Noun | English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Noun? |

|
| What are the different types of Nouns? |

|
| Rules of Nouns |

|
| Use of Possessive Case |

|
What is a Noun?
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, quality, condition, and action. Nouns are used as subjects of sentences and as the objects of verbs and prepositions.
Examples of Nouns: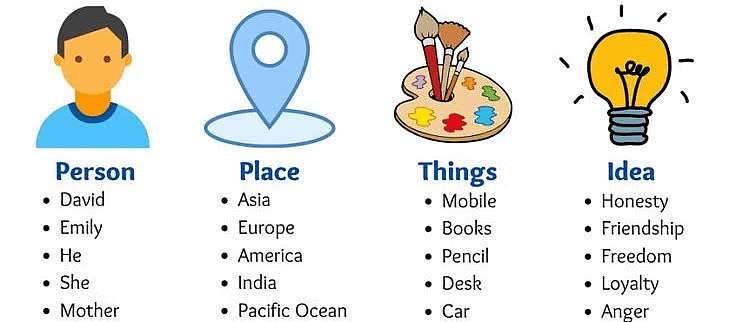
What are the different types of Nouns?
Nouns in English are broadly classified into 8 types:
- Common Noun – A common noun is a word that names general items, people, or places rather than specific ones. It is used for things that belong to the same group or type, such as girl, doctor, school, or country. These nouns do not begin with capital letters unless they start a sentence.
- Proper Noun – Proper nouns refer to particular places, persons and things, for example, Mark, New York, the White House.
What is the difference between common and proper nouns?
Here is a list of some Common and Proper Nouns: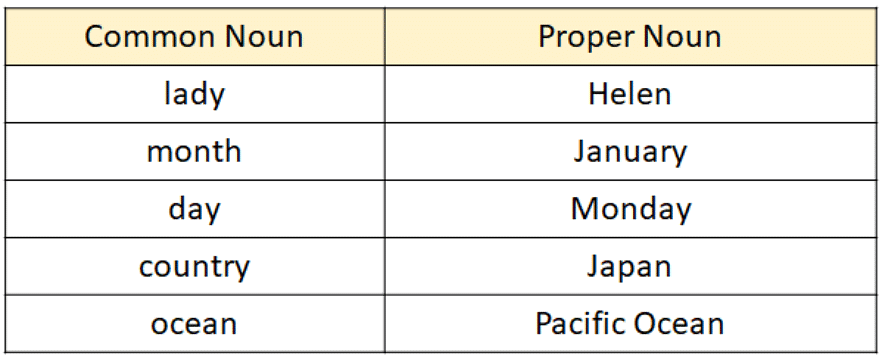 When we look at the two main types of noun – proper and common – we can differentiate between the two by saying that a common noun is a general way of classifying something, and a proper noun is a specific way of classifying something.
When we look at the two main types of noun – proper and common – we can differentiate between the two by saying that a common noun is a general way of classifying something, and a proper noun is a specific way of classifying something.
So, for example, the word dog is a common noun; but if your dog was called Fido, the word Fido is a proper noun:- Dog = common noun
- Dog’s name (Fido, in this case) = proper noun
More examples of the difference between common and proper nouns: - My favorite newspaper (common noun) is the Washington Post (proper noun).
- Her husband (common noun) is called Frank (proper noun).
- The award-winning Babe Ruth (proper noun) is the greatest baseball player (common noun) in history.
You may have noticed from the examples that common nouns are not usually capitalized, unless they begin a sentence, whereas proper nouns are normally capitalized. You will also notice that both types of nouns can be more than a single word.
- Collective Nouns – Collective nouns refer to a group of people, animals, or things seen as one unit. They are usually singular but become plural when referring to multiple groups. Examples: team, family, crowd, committee, group, flock, audience, pack.
- Concrete Nouns –these are the names used for the things that have physical existence and we can see, such as a table, chair, mobile phones, etc.
- Abstract Nouns – are the exact opposite of concrete nouns. These are the names given to an idea, conditions, or a quality. Basically, the name is used to refer to something that cannot be seen but exists; it does not have a physical form
Example:
(i) Love, fear, anger, joy, excitement, and other emotions are abstract nouns.
(ii) Courage, bravery, cowardice, and other such states are abstract nouns.
(iii) Desire, creativity, uncertainty, and other innate feelings are abstract nouns. - Material Nouns – these are the names used to refer to substances, materials or things that are made up of an alloy. Examples: silver, gold, metal, cotton, etc.
