Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Science for Class 6 > NCERT Summary: Exploring Magnets
NCERT Summary: Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction
- Magnets are objects that can attract materials like iron and have been used for navigation for centuries. They are found in many everyday items such as toys, pencil boxes, and school supplies.
- Magnets can be natural (lodestones) or artificial (man-made using iron or metals).

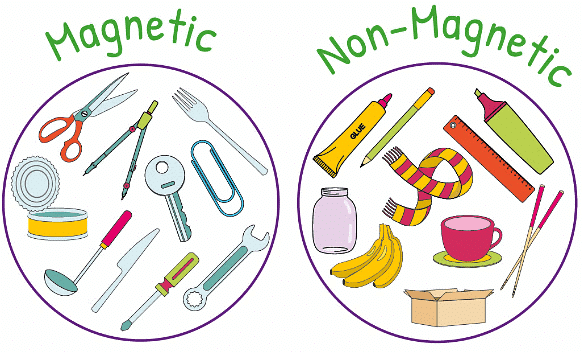
Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Magnetic Materials: These materials are attracted to magnets, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
- Non-magnetic Materials: These do not respond to magnets, including wood, plastic, rubber, and glass.
[Question: 1727556]
Poles of a Magnet
- Every magnet has two poles: the North Pole and the South Pole.
- Magnetic force is strongest at the poles.
- A single pole cannot exist – even if a magnet is broken into smaller pieces, each piece will still have both poles.

Finding Directions
- A freely suspended bar magnet always aligns itself along the north-south direction.
- The end pointing towards the north is called the North-seeking pole, and the other is the South-seeking pole.
- This property is used in a magnetic compass, a device that helps find directions by using a freely rotating magnetised needle.
Making a Simple Compass
- A needle can be magnetised by rubbing it repeatedly in one direction with a bar magnet.
- The needle is floated on a cork in water — it aligns itself in the north-south direction and acts as a simple compass.
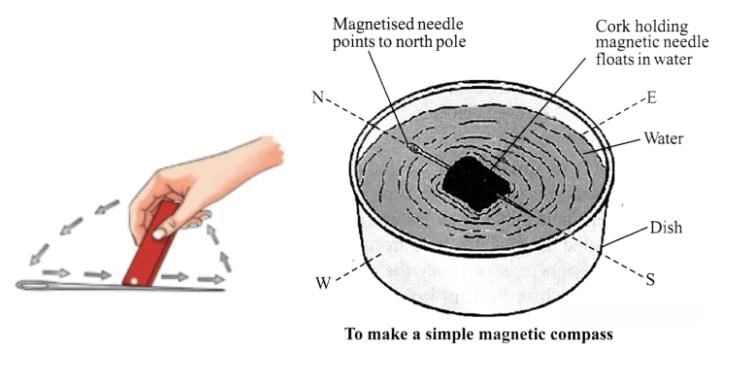
- Ancient Indians used a similar device called Matsya-yantra (fish-shaped magnet in oil) for navigation.
Comparison Between a Freely Suspended Magnet and a Magnetic Compass
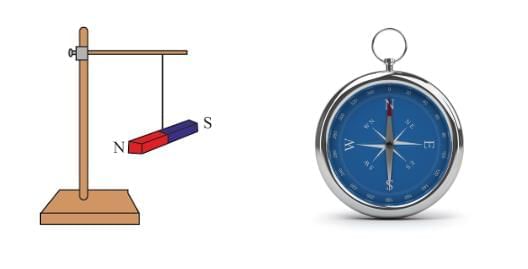
- Working: Both devices align with the Earth's magnetic field. The freely suspended magnet shows the basic property of magnetic alignment, while the compass is a portable, practical tool for navigation.
- Practical Use: The compass is more convenient for on-the-go navigation, while a freely suspended magnet is used primarily for learning or experiments.
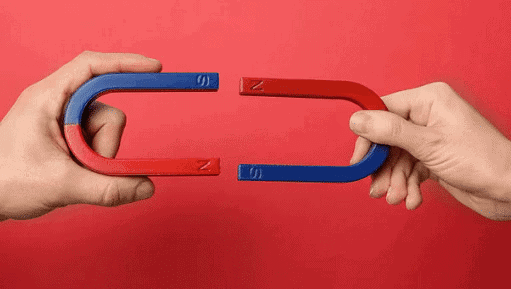
Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets
- Unlike poles attract (North–South).
- Like poles repel (North–North or South–South).
- The property of repulsion is used to identify magnets (since non-magnets only attract but do not repel).
[Question: 1727557]
Magnetic Effect Through Materials
- Magnetic force can act through non-magnetic materials like wood, cardboard, plastic, or glass.
- This means magnets can attract objects even if such materials are placed between them.
Fun with Magnets
Magnets can be used to make games and activities such as:
- Moving steel balls through a maze by holding a magnet below the surface.
- Picking paper clips from water without touching them.
- Making cars with magnets that either repel or attract each other, depending on pole alignment.
Care of Magnets
(i) Do not drop, hammer, or heat magnets as they can lose their magnetism.
(ii) Store properly:
- Keep bar magnets in pairs with opposite poles on the same side.
- Place a wooden piece between them and soft iron keepers across the poles.
Key Points
- Magnetic materials: Iron, Nickel, Cobalt.
- Non-magnetic materials: Plastic, Wood, Rubber, Glass.
- Magnet always has two poles – North and South.
- Freely suspended magnet rests in the north-south direction.
- Compass needle shows directions based on Earth’s magnetic field.
- Like poles repel and unlike poles attract.
- Magnetic effects work through non-magnetic materials.
The document NCERT Summary: Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Science for Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
66 videos|279 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Exploring Magnets - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the main differences between magnetic and non-magnetic materials? |  |
Ans. Magnetic materials are those that can be magnetized and exhibit magnetic properties, such as iron, cobalt, and nickel. They contain unpaired electrons, which contribute to their magnetic moments. On the other hand, non-magnetic materials, like wood, plastic, and most metals, do not exhibit magnetism as their electron spins are paired, canceling out any magnetic effect.
| 2. How can I determine the poles of a magnet? |  |
Ans. The poles of a magnet can be identified using a compass. A compass needle has a magnetic north and south pole; when brought close to a magnet, the north pole of the compass will point towards the south pole of the magnet, and the south pole of the compass will point towards the north pole of the magnet. Additionally, the ends of a magnet are typically marked as 'N' for north and 'S' for south.
| 3. How can magnets be used to find directions? |  |
Ans. Magnets can be used to find directions through the use of a compass, which contains a small magnet that aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field. By holding a compass level and away from other magnetic sources, one can determine the cardinal directions: north, south, east, and west, allowing for accurate navigation.
| 4. What is the difference between attraction and repulsion between magnets? |  |
Ans. Attraction occurs when opposite poles of two magnets come close to each other, such as a north pole and a south pole, causing them to pull towards one another. Conversely, repulsion occurs when like poles (north-north or south-south) are brought together, resulting in the magnets pushing away from each other. This fundamental interaction is due to the magnetic fields produced by the magnets.
| 5. What are some fun activities or experiments that can be done with magnets? |  |
Ans. There are various fun activities that can be done with magnets, such as creating a simple compass, using magnets to pick up small metallic objects, and experimenting with magnetic fields using iron filings. Another engaging activity is to make a magnetic slime or try to build a simple electric motor, which can demonstrate the principles of magnetism in an enjoyable way.
Related Searches

















