is similar to the waxy coating on leaves, which keeps excess water from entering the plant.
Page No. 19
Activity 10
Who Eats Whom?—A River Food Chain Game
- Distribute slips of paper to students. Each student writes what they choose to be (for example, small fish, big fish, frog, bird, human, crocodile, otter, etc.)
- Ask the students to think about what they eat, and who eats it.
- Use a string to connect the students who depend on each other for food.
- Discuss what would happen if one animal disappears (for example, what if all the fish are gone?).
Answer: Example of a river food chain:
- Plants in water → Small fish → Bigger fish → Bird (like kingfisher) → Human
- If all small fish disappear, bigger fish and birds will not get food, breaking the chain.
- Every link is important for the balance of the river ecosystem.
Page No. 20
Let us reflect
1. Match the following:
Answer:
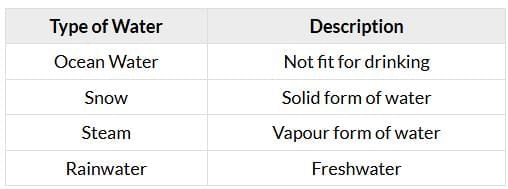
2. Why do you think most of the water on Earth cannot be used for drinking or farming?
Answer:
- Most of the water on Earth is in oceans and seas, and this water is salty.
- Saltwater cannot be drunk by humans or animals and is not useful for watering crops because the salt harms plants.
- Only a small part of the Earth’s water is freshwater found in rivers, lakes, rain, and underground, which we can use for drinking, farming, and other daily needs.
3. A large number of living beings live near water bodies. Why?
Answer:
- Water bodies such as ponds, lakes, rivers, and wetlands are vital for many living things.
- These areas provide animals and plants with the necessary water for their survival.
- They offer not just water, but also food, shelter, and a suitable environment for various creatures.
- Freshwater is crucial for life, making it essential for many species to live near water sources.
- Animals and plants depend on these water bodies to drink, eat, and find a safe place to thrive.
4. What would happen if it did not rain in your region for two years?
Answer: If there was no rain for two years:
- Rivers, ponds, and lakes might dry up.
- The groundwater level would fall since it would not be replenished by rainwater.
- Crops and plants would not get water and may die, causing problems for farmers and animals that depend on plants for food.
- People might face water shortages for drinking and daily use, leading to hardships and possibly drought conditions.
5. What do you think happens to rainwater in a forest compared to a city?
Answer: In a forest, the soil is loose and filled with trees and plants.
- This environment allows rainwater to easily soak into the ground.
- When rainwater seeps into the soil, it helps to refill the underground water supply, also known as groundwater.
- This process is important as it keeps rivers and ponds full of water.
In many cities, a lot of roads and yards are covered with cement or concrete.
- This covering prevents rainwater from soaking into the soil.
- Instead of being absorbed, water quickly flows away through drains.
- Because the water does not go back into the ground, it is hard for groundwater levels to rise.
- Sometimes, this situation can lead to water shortages.
6. Can you design a house or school that conserves water wisely? What would it include?
Answer: A house or school that saves water can include:
- Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for future use.
- Soak pits or gardens to help water soak into the ground and recharge groundwater.
- Water-saving taps, toilets, and faucets that prevent wastage.
- Use of water tanks to store and reuse water.
- Awareness posters or programs encouraging everyone to use water carefully and not waste it.
- Planting many trees and plants around to keep the soil healthy and allow water to soak in.
7. Let us make a fish by folding a piece of paper.
Answer: (This is a fun craft activity to make a fish by folding paper following step-by-step instructions. It helps understand the shapes and parts of a fish and connects with studying life in water.)
Step 1: Take a rectangular strip of paper and fold it in half from top to bottom (horizontally), pressing the crease well. Step 2: Unfold and now fold both the top and bottom edges towards the centre crease, creating two flaps. Press the folds neatly.
Step 2: Unfold and now fold both the top and bottom edges towards the centre crease, creating two flaps. Press the folds neatly. Step 3: Hold both ends of the strip and bring them together downward, so the strip forms a “V” shape (it looks like a folded tunnel from the edge).
Step 3: Hold both ends of the strip and bring them together downward, so the strip forms a “V” shape (it looks like a folded tunnel from the edge).
Step 4: Continue holding the shape and squeeze the folded ends so that they shift and one edge stands vertically. This forms a fish with a body and a tail.
Step 5: Fold out the two ends (the tail fins) to form a triangle on either side at the tail. The fish now looks more three-dimensional.
Step 6: Draw an eye and some scales on the head part. Your paper fish is now ready!
You can decorate your paper fish however you like! If you want the exact illustrations from the book, you can request help from your teacher. This simple origami craft is easy, fun, and needs only a square piece of paper.
|
14 videos|144 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Water—The Essence of Life NCERT Solutions - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. Why is water often referred to as the essence of life? |  |
| 2. What are the different forms of water found in nature? |  |
| 3. How does the water cycle work? |  |
| 4. What are some ways to conserve water? |  |
| 5. Why is clean drinking water important for health? |  |





















