Overview: Ranking | Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude for UGC NET PDF Download
Introduction
- As CAT aspirants embark on their journey to secure a coveted spot in their desired B-schools, a common objective unites them: the pursuit of the best opportunities aligned with their expected performance and percentiles.
However, the critical question arises: how do aspirants make informed choices? When faced with admission offers from multiple IIMs, aspirants often confront the decision-making process with clarity. - This decision hinges on the rankings assigned to these institutions, influenced by various factors such as past performance, faculty expertise, departments, campus infrastructure, academic offerings, industrial exposure, and more.
- In essence, rankings serve as a means to evaluate and position objects, individuals, or institutions based on their standing, performance, size, distance, height, weight, and other relevant criteria. Arranging items in either ascending or descending order according to established norms of ranking provides a measurable perspective.
- In the Logical Reasoning module of the CAT exam, candidates may encounter one or more questions that leverage the concept of Ranking. It is imperative for aspirants to comprehend the strategies and skills required to adeptly solve such Logical Reasoning problems.

Step-by-step approach to solving ranking questions
Carefully analyze the provided information by reading it attentively.
Identify various clues within the information and construct a table.
Create a structure based on the question's requirement for establishing rankings.
Populate the table with relevant clues and essential information. This approach minimizes the need to repeatedly refer to the textual information, enabling efficient responses to multiple questions.
Interpret indirect clues and position them appropriately within the table. Visualize the logical progression of the question.
Leave blank spaces in the prepared table for information that remains undecoded until a suitable insertion is determined.
Example
Question is followed by two statements, A and B. Answer the question using the following instructions –
Mark (a) if the question can be answered by using statement A alone but not by using statement B alone
Mark(b) if the question can be answered by using statement B alone but not by using statement A alone.
Mark(c) if the question can be answered by using either of the statements alone.
Mark(d) if the question can be answered by using both the statements together but not by either of the statements alone
Mark(e) if the question cannot be answered on the basis of the two statements.
Q1: In a particular school, sixty students were athletes. Ten among them were also among the top academic performers. How many top academic performers were in the school?
A. Sixty percent of the top academic performers were not athletes
B. All the top academic performers were not necessarily athletes.
(a) (a)
(b) (b)
(c) (c)
(d) (d)
(e) (e)
Q.2 – Five students Atul, Bala, Chetan, Dev and Ernesto were the only ones who participated in a quiz contest. They were ranked based on their scores in the contest. Dev got a higher rank as compared Ernesto, while Bala got a higher rank as compared to Chetan. Chetan’s rank was lower than the medium. Who among the five got the highest rank?
A. Atul was the last rank holder.
B. Bala was not among the top two rank holders.
Approach to answer –
1. (a) should be the right answer. As per Statement A- 60 percent of top academic performers were not athletes; but 40 percent were athletes. Ten among the athletes were also top academic performers, hence it can now be resolved that number of top academic performers can be found as athletes plus non – athletes, so A is sufficient to answer the question. Now let us analyse the statement B.- All the top academic performers were not necessarily athletes, well –we need more information in this regard which is not available in the statement B. Therefore, option (a) is the right answer.
2. (d) is the right answer. Try to form a table on the basis of Statement A– Atul was the last rank holder meaning the following –
1. (a) should be the right answer. As per Statement A- 60 percent of top academic performers were not athletes; but 40 percent were athletes. Ten among the athletes were also top academic performers, hence it can now be resolved that number of top academic performers can be found as athletes plus non – athletes, so A is sufficient to answer the question. Now let us analyse the statement B.- All the top academic performers were not necessarily athletes, well –we need more information in this regard which is not available in the statement B. Therefore, option (a) is the right answer.
2. (d) is the right answer. Try to form a table on the basis of Statement A– Atul was the last rank holder meaning the following –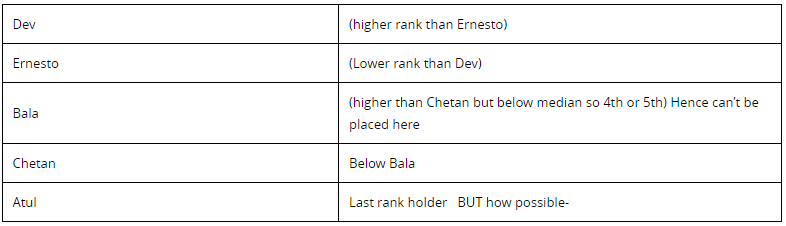
The possibilities, however, bring B and D, hence as per our approach we find that answer can not be formed based on statement A only.
