NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - The Mughal Empire
| Table of contents |

|
| Let's Recall |

|
| Let's Understand |

|
| Let's Discuss |

|
| Let's Do |

|
Let's Recall
Q1. Match the following: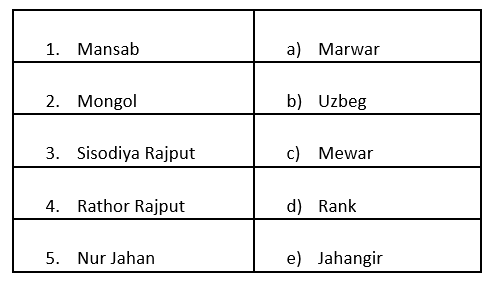 Ans:
Ans: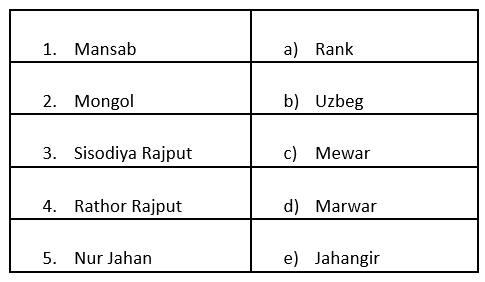
Mansab → Rank: The Mansabdari system was introduced by Akbar in the Mughal Empire, where Mansab referred to the rank or position of an officer.
Mongol → Uzbek: The Mongols and Uzbeks shared historical connections; Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire, was an Uzbek descendant.
Sisodiya Rajput → Mewar: The Sisodiya Rajput clan ruled the kingdom of Mewar, with famous rulers like Maharana Pratap.
Rathor Rajput → Marwar: The Rathor Rajput clan ruled over Marwar, which is present-day Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Nur Jahan → Jahangir: Nur Jahan was the wife of Mughal Emperor Jahangir and played a significant role in Mughal administration.
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The five Deccan Sultanates were Berar, Khandesh, Ahmadnagar, ____________ and _____________.
Ans: The five Deccan Sultanates were Berar, Khandesh, Ahmadnagar, Bijapur, and Golconda.
(b) If zat determined a mansabdar’s rank and salary, sawar indicated his ____________.
Ans: If zat determined a mansabdar’s rank and salary, sawar indicated his number of cavalrymen.
(c) Abul Fazl, Akbar’s friend and counselor, helped him frame the idea of ____________ so that he could govern a society composed of many religions, cultures, and castes.
Ans: Abul Fazl, Akbar’s friend and counselor, helped him frame the idea of sulh-i-kul so that he could govern a society composed of many religions, cultures, and castes.
Q3. What were the central provinces under the control of the Mughals?
Ans: The central provinces under the control of the Mughals were Delhi, Sindh, Kabul, Mewar, Marwar, Gujarat, Bihar, Bengal, Orissa and Deccan.
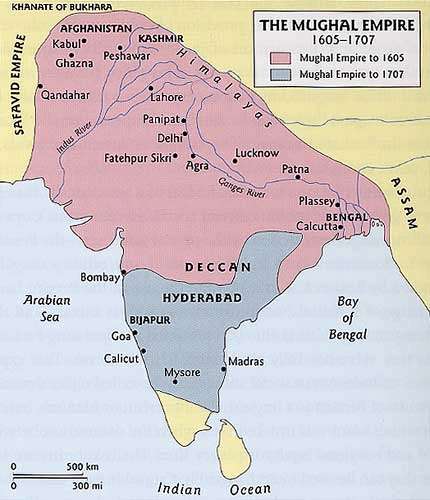 Showing central provinces under the control of Mughals
Showing central provinces under the control of Mughals
Ans: The relationship between a mansabdar and a jagir in the Mughal Empire was both financial and administrative:
- A mansabdar was a high-ranking official appointed by the emperor.
- Their rank and salary, known as zat, determined their position.
- They were assigned a jagir, which was a land area for revenue collection.
- Mansabdars typically did not live on their jagirs; instead, they sent agents to manage revenue.
- In addition to overseeing their jagirs, they served the empire in various roles.

Let's Understand
- Collecting revenue directly from the peasants.
- Acting as village chieftains in rural areas, especially when no official from the Mughal court was present.
- Sometimes leading or joining rebellions alongside peasants of similar castes against the Mughal rulers.

