Past Year Questions: Fluid Statics | Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Fluid pressure and Its measurement
Q.1. A cube of side 100mm is placed at the bottom of an empty container on one of its faces. The density of the material of the cube is 800 kg/m3. Liquid of density 1000 kg/m3 is now poured into the container. The minimum height to which the liquid needs to be poured into the container for the cube to just lift up is _____ mm.
[2019 : 2 Marks, Set-1]
Ans. Given, side of cu be (a) = 100 m
Density of material of cube = 800 kg/m3
Poured liquid density = 1000 kg/m3
Now, Minimum height to which the liquid needs to be poured into the container for the cube to just lift up, should satisfy the condition
FB ≥ (mg)block
ρfgVfd ≥ ρV)block x g
1000 x 0.1 x 0.1 x h ≥ 800 x 0.1 x 0.1 x 0.1
h ≥ 0.08 m
h ≥ 80 mm
Q.2. For the stability of a floating body the
[2017 : 1 Mark, Set-2]
(a) centre of buoyancy must coincide with the centre of gravity
(b) centre of buoyancy must be above the centre of gravity
(c) centre of gravity must be above the centre of buoyancy
(d) metacentre must be above the centre of gravity
Ans. d
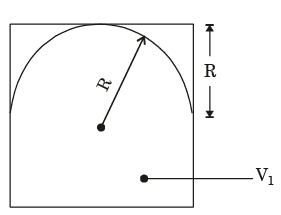
Q.3. Consider a frictionless, massless and leak-proof plug blocking a rectangular hole of dimensions 2R × L at the bottom of an open tank as shown in the figure. The head of the plug has the shape of a semi-cylinder of radius R. The tank is filled with a liquid of density ρ up to the tip of the plug.
The gravitational acceleration is g. Neglect the effect of the atmospheric pressure.
[2016 : 2 Marks, Set-1]
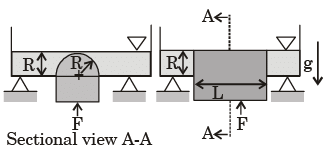
The force F required to hold the plug in its position is
(a) 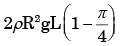
(b) 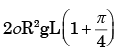
(c) ρR2δgL
(d) π/2ρR2gL
Ans. a
Solution:
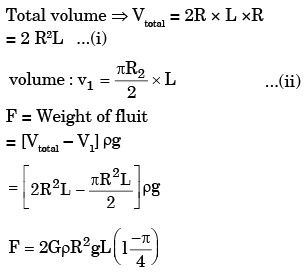
Q.4. An inverted U-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure difference between two pipes A and B, as shown in the figure. Pipe A is carrying oil (specific gravity = 0.8) and pipe B is carrying water. The densities of air and water are 1.16 kg/ m3 and 1000 kg/m3, respectively. The pressure difference between pipes A and B is________kPa.
Acceleration due to gravity: g = 10 m/s2
[2016 : 2 Marks, Set-1]
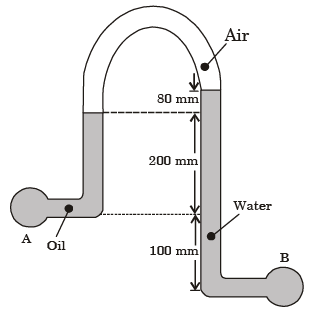
Ans.
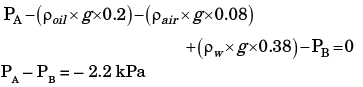
Q.5. For a floating body, buoyant force acts at the
[2016 : 1 Mark, Set-1]
(a) centroid of the floating body
(b) center of gravity of the body
(c) centroid of the fluid vertically below the body
(d) centroid of the displaced fluid
Ans. d
Solution: For floating body Buoyancy force acts through the center of buoyancy which is C.G for displaced volume.
Q.6. The large vessel shown in the figure contains oil and water. A body is submerged at the interface of oil and water such that 45 percent of its volume is in oil while the rest is in water.
The density of the body is _______ kg/m3.
The specific gravity of oil is 0.7 and density of water is 1000 kg/m3.
Acceleration due to gravity: g = 10 m/s2. [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-2]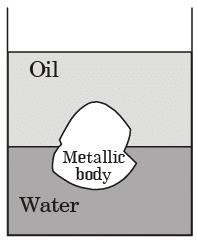
Ans. 865
Solution: ρbxg.V = ρoil x g x 0.45 V + ρwater x g x 0.55 V
⇒ ρb = 865 kg/m3
Q.7. The difference in pressure (in N/m2) across an air bubble of diameter 0.001 m immersed in water (surface tension = 0.072 N/m) is_____.
[2014 : 1 Mark, Set-2]
Ans.
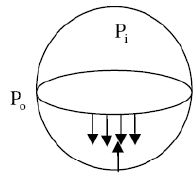
Surface tension in a bubble = Δp.r/4
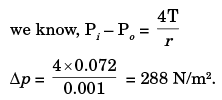
Q.8. For a completely submerged body with centre of gravity G and centre of buoyancy B, the condition of stability will be
[2014 : 1 Mark, Set-1]
(a) G is located below B
(b) G is located above B
(c) G and B are coincident
(d) Independent of the locations of G and B
Ans. a
Solution:
Q.9. An aluminium alloy (density 2600 kg/m 3) casting is to be produced. A cylindrical hole of 100 mm diameter and 100 mm length is made in the casting using sand core (density 1600 kg/m3). The net buoyancy force (in Newton) acting on the core is _______. [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-1]
Ans. d = 1600 kg/m3
ρ = 2600 kg/m3
Net buouancy force = weight of liquid displaced - weight of solid body
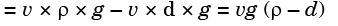
= π/4d2 L × g (ρ - d)
= π/4 × 0.12 × 0.1 × 9.81 (2600 – 1600) = 7.7 N.
Q.10. A spherical balloon with a diameter of 10 m, shown in the figure below is used for advertisements. The balloon is filled with helium (RHe = 2.08 kJ/kgK) at ambient conditions of 15°C and 100 kPa. Assuming no disturbances due to wind, the maximum allowable weight (in Newton) of balloon material and rope required to avoid the fall of the balloon (Rair = 0.289 kJ/kgK) is_______.
[2014 : 2 Marks, Set-2]
Ans.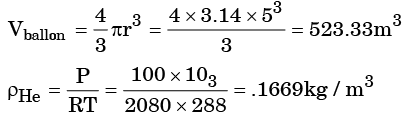
Total mass = .1669 × 523.33 = 87.36 kg
mass of air:
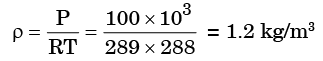
Mass of displaced volume of air
= 1.2 × 523.33 = 628 kg
Net Buoyant mass = 628 – 87. 36 = 540.64 kgl
Allowable Mass, Mallowable = 540.64 × 9.81 = 5303.67 N
Q.11. A hinged gate of length 5 m, inclined at 30° with the horizontal and with water mass on its left, is shown in figure below. Density of