NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - Security in the Contemporary World
Q1: Match the terms with their meaning:
(i) Confidence Building Measures (CBMs)
(ii) Arms Control
(iii) Alliance
(iv) Disarmament
(a) Giving up certain types ofweapons.
(b) A process of exchanging information on defence matters between nations on a regular basis.
(c) A coalition of nations meant to deter or defend against military attacks.
(d) Regulates the acquisition of development of weapons.
Ans: (i)-(b); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(c); (iv)-(a).
Q2: Which among the following would you consider as a traditional security concern/non-traditional/not a threat?
(a) The spread of chikungunya/dengue fever
(b) Inflow of workers from a neighbouring nation.
(c) Emergence of a group demanding nationhood for their region.
(d) Emergence of a group demanding autonomy for their region.
(e) A newspaper that is critical of the armed-forces in the country.
Ans:
(a) Non-traditional
(b) Non-traditional
(c) Traditional
(d) Not a threat
(e) Not a threat
Q3: What is the difference between traditional and non-traditional security? Which category would the creation and sustenance of alliances belong to?
Ans:Creation and sustenance of alliances belong to traditional notion of security.
Q4: What are the differences in the threats that people in the third world face and those living in the First World face?
Ans: The threats are different in the third world and first world peoples because their regions are changed, hence they face different security challenges.in the following manner:
- The newly independent countries faced the military conflicts even with their neighbouring states.
- These countries faced threats not only from outside their borders, mostly from neighbours, but also from within.
- Internally, new states worried about threats from separatist movements which wanted to form independent countries.
- Sometimes, the external and internal threats merged.
- For the new states, external wars with neighbours and internal wars posed a serious challenge to their security.
Q5: Is terrorism a traditional or non- traditional threat to security?
Ans: Terrorism is a non-traditional threat to wound the peace and order in the country:
- Terrorism refers to political violence to target civilians deliberately and indiscriminately.
- Civilians are usually terrorised to be it as a weapon against national government and other parties in the conflict.
- Terrorism involves hijacking planes or planting bombs in trains, cafes, markets and other crowded places.
- After a terrorist attack on World Trade Centre on 11 September 2001, the other governments and public also are paying more attention to terrorism.
Q6: What are the choices available to a state when its security is threatened, according to traditional security perspective?
Ans: Traditional security perspective emphasises on compromises to limit the violence by giving following three choices to the state if its security is threatened:
- To surrender when actually confronted by war, but they will not advertise this as the policy of country.
- To prevent the other side from attacking by promising to raise the costs of war to an unacceptable level.
- To defend to protect itself when war actually breaks out so as to deny the attacking country its objectives and to turn back or to defeat the attacking forces altogether.
- Hence, state’s security policy is to prevent war which is called deterrence and with limiting or heading war called defence.
Q7: What is Balance of Power? How could a state achieve this?
Ans: ‘Balance of Power’ is a balance between bigger and smaller countries by cooperating with each other economically and technologically. A smaller country is always suspicious to break out a war from bigger or powerful country. Hence, they maintain a balance of power to build up one’s military power together with economic and technological power-to protect one’s own security.
Q8: What are the objectives of military alliances? Give an example of a functioning military alliance with its specific objectives.
Ans: Objectives:
- Alliance building is important component of traditional security to threats to deal between states and nations to deter or defend against military attacks.
- Alliances are formalised in written treaties and identification of who constitutes the threats.
- Alliances are formed to increase their effective power relative to another alliance.
- Alliances are based on national interests and can change when national interest change.
Example: The US backed the Islamic militants in Afghanistan against the Soviet Union in 1980s, but later attacked them when Al-Qaeda, a group of Islamic militants, led by Osama Bin Laden launched terrorist strikes against America on 11th September 2001.
Q9: Rapid environmental degradation is causing a serious threat to security. Do you agree with the statement? Substantiate your arguments.
Ans: Yes, we agree with the statement because in some situations one country may have to disproportionately bear the brunt of a global problem i.e. environmental degradation causing a serious threat to security, for example, due to global warming, a sea level rise of 1.5-2.0 meters would flood 20% of Bangladesh, inundate most of Maldives and threaten nearly half the population of Thailand, Hence, international cooperation is vital due to global nature of these problems.
Q10: Nuclear weapons as deterrence or defence have limited usage against contemporary security threats to states. Explain the statement.
Ans: Nuclear weapons have limited usage due to arms-control method of cooperation. One of the arms-control treaty was the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968 to regulate the acquisition of nuclear weapons. As per this treaty those countries that had fasted and manufactured nuclear weapons before 1967 were allowed to keep their weapons and those that had not done so were to give up the right to acquire them. The NPT did not abolish nuclear weapons rather it limited the number of countries that could have them.
Q11: Looking at the Indian scenario, what type of security has been given priority in India, traditional or non-traditional? What examples could you cite to substantiate the arguments?
Ans: India has faced traditional (military) and non-traditional threats to its security that have emerged from within as well as outside its borders. Its security strategy has four broad components ie:
To strengthen its military capabilities because:
- India has been involved in conflict with its neighbours as Pakistan in 1947-48,1965,1971 and 1999 and China in 1962.
- In South Asian Region, India is surrounded by nuclear armed countries. Hence India’s decision to conduct nuclear test in 1998 was justified to safeguard national security.
- India first tested nuclear device in 1974.
To strengthen international norms and international institutions:
- India’s first Prime Minister J.L. Nehru supported Asian solidarity, disarmament, decolonisation and the UN as a forum to settle down international conflict.
- India took initiatives to bring about a universal and non- discriminatory non-proliferation regime to enjoy some rights and obligations with respect to weapons of mass destruction.
- It used non-alignment to help to carve out an area of peace outside the blocs.
- India signed Kyoto Protocol in 1997 to be a part of roadmap for reducing the emissions of greenhouse gases to check global warming.
To meet security challenges within the country:
- Several militant groups from areas such as Nagaland, Mizoram, Punjab, Kashmir have sought to break away from India.
- India makes efforts to preserve national unity by adopting a democratic political system by providing freedom of speech and expression alongwith the right to vote.
To develop its economy:
- India develops the way to lift vast mass of citizens out of poverty, misery and huge economic inequalities.
- A democratically elected government is supposed to combine economic growth with human development without any demarcation between the rich and the poor.
Q12: Read the cartoon below and write a short note in favour or against the connection between war and terrorism depicted in this cartoon.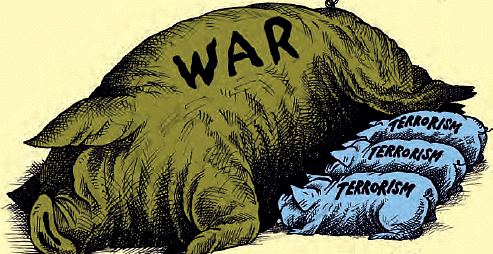 Ans: Terrorism is non-traditional threat to security as it is goal oriented political
Ans: Terrorism is non-traditional threat to security as it is goal oriented political
|
145 videos|630 docs|203 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - Security in the Contemporary World
| 1. What are the key challenges in maintaining security in the contemporary world? |  |
| 2. How does cybersecurity play a role in ensuring security in the contemporary world? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of international cooperation in addressing security issues in the contemporary world? |  |
| 4. How does social unrest impact security in the contemporary world? |  |
| 5. What role do international organizations play in maintaining security in the contemporary world? |  |




























