Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation > New EXIM Policy
New EXIM Policy | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| EXIM Infrastructure |

|
| Export Promotion Incentives |

|
| Stakeholders |

|
Introduction
- Foreign trade in India is promoted and facilitated by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MoCI). The DGFT issues the authorisation to exporters and monitors their corresponding obligations through a network of 38 regional offices. The DGFT also implements the Foreign Trade Policy of India.
- Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) is the prime policy that lays down simple and transparent procedures which are easy to comply with and administer for efficient management of foreign trade in India. The Policy aims at enhancing the country’s trade for economic growth and employment generation. The Customs Tariff Act and the Central Excise Tariff Act are the other two important Acts that lay down how the Customs and Excise duties shall be levied on trade, respectively.
- India’s overall exports (Merchandise and Services combined) in FY 2022-23 exhibited a positive growth of 13.84% over FY 2021-22 to achieve $770.18 bn worth of exports. Merchandise exports have registered highest ever annual exports of $ 447.46 bn with 6.03% growth during FY 2022-23 surpassing the previous year record exports of $ 422 bn. Services export lead the overall exports growth and has set a new record annual value of $ 322.72 bn with growth rate at 26.79% during FY 2022-23 over FY 2021-22.
- Under merchandise exports, 17 of the 30 key sectors exhibited positive growth during FY 2022-23 as compared to FY 2021-22. These include Oil Meals (55.13%), Electronic Goods (50.52%), Petroleum Products (40.1%), Tobacco (31.37%), Oil Seeds (20.13%), Rice (15.22%), Cereal Preparations & Miscellaneous Processed Items (14.61%), Coffee (12.29%), Fruits & Vegetables (11.19%), Other Cereals (9.74%), Tea (8.85%), Leather & Leather Products (8.47%), Ceramic Products & Glassware (7.83%), Marine Products (3.93%), Drugs & Pharmaceuticals (3.25%), Organic & Inorganic Chemicals (3.23%) and RMG of all Textiles (1.1%). India’s overall exports in December 2023 stands at $38.45 Bn.
Question for New EXIM PolicyTry yourself: What is the role of the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) in India?View Solution
EXIM Infrastructure
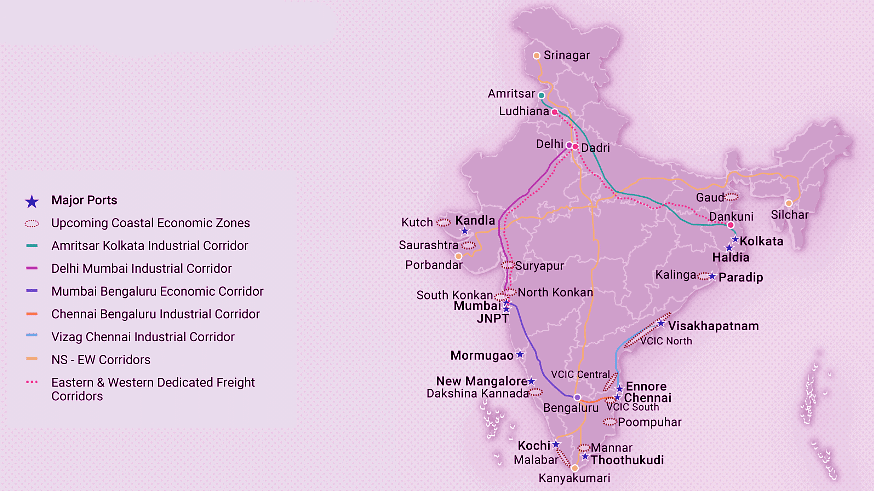
About 95% of India’s merchandise trade (by volume) is handled by its maritime transport. Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT) in Maharashtra is India’s largest port, handling 55% of container cargo across all major ports. Currently, the country has a presence of 290 inland container depots and freight stations for trade (includes those under implementation).
- Port Network: To reduce the logistics cost for cargo and promote port-led industrial development, the Government of India launched the Sagarmala Programme under which 6 new major ports and 14 coastal economic zones have been identified for development. The Programme's four main pillars are port-modernization, better port-connectivity, port-led industrialization and coastal community development.
- Road Network: With a targeted construction of 40 km of national highway every day during 2018-19, the world’s 2nd largest road network in India is aiming to reach the pinnacle soon. For efficient movement of goods and better district-level connectivity, the project of Bharatmala Pariyojana was launched by the Government of India in 2015. The Project aims to develop 50 new industrial corridors, add 34,800 km of road network in its Phase-I, including 10,000 km of the residual road network under NHDP and connect 550 districts through four-lane national highways.
- Rail Network: Trade through railways in India is also prominent, with the Indian Railways transporting over 1.2 bn tons of freight in 2017-18. There are 6 high-capacity, high-speed freight corridors coming up in the country to support the Indian Railways to manage 40% modal freight share of the economy.
Export Promotion Incentives
Raw Materials & Inputs
- Duty Exemption Schemes:
- Advance Authorisation (AA): Duty-free import of inputs that are exempted from Basic Customs Duty, however, IGST is payable. Minimum value addition required to be achieved under the Scheme is 15%.
- Duty-Free Import Authorisation (DFIA): Importer is exempted only from payment of Basic Customs Duty. Minimum value addition required to be achieved under the Scheme is 20%.
- Duty Drawback (DBK) Scheme: Enables post export replenishment/ remission of duty on inputs used in the export product
