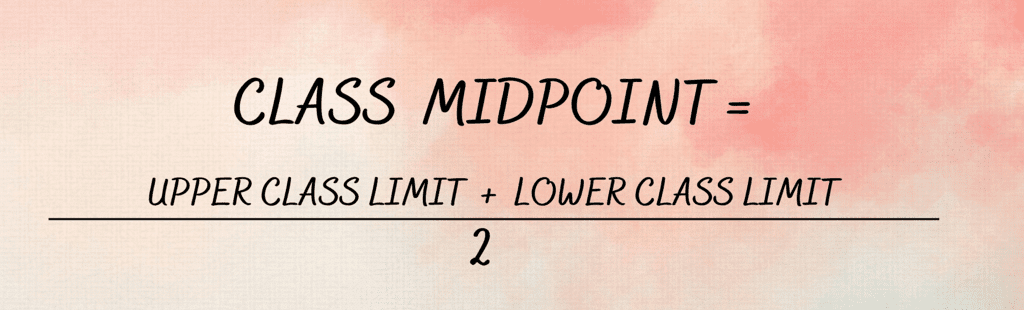NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Organisation of Data
Q1: Which of the following alternatives is true?
(i) The class midpoint is equal to:
(a) The average of the upper-class limit and the lower-class limit.
(b) The product of the upper-class limit and the lower-class limit.
(c) The ratio of the upper-class limit and the lower-class limit.
(d) None of the above.
Ans: (a)
The class midpoint, also known as class mark, is equal to the average of the upper class limit and the lower class limit. It is known by adding the values of upper and lower limits and dividing the total by 2.
(ii) The frequency distribution of two variables is known as
(a) Univariate Distribution
(b) Bivariate Distribution
(c) Multivariate Distribution
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
The frequency distribution of two variables is known as Bivariate Frequency Distribution. In other words, Bivariate Frequency Distribution shows the series of statistical data having frequencies of two variables such as the data on income and expenditure of the households.
(iii) Statistical calculations in classified data are based on
(a) the actual values of observations
(b) the upper-class limits
(c) the lower class limits
(d) the class midpoints
Ans: (d)
The calculations in classified data or continuous series are based on the class midpoints. The items in a continuous series cannot be exactly measured. Consequently, the class midpoints are calculated.
(iv) Range is the
(a) difference between the largest and the smallest observations
(b) difference between the smallest and the largest observations
(c) average of the largest and the smallest observations
(d) the ratio of the largest to the smallest observation
Ans: (a)
The range is defined as the difference between the largest and the smallest observations.
Algebraically,
R = H – L
Where,
R denotes range
H is the highest value
L is the lowest value
Q2: Can there be any advantage in classifying things? Explain with an example from your daily life.
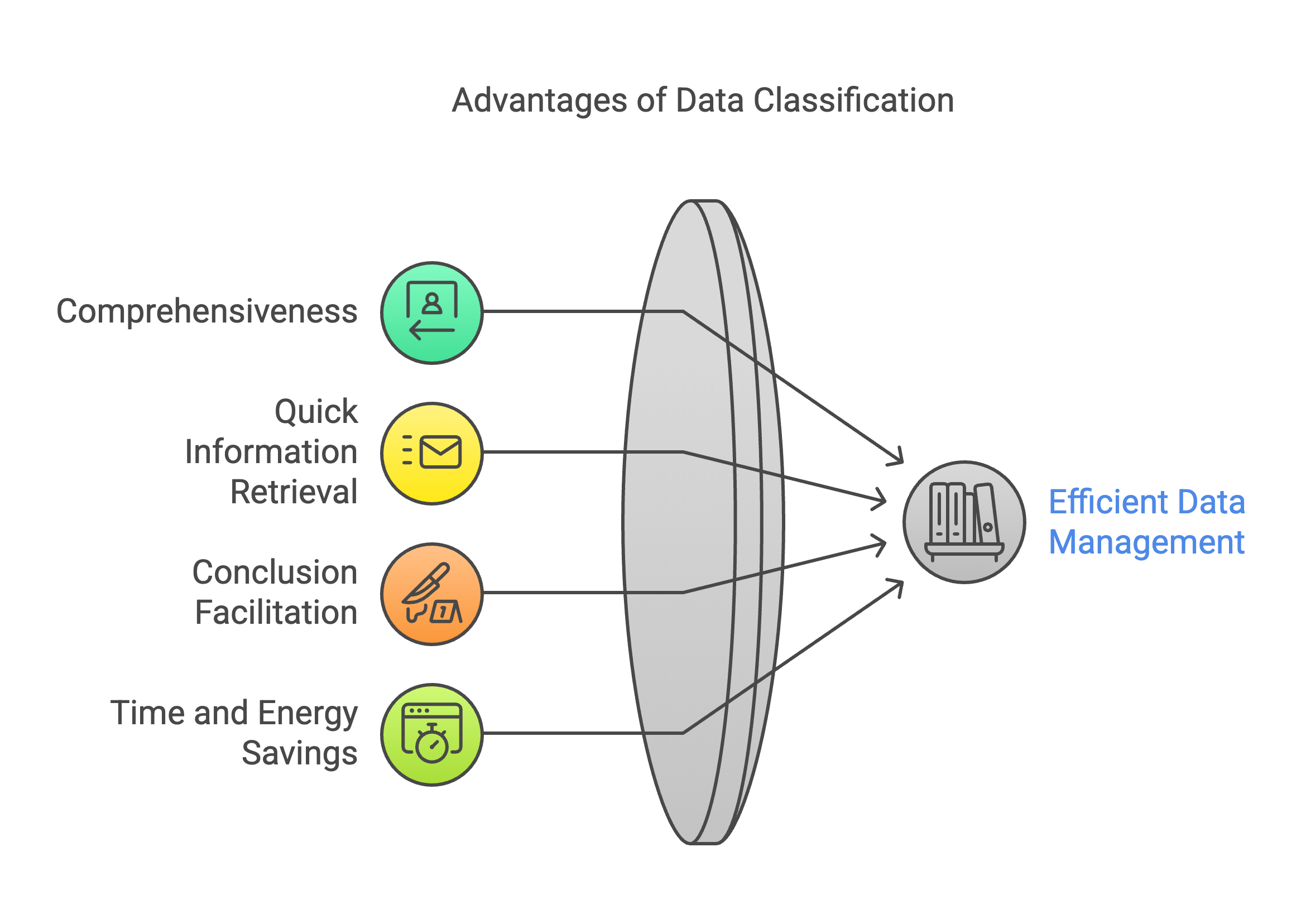
Ans: Yes, there are many advantages to classifying things. The following are the advantages associated with classification:
- Saves Time and Energy- Classification of things not only saves our time but also our energy which would otherwise be utilized in searching for an entire lot of things.
- Quick Information- Information can be easily collected from classified things.
- Easy Classification- Classification facilitates comparisons and helps in drawing fast conclusions or inferences.