Now analyse the statement B – According to this statement nothing substantial is divulged to us. Many combinations could come up with the placement of first rank. It could be either Atul or Dev. We are required to use both the statements and if we use statement B along with A, we arrive at the right possibility of Dev being the topper conforming to the given information.
Seven Principle to remember to solve ranking and order in the banking question paper
Principle #1:
The total count of individuals or objects within a group or class corresponds to one less than the combined sum of their positions from both ends (either right and left, or top and bottom). This adjustment accounts for the fact that the same individual or object is included twice in the summation, resulting in the final answer being one less than the computed total.
Total count=Sum of positions from both sides−1
Example: In a row of persons, the position of Saket from the left side of the row is 27th and position of Saket from the right side of the row is 34th. Find the total number of students in the row?
(a) 60
(b) 61
(c) 62
(d) 59
Sol:
Total number of students
= (Position of Saket from left + Position of Saket from right) -1
Total number of students = (27 + 34) – 1 = 61 – 1 = 60.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Principle #2:
The total count of persons/objects within a group is determined by adding the number of persons/objects before or after the specified individual in a row to the position of the same individual from the opposite side.
Total no. of persons/objects = No. of persons/objects before or after the given person in a row + Position of the same person from the other side. An orderly arrangement of pencils in a linear way.
An orderly arrangement of pencils in a linear way.
Example 2: In a row of persons, the position of Aparna Nair from the left side of the row is 27th and there are 5 persons after her in the row. Find the total no. of persons in the row?
Sol:
No. of persons in the row = Position of Aparna from left + No. of persons after Aparna
⇒ Total no. of persons = 27 + 5 = 32
Principle #3:
When the positions of two persons/objects are provided from opposite ends, along with the total count of persons/objects, the problem can be approached in two distinct methods to ascertain the number of persons between them.
Case 1:
Overlapping:
The total number of objects or persons in a group is always lesser than the addition of the position of two objects or persons from ends.
Example: The number of objects between two different persons = Total number of books – (Sum of positions of two different persons from opposite sides)
There are 24 students in dance class, and the teacher is planning for an arrangement of students on stage. Sampratha is 9th from the left side of the row and Supreetha is 22nd from the right side of the row. Find the number of dancers standing between the sisters Sampratha and Supreetha?
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 7
Sol:
Adding the position of Sampratha and Supreetha we get:
= 9 + 22 = 31
The result ‘31’ is greater than the total number of students in a dance class.
Therefore the number of dancers standing between the sisters will be = [(Position of Sampratha from left + Position of Supreetha from right) – Total number of dancers – 2]
The number of dancers between Sampratha and Supreetha
= (9+22) – 24 – 2 = 31 – 24 – 2 = 5.
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Case 2:
Non – overlapping:
The total number of objects or persons in a group is always greater than the addition of the position of two objects or persons from ends.
Example: There are 64 history books arranged in a row at central library Bangalore. Ancient history is 25th from the left side of the row and Middivel history is 30th from the right side of the row. What is the total number of books between Ancient and Middivel history?
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 9
Sol:
Adding the position of ancient and midlevel history books, we get:
Ancient histroy+ Middivel history = 25 + 30 = 55
Hence the number ‘55’ should be less than the total number of books.
∴ The number of books between ancient and midlevel history = Total number of books – (Place value of Ancient history book from left + Place value of Middivel history from right)
The number of books between ancient and midlevel history = 64 – (25+30) = 64 – 55 = 9
Hence the correct is option D.
Principle #4:
In cases of non-predictable order/ranking where the question data only offers information about the positions of different objects or persons, determining the total number of objects or people in a group or class is impossible. This is due to the potential scenarios of overlapping or non-overlapping cases. In such situations, it is advisable to recognize the impossibility of finding a final answer and save time by not attempting to solve such questions.