- Countable Nouns – that can be counted like one pen, two ladies, one chair, etc. These nouns take articles (a, an, the) with them. Countable nouns usually have both singular and plural forms. Countable nouns can be counted in the numbers 1, 2, 3…. Examples are desk, pen, person.
Example:
(i) There is one chair in this room (in this example, the word 'chair' is singular and countable)
(ii) There are 10 chairs in the house. (In this example, the word 'chair' is plural and countable.) - Uncountable Nouns – the nouns that cannot be counted. Uncountable nouns are always singular. Uncountable nouns can not be counted in any numbers. Rather, they are considered an entire item. Some most commonly used uncountable nouns are water, health, and money.
Example:
(i) There is no more milk in the kitchen.
(ii) Please take good care of your furniture.
(iii) I need some Water.
Other examples of uncountable nouns include:
Advice, Anger, Baggage, Beauty, Gasoline, Information, Luggage, Smog, Wheat
Sometimes a noun is used as an uncountable noun when it refers to the entire idea or substance, but it can be used as a countable noun when used in a context involving: Countable pieces or containers for things.
Examples:
1. Uncountable: I prefer tea to Coke.
Countable: Two teas (two cups of tea) for us, please.
2. Uncountable: I love cheese.
Countable: There are so many cheeses to choose from.
3. Uncountable: She has shiny hair.
Countable: I found a hair today in my sandwich. It grossed me out.
4. Uncountable: He is great at sports.
Countable: Skiing is a popular sport in Austria.
Abstract nouns and proper nouns are always uncountable while Common and Concrete nouns can be both countable as well as uncountable nouns.
The army is at its best to protect the country.
Rules of Nouns
Rule No. 1: Some nouns are used in the singular form.
Example:
Rule No. 2: Some nouns are always used in the Plural Form.
Example:
Note: As a common noun ‘people’ means a ‘nation’ and is used in both singular and plural as:
- There are many different people in Europe.
- There is a mad race for power among the people of Europe.
Rule No. 3: Collective Nouns (like committee, jury, house, ministry, family, mob, crowd, audience, police, team, number, board, staff, and public) are used with:
- Singular verbs like is, was, and has when the members in the group act as one body or one unit.
- Plural verbs like are, have, and were are used when the members act as different individuals within the same group.
Rule No. 4: Some nouns have only plural forms and consequently are followed by a plural verb. (Many of these are used with the phrase “a pair of” as they refer to something made up of two parts).
Example: alms, riches, scissors, trousers, pants, clippers, tongs, bellows, gallows, fangs, eyeglasses, goggles, ashes, arrears, athletics, belongings, breeches, braces, binoculars, congratulations, dregs, earnings, fetters, lodgings, odds, outskirts, particulars, proceeds, proceedings, regards, remains, savings, spectacles, surroundings, valuables, wages, etc. Rule No. 5: Some nouns have the same form in both singular and plural forms and are expressed as singular or plural only by the use of a verb.
Rule No. 5: Some nouns have the same form in both singular and plural forms and are expressed as singular or plural only by the use of a verb.
Example: deer, swine, sheep, salmon (a type of fish), and offspring.
- There is a sheep in the yard.
- There are many sheep in the yard.
The words ‘fish’ and ‘hair’ are used in both singular and plural forms in a sentence, but they can be used as ‘fishes’ and ‘hairs’ in some specific sense.
- ‘Fish’ is used in the plural form to describe one fish or a group of fish of the same species (one type). The word ‘fishes’ is used to describe a variety of fish of different species (different types).
Example:
(i) The fishes of this river include salmon and sturgeon.
(ii) A fish is a cold-blooded vertebrate animal which lives in water. - Hair is singular when used collectively (e.g., Her hair is shiny). However, when referring to individual strands, the plural form ‘hairs’ is used (e.g., I found two hairs on my shirt.)
Rule No. 6: A compound noun (numerical adjective + noun) is not used in the plural if a noun does the work of an adjective.
Example: Ten-day tour, A ten-mile race, A ten-year-old boy.
Rule No. 7: Abstract and Material Nouns have no plural forms. When they are put in the Plural, they are used as Common Nouns.