The advantage of classification can be better understood with the help of a daily life example. A post office on a regular basis sorts letters and then classifies them according to various attributes. Letters are classified first according to the states, then according to the cities and streets. Thus, this process of classification helps the postman to deliver posts quickly, efficiently, and in a non-haphazard manner.
 Q3: What is a variable? Distinguish between a discrete and a continuous variable.
Q3: What is a variable? Distinguish between a discrete and a continuous variable.
Ans: A measurable characteristic whose value changes over time is called a variable. It refers to that quantity that keeps on changing and which can be measured by some unit. For example, if we measure the height of students in a class, then the height is regarded as a variable. A variable can be either discrete or continuous.
Q4: Explain the ‘exclusive’ and ‘inclusive’ methods used in the classification of data.
Ans:
- Exclusive Method – This method is used for those series in which the upper limit of one class becomes the lower limit of the next class. It is called an exclusive series because the frequencies of the upper limit of a class interval are not included in that particular class. In such a type of series, the upper limit of one class becomes the lower limit of the next class, for example, 0–10, 10–20, 20–30, and so on. The upper limit is excluded but the lower limit is included in the class interval. This method is most appropriate for data of continuous variables.
- Inclusive Method – Under this method of classification of data, the classes are formed in such a manner that the upper limit of a class interval does not repeat itself as the lower limit of the next class interval. In such a series, both the upper limit and the lower limit are included in the particular class interval, for example, 1–5, 6–10, 11–15, and so on. The interval 1–5 includes both the limits i.e. 1 and 5
Q5: Use the data in Table 3.2 that relate to monthly household expenditure (in Rs) on food of 50 households and obtain the range of monthly household expenditure on food.
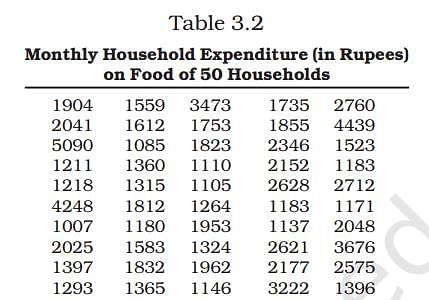 (i) Obtain the range of monthly household expenditure on food.
(i) Obtain the range of monthly household expenditure on food.
Ans:
Calculation of Range
Range = Highest Value – Lowest Value
Highest Value = 5090
Lowest Value = 1007
So, Range = 5090 – 1007 = 4083
(ii) Divide the range into an appropriate number of class intervals and obtain the frequency distribution of expenditure.