Example 5: Deepavali or Diwali a festival lights in India. One can find the row of lamps in every house these days. Chaitra lights a row of the lamp in her home. A square-shaped lamp is at 18th from left, and a circular-shaped lamp is at 25th position in a row from right. Find the total number of lamp Chaitra had lit?
(a) 27
(b) 30
(c) 43
(d) Cannot be determined.
Sol: The scenario can be either be of Overlapping or non-overlapping one. Hence the correct answer is option D.
Principle #5:
Swapping of positions to determine the order/ranking involves interchanging the placement or position of two objects/persons. The position of the second person from the same side before interchanging is calculated as follows:
Place value or position of the second person from the same side before interchanging = Position of 2nd person from the same side before interchanging + (Position of 1st person after interchanging – position of 1st person before interchanging from the same side)
Example: Soldiers Punita and Mitali and are standing in a row of female soldiers. Punita is 18th from the left side of the row, and Mitali is 24th from the right side of the row. If they interchange their positions, Punita becomes 31st from left. Find:
- The new position of Mitali from the right side
- The total number of female soldiers in a row.
- Number of soldiers standing between Punita & Mitali
Sol:1
The new position of Mithali from right side = Position of Mithali from the right side before interchanging + (Position of Punita from the left side after interchanging – Position of Punita from the left side before interchanging)
New position of Mithali from right side = 24 + (31 – 18) = 24 + 13 = 37
The new position of Mithali is 37th.
Sol 2:
The total number of person between A and B can be found in two different ways.
- Total no. of persons = (A’s position from right before interchanging + A’s position from left before interchanging) – 1
or - Total no. of persons = (B’s position from right after interchanging + A’s position from left before interchanging) – 1
Since we don’t know the position of Punita from right before interchanging. We can’t use the first method. We can use the second method as we know both the values.
The Total number of female soldiers = (Mithali’s position from right before interchanging + Punita’s position from left before interchanging) – 1
= 37+18 -1 = 54.
Sol 3:
To find the total number of people between any two persons.
No. of persons between A & B = (Position of A from left after interchanging– Position of A from left before interchanging) – 1
The total numbers of soldiers between Punita & Mithali = (Position of Punita from left after interchanging– Position of Punita from left before interchanging) – 1
= (31 – 18) – 1 = 13 – 1 = 12
Principle #6:
If the positions of two objects from opposite sides of the row are known and there is a third object right in the middle of the two, then the total number of objects can be evaluated based on the position of the third object.
Case 1:
The position of the third object is known from both the sides
Case 2:
The position of the third object is known from either of the sides.
Example: There is a pride of lions and its cubs in a row, the position of eldest lioness from the left side of the row is 9th & position of youngest lioness from the right side of the row is 8th. If the newborn cub is sitting just in the middle of eldest & youngest and position of cub from the left side of the row is 15th. Find the total number of lions the row?
Sol:
Position of a cub from left is 15th, and the eldest lioness from left is 9th so there are 15 – 9 – 1 = 5 lions are sitting between eldest and youngest lioness. As the cub is sitting in the middle of the eldest and youngest lioness so there must also be 5 persons sitting between the youngest lioness and a cub.
Thus position of a cub from right =
Position of youngest from right + 5 + 1 =
= 8 + 6 = 14
Total number of lions = (Sum of positions of cubs from both sides – 1)
= (15 + 14) – 1 = 29 – 1 = 28
Principle #7:
To determine the minimum number of members in the group, the formula is as follows:
The Minimum number of persons = Sum of positions of persons from both sides – Persons between them – 2.
Example: If the position of A from the left side of a row is 15th and position of B from the right side of a row is 19th and only 1 person is sitting in the middle of A & B. Find the minimum number of persons that can be seated in this row?
Sol:
The total number of persons = 15 + 19 – 1 – 2 = 31.
Aspirants preparing for different competitive exams can out the video explanation of Sequencing, Order and Comparison below. It will help to understand the basing concept and strategies to take such questions in the examination even better.
|
46 videos|95 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Ranking - Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude for UGC NET
| 1. What is the CAT exam? |  |
| 2. How often is the CAT exam conducted? |  |
| 3. What is the eligibility criteria for the CAT exam? |  |
| 4. How can I register for the CAT exam? |  |
| 5. What is the exam pattern and duration of the CAT exam? |  |
