Capital Goods & Machinery
- Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme (EPCG): Importers have to pay IGST and take input tax credit as applicable under the GST rules. The capital goods imported can also be used for domestic production. Importer under the Scheme has an Export Obligation (EO) equivalent to 6 times of duties, cess and taxes saved on capital goods, to be fulfilled in 6 years from the date of issue.
Finished Goods
- Merchandise Export-Import Scheme (MEIS)/ Service Export-Import Scheme (SEIS): Duty Credit Scrips are provided against exports that can be used to pay Customs or Excise Duties. However, the scrips cannot be used to pay for any type of GST.
International Markets
- Duty-free import of goods/ procurement by SEZ: Only Basic Customs Duty is paid for the development, operation and maintenance of SEZ. Authorised operations shall be exempted from payment of IGST. A portion of taxes paid will be neutralized by Input Tax Credit
Question for New EXIM PolicyTry yourself: What is the main objective of the Sagarmala Programme launched by the Government of India?View Solution
Stakeholders
Exim Trade Facilitation Bodies
- Agriculture & Processed Food Products Export Development Authority
- Commodity Boards
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation
- Export Inspection Council
- Export Promotion Councils
- Federation of Indian Export Organizations
- Indian Institute of Foreign Trade
- Indian Institute of Packaging
- India Trade Promotion Organization
- Marine Products Export Development Authority
The document New EXIM Policy | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on New EXIM Policy - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the significance of EXIM infrastructure in promoting exports? |  |
Ans. EXIM infrastructure plays a crucial role in promoting exports by providing the necessary facilities and support for trade activities. It includes ports, airports, railways, roads, and other transportation systems that help in the smooth movement of goods. Additionally, it also encompasses customs clearance facilities, warehouses, and other logistics services, which are essential for efficient export operations.
| 2. What are export promotion incentives? |  |
Ans. Export promotion incentives are measures taken by the government to encourage and support the export activities of businesses. These incentives can include financial incentives such as tax exemptions, subsidies, grants, and loans, as well as non-financial incentives like export credit insurance and technical assistance. These incentives aim to reduce the cost of exports, enhance competitiveness, and stimulate export growth.
| 3. Who are the stakeholders involved in the new EXIM policy? |  |
Ans. The stakeholders involved in the new EXIM policy include the government, exporters, importers, trade associations, financial institutions, logistics service providers, and regulatory authorities. The government formulates and implements the policy, while exporters and importers are directly impacted by the policy changes. Trade associations represent the interests of the business community, financial institutions provide funding support, logistics service providers facilitate the movement of goods, and regulatory authorities ensure compliance with trade regulations.
| 4. How can exporters benefit from the new EXIM policy? |  |
Ans. Exporters can benefit from the new EXIM policy in several ways. Firstly, the policy may provide financial incentives such as tax exemptions or subsidies, which can reduce the export cost and improve profitability. Secondly, it may offer simplified procedures and faster clearance processes, making it easier for exporters to comply with regulatory requirements. Additionally, the policy may focus on market diversification and provide support for exploring new export destinations, thereby expanding the market opportunities for exporters.
| 5. What role does the UPSC play in relation to the new EXIM policy? |  |
Ans. The UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) is not directly involved in the formulation or implementation of the new EXIM policy. However, it plays a significant role in selecting candidates for administrative positions in various government departments, including those involved in trade and commerce. The UPSC conducts examinations and interviews to assess the suitability of candidates for these positions, ensuring that competent individuals are appointed to contribute to the effective implementation of the EXIM policy.
Related Searches




















