UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Nuclear Power Plants in India
Nuclear Power Plants in India - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Nuclear energy is an important component of the country’s energy mix and is being pursued along with other sources of energy in an optimal manner. It is a clean, environment-friendly baseload source of power available 24X7. It also has huge potential which can ensure the long-term energy security of the country in a sustainable manner.
- Nuclear Power is the fifth-largest source of generating electricity in India after coal, gas, wind power, and hydroelectricity.
- As of 2021, there are 22 reactors with an installed capacity of 6780 MWe operating above 80% plant load factor in the country. Among these eighteen reactors are Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) and four are Light Water Reactors (LWRs).
- The nuclear energy program in India was launched around the time of independence under the leadership of Homi J. Bhabha.
- Asia’s first nuclear reactor is the Apsara Research Reactor situated in Mumbai. The domestic uranium reserve in India is small and the country is dependent on uranium imports from other countries to provide fuel to its nuclear power industry. Since the 1990s, Russia has been a major supplier of nuclear fuel to India.
Nuclear Power Plants in India – Operational

Nuclear Power Plants in India – Under Construction
 Nuclear Power Plants in India – Planned (Future projects)
Nuclear Power Plants in India – Planned (Future projects)


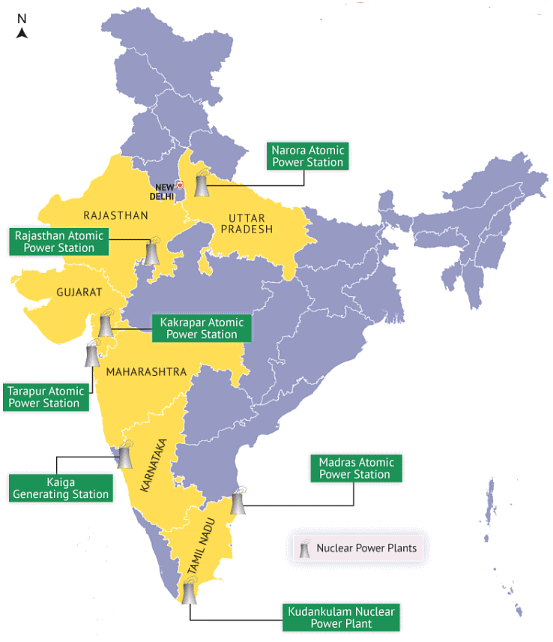
Kalpakkam:
- Located 80 km south of Chennai on the Coromandel Coast
- Known for MAPS and IGCAR
- India’s first fully indigenously constructed nuclear power station
- Has two indigenously built CANDU type PHWRs called MAPS-1 and MAPS-2
Kaiga:
- Nuclear power station located in the Uttar Kannada district in Karnataka
- Has four units with one still under construction
- All of the four are small-sized CANDU plants of 220 MW.
Kakrapar:
- Located near Surat on the bank of the Tapi in Gujarat
- It consists of two 220 MW PHWRs
- There is also a plant for producing heavy water in the area
- In January 2003 the CANDU Owners Group (COG) distinguished KAPS-1 as the worldwide best PHWR of its class.
Rawatbhata:
- Located on the bank of the Chambal River about 65 km from Kota, just 3 km from the Rana Pratap Sagar
- RAPS is India’s first pressurized water reactor of the CANDU type
- Installed capacity of 6 reactors – 1190 MW.
Tarapur:
- Located in Maharashtra to the north of Mumbai
- First nuclear reactor of India
- With a total capacity of 1400 MW Tarapur is the largest nuclear power station in the country
- First reactors were BWR which were the first of their kind in Asia.
Narora:
- Located in the Bulandshahar district of Uttar Pradesh on the bank of the Ganga
- Its twin reactors are Indianised version of the Canadian CANDU type which operate on natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as the moderator cum primary coolant.
Koodankulam:
- Located in the Tirunelveli district of TN
- Under construction with the Russian assistance
- Two 1000 MW reactors of the VVER- 1000 model are being constructed
- Both are water-cooled water-moderated power reactors
- When completed they will become the largest nuclear power generation complex of India
Chhaya mithi virdi:
- A proposed new nuclear site to be located in Gujarat near Alang Port
- It will be established with the help of the USA.
Kovvada:
- Proposed 2000 MW nuclear plant in Ranasthalam Mandal in the Srikakulam district of AP
- It will be established with assistance from the USA
- The Ministry of Environment and Forest has refused to give it the environmental clearance.
Haripur:
- A coastal village of East Medinipur district of West Bengal
- It will be established with the Russian assistance
- Proposed Capacity – 10,000 MW
- People are protesting against the reactor.
Jaitapur:
- Located in Maharashtra
- It is proposed to construct 6 European Pressurized Reactors designed and developed by Areva of France
- Each reactor will be of 1650 MW totaling 9900 MW
- Controversial as it comes under the Zone- V (earthquake)
FAQs on Nuclear Power Plants in India - UPSC
| 1. What is the current status of nuclear power plants in India? |  |
| 2. What is the role of nuclear power in India's energy mix? |  |
Ans. Nuclear power plays a significant role in India's energy mix. It provides a reliable and continuous source of electricity, which helps in meeting the growing energy demands of the country. Additionally, nuclear power helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
| 3. How does India ensure the safety and security of its nuclear power plants? |  |
Ans. The safety and security of nuclear power plants in India are ensured through a multi-layered approach. The Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL), which operates these plants, follows strict safety guidelines and international best practices. Regular inspections, maintenance, and training programs are conducted to ensure the highest level of safety and security.
| 4. What are the advantages of nuclear power plants in India? |  |
Ans. Nuclear power plants offer several advantages for India. Firstly, they provide a steady and reliable source of electricity, which is crucial for the country's economic growth. Secondly, nuclear power is a clean energy source that helps reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Lastly, nuclear power plants contribute to energy diversification, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
| 5. What are the challenges faced by nuclear power plants in India? |  |
Ans. Nuclear power plants in India face various challenges, including public perception and concerns regarding safety and environmental impacts. Additionally, there are challenges related to waste management and the availability of skilled manpower. The high capital cost involved in building nuclear power plants is also a significant challenge that needs to be addressed.
Download as PDF
Related Searches