Q6. How were the debates with religious scholars important in the formation of Akbar's ideas on governance?
Ans: Akbar, a Mughal ruler, was curious about religious and social customs. He arranged debates among scholars of different religions. These debates revealed that religious rituals often disrupted social harmony. Akbar developed the idea of ‘sulh-i-kul’ (universal peace), which promotes tolerance, justice, and peace. His minister, Abul Fazl, played a key role in shaping this vision of governance. Akbar's successors, Jahangir and Shah Jahan, continued to uphold this policy.  A painting representing Akbar's Court
A painting representing Akbar's Court
Q7. Why did the Mughals emphasize their Timurid and not their Mongol descent?
Ans: The Mughals preferred to highlight their Timurid ancestry over their Mongol roots for several reasons:
- Genghis Khan, the Mongol leader, is often remembered for his brutal conquests and destruction across Central Asia.
- In contrast, Timur (or Tamerlane) is celebrated in Indian history for his capture of Delhi in 1398.
- The Mughal rulers sought to associate themselves with Timur's legacy, viewing him as a more noble ancestor.
- This emphasis helped them cultivate a sense of pride and legitimacy in their rule.
 Timur
Timur
Let's Discuss
Ans: The Mughal Empire’s main income source was revenues collected from peasants and agricultural products.
- The primary income came from taxes collected on agricultural products by zamindars.
- Zamindars submitted these taxes to the mansabdars, who then contributed to the Mughal treasury.
- This revenue funded salaries for soldiers and government officials, as well as public welfare projects.
- Land revenue was crucial for maintaining law and order throughout the empire.
 A painting representing Zamindar collecting Revenue from people
A painting representing Zamindar collecting Revenue from people
Q9. Why was it important for the Mughals to recruit mansabdars from diverse backgrounds and not just Turanis and Iranis?
Ans: The Mughals recruited mansabdars from various backgrounds, not just Turanis and Iranians, for several reasons:
- This strategy promoted stability across the empire's diverse regions.
- It helped to gain the trust of local populations.
- Recruiting from different groups maintained a balance of power within the administration.
- This approach reduced potential unrest caused by perceived favouritism.
- It allowed the Mughals to respect the empire's diversity and strengthen their control.
Q10. Like the Mughal Empire, India today is also made up
of many social and cultural units. Does this pose a
challenge to national integration?
Ans: No, this does not challenge India's unity. India is known for its unity in diversity, with many cultures living together. Key points include:
- While conflicts may occur, they are usually resolved peacefully.
- In times of external threats, such as the Kargil War, Indians come together, showing strong patriotism.
- This collective spirit proves that differences do not weaken the country's strength and resilience.
Q11. Peasants were vital for the economy of the Mughal
Empire. Do you think that they are as important today?
Has the gap in the income between the rich and the
poor in India changed a great deal from the period of
the Mughals?
Ans: Peasants continue to play a vital role in India's agricultural economy, much like during the Mughal era. Their contributions include:
- Growing essential crops for the nation's food supply.
- Providing land revenue, which supports government development projects.
- Forming the backbone of the economy.
However, significant challenges remain:
- A persistent wealth gap exists between the rich and the poor.
- Many peasants lack access to modern farming resources, such as quality seeds.
- Agriculture often leads to seasonal income, resulting in periods of unemployment.
Let's Do
Q12. The Mughal Empire left its impact on the different regions of the subcontinent in a variety of ways. Find out if it had any impact on the city, village, or region in which you live.
Ans: Delhi, the capital of the Mughal Empire, experienced significant transformation during this period. The empire's influence is evident in the city's architecture and cultural landmarks, including:
- Red Fort - A symbol of Mughal power and grandeur.
- Jama Masjid - One of the largest mosques in India.
- Humayun's Tomb - A UNESCO World Heritage site showcasing Mughal architecture.
- Chandni Chowk - A vibrant market reflecting the bustling life of the era.
- Mughal gardens - Beautifully designed landscapes that enhance the city's charm.
These remarkable structures are lasting legacies of the Mughal emperors, contributing to the city's rich history and vibrant culture.
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - The Mughal Empire
| 1. What were the main achievements of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 2. Who were the prominent rulers of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 3. How did the Mughal Empire impact Indian culture? |  |
| 4. What were the causes of the decline of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 5. How did the Mughal Empire contribute to the economy of India? |  |
















