Best Study Material for UPSC Exam
UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > NCERT Summary: Inside our Earth
NCERT Summary: Inside our Earth | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Rocks and Minerals |

|
| Minerals |

|
| Mind map |

|
Introduction
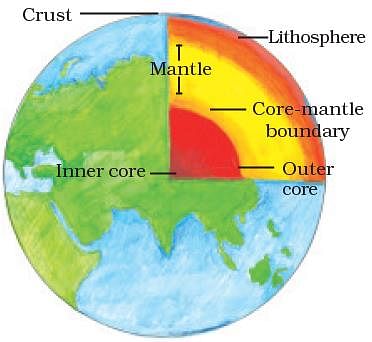 Interior of the Earth
Interior of the Earth
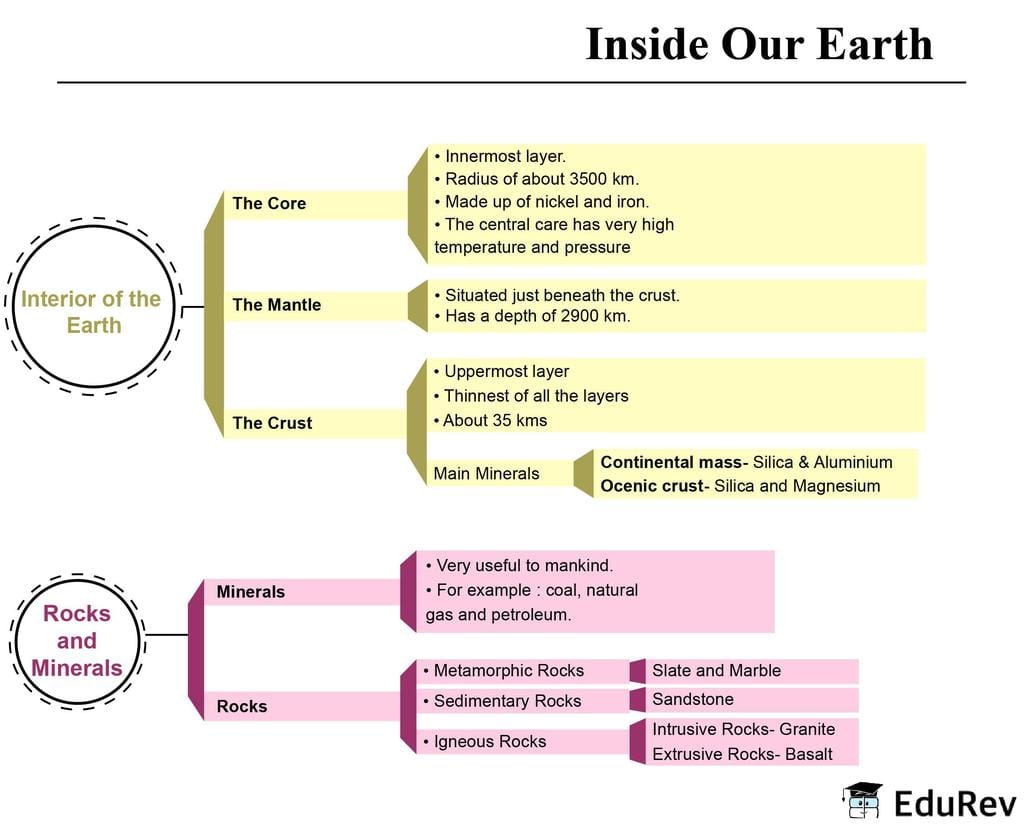
- Crust- uppermost layer over the earth s surface, thinnest of all the layers, 35 km. on the continental masses and only 5 km. on the ocean floors.
- Sial- The main mineral constituents of the continental mass are silica and alumina
- Sima-The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium
- Mantle-Just beneath the crust extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust.
- Nife- innermost layer, the radius of about 3500 km, mainly made up of nickel and iron. Do you know?
- The crust forms only 1 percent of the volume of the earth, 84 percent consists of the mantle and 15 percent makes the core.
- The radius of the earth is 6371 km. the central core has a very high temperature and pressure. Question for NCERT Summary: Inside our EarthTry yourself:Which one of the following is the dominant element of the earth crust?View Solution
Rocks and Minerals
Three major types of rocks: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks.
1. Igneous rocks
- When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks thus formed are called igneous rocks also called primary rocks
- Two types of igneous rocks: intrusive rocks and extrusive rocks
- Extrusive igneous rocks-
- When molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid.
- Rocks formed in such a way on the crust.
- They are very fine-grained structure. For example, basalt
- Deccan plateau is made up of basalt rocks
➢ Intrusive igneous rocks
- When the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust, solid rocks are formed.
- Solid rocks so formed are called intrusive igneous rocks.
- Form large grains.
- Granite is an example of such a rock.
- Sediments: smaller particles of rocks
2. Sedimentary rocks
- Loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks, sandstone is made from grains of sand. These rocks may also contain fossils of plants, animals, and other microorganisms that once lived on them.
3. Metamorphic rocks
- Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure.
- For example, clay changes into slate and limestone into marble.
Minerals
- Minerals are very important to humankind. Some are used as fuels. For example, coal, natural gas, and petroleum.
- They are also used in industries - iron, aluminium, gold, uranium, etc, in medicine, in fertilizers, etc.
 |
Download the notes
NCERT Summary: Inside our Earth
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Mind map
The document NCERT Summary: Inside our Earth | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
180 videos|482 docs|193 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Inside our Earth - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main types of rocks found on Earth? |  |
| 2. How are minerals classified? |  |
Ans. Minerals are classified based on their chemical composition and crystal structure. They can be categorized into two main groups: silicate minerals, which contain silicon and oxygen, and non-silicate minerals, which do not. Common examples include quartz (a silicate) and calcite (a non-silicate).
| 3. What is the difference between rocks and minerals? |  |
Ans. The main difference between rocks and minerals is that minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances with a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, while rocks are solid aggregates composed of one or more minerals. For example, granite is a rock made up of quartz, feldspar, and mica minerals.
| 4. What are some common uses of minerals? |  |
Ans. Minerals have various uses in daily life and industry. For example, quartz is used in electronics and glass manufacturing, calcite is important in the production of cement, and gypsum is used in drywall and plaster. Additionally, minerals like iron and copper are essential for construction and electrical wiring.
| 5. How do rocks and minerals contribute to Earth's processes? |  |
Ans. Rocks and minerals play a crucial role in Earth's processes such as the rock cycle, which involves the continuous transformation of rocks from one type to another through processes like erosion, sedimentation, and metamorphism. They also contribute to soil formation, influence ecosystems, and are vital for natural resources and human activities.
Related Searches