Ans: Preparing Tally Marks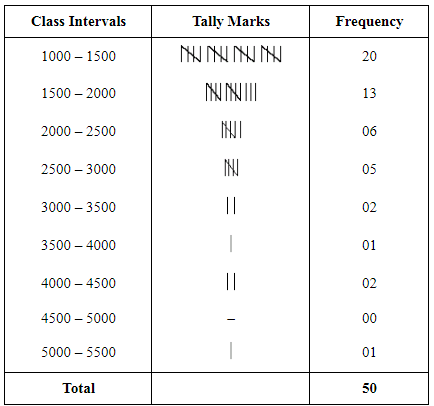
(iii) Find the number of households whose monthly expenditure on food is
(a) less than Rs 2000
(b) more than Rs 3000
(c) between Rs 1500 and Rs 2500
Ans:
a) Number of households whose monthly expenditure on food is less than Rs 2000
= 20 + 13 = 33
b) Number of households whose monthly expenditure on food is more than Rs 3000
= 2 + 1 + 2 + 0 + 1 = 6
c) Number of households whose monthly expenditure on food is between Rs 1500 and Rs 2500
= 13 + 6 = 19
Q6: In a city, 45 families were surveyed for the number of domestic appliances they used. Prepare a frequency array based on their replies as recorded below.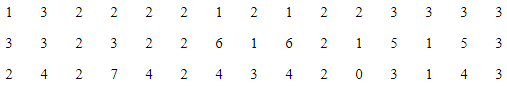 Ans: Frequency Array of appliances being used by households
Ans: Frequency Array of appliances being used by households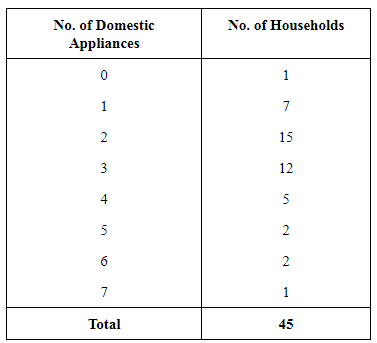
Q7: What is ‘loss of information’ in classified data?
Ans: ‘Loss of information’ is a major drawback of the classified data. The classification or grouping of raw data into classes makes it more concise and understandable. But simultaneously there exists a loss of information. The calculations involved in the classified data or the continuous series are based on the class midpoints. The items in such series cannot be exactly measured and consequently, an individual observation loses its importance during the statistical calculations. Further, the statistical calculations are based on the values of the class marks, ignoring the exact observations of the data leading to the problem of loss of information.
Q8: Do you agree that classified data is better than raw data?
Ans: The classified data has the following advantages over the raw data.
- Comprehensive- Raw data are large and entangled, whereas classified data are comprehensive and easily manageable.
- Quick Information- It is troublesome to pick up information from unclassified data. Information can be easily collected from the classified data.
- Conclusions - Classification facilitates comparisons and helps in drawing fast conclusions or inferences.
- Saves Time and Energy- Classified data not only saves our time but also our energy, which would otherwise be utilized in searching for an entire lot of things.
Q9: Distinguish between Univariate and Bivariate frequency distribution.
Ans:
- The frequency distribution of a single variable is called a Univariate Distribution. The income of people, marks scored by students, etc. are examples of Univariate Distribution.
- The frequency distribution of two variables is called Bivariate distribution. Sales and advertisement expenditure, weight and height of individuals, etc. are examples of Bivariate distribution.
Q10: Prepare a frequency distribution by inclusive method taking a class interval of 7 from the following data: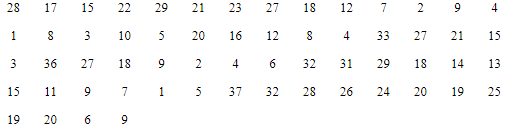
Ans: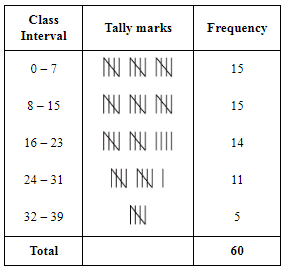
Q11: “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog”
Examine the above sentence carefully and note the number of letters in each word. Treating the number of letters as a variable, prepare a frequency array for this data.
Ans: To prepare a frequency array for the number of letters in each word in the sentence "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", we count the number of letters in each word and then create a frequency array showing how many times each number of letters occurs. Here's the breakdown:
- "The" has 3 letters
- "quick" has 5 letters
- "brown" has 5 letters
- "fox" has 3 letters
- "jumps" has 5 letters
- "over" has 4 letters
- "the" has 3 letters
- "lazy" has 4 letters
- "dog" has 3 letters
Frequency Array:

|
59 videos|290 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Organisation of Data
| 1. What is the importance of data organization in commerce? |  |
| 2. What are the common methods of organizing data in commerce? |  |
| 3. How can technology aid in the organization of data for businesses? |  |
| 4. What role does data analysis play in the organization of data? |  |
| 5. What challenges do businesses face in organizing data? |  |