Example: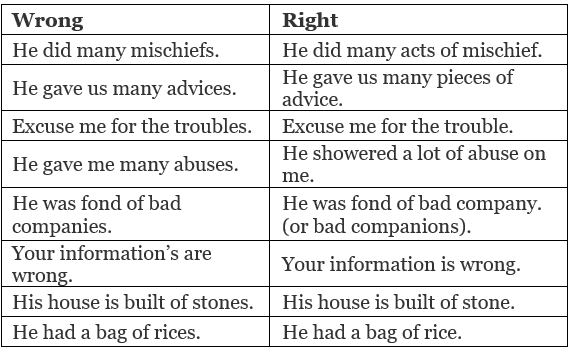
Rule No. 8: Some nouns have different meanings in singular and plural.
Example: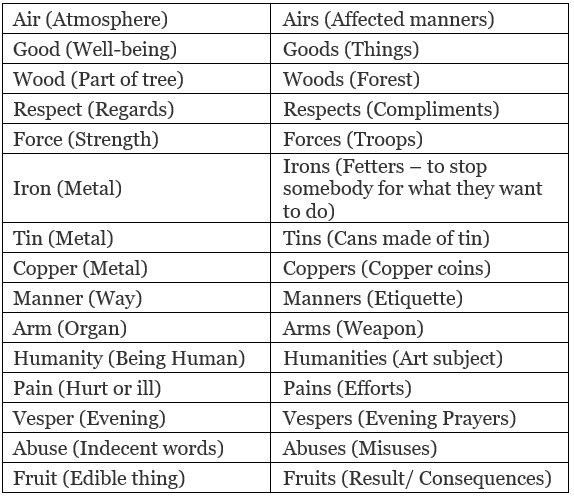
Rule No. 9: The plural of a compound noun is usually made by adding “s” to the principal word.
Example:
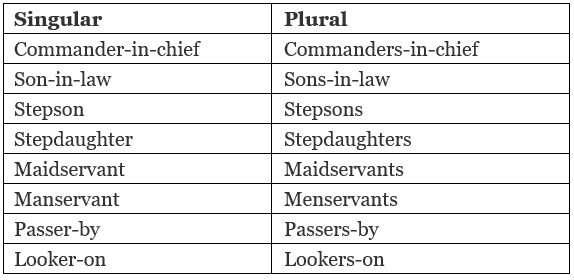
Rule No. 10: Material nouns like marble, brick, stone, glass, iron, etc., are not used in a plural form when they are used as a building/construction material. We use these words in the singular only.
Example: This house is made of brick.
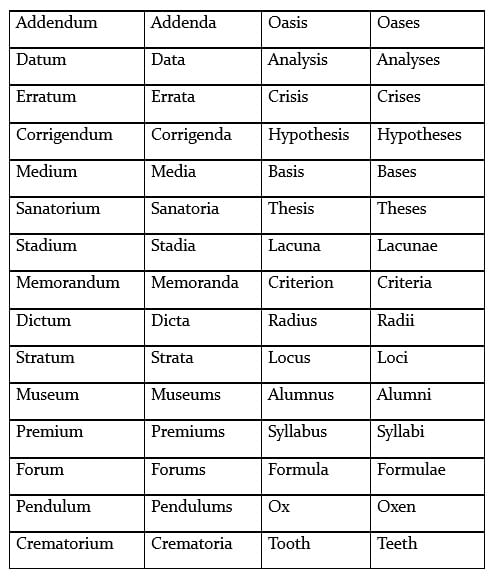
Rule No. 11: Plural forms of certain nouns
Example:
The mother-in-laws (1)/ gathered together(2)/ to discuss family issues(3)/ that need to be sorted out (4)/ No error (5)
Use of Possessive Case
- When the Noun denotes some living thing.
Example: The rat’s tail, the man’s hands. - When the Noun denotes some personified things.
Example: Duty’s call, England’s heroes. - When the Noun denotes time, space, or weight.
Example: A day’s march, a week’s holiday, in a year’s time, a meter’s length, a pound’s weight. - When the Noun denotes anything without life, it is generally expressed by the Preposition ‘of’.
Examples:
(i) ‘The legs of the chair’; not ‘the chair’s legs’.
(ii) ‘The pages of the book’; not ‘the book’s pages’.
(iii) ‘The roof of the house’; not ‘the house’s roof’.
(iv) ‘The cover of the book’; not ‘the book’s cover’.
|
133 videos|235 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Noun - English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL
| 1. What is a noun? |  |
| 2. What are the rules of nouns? |  |
| 3. What is the use of the possessive case noun? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of nouns in CLAT exam? |  |
| 5. Can you provide examples of common and proper nouns? |  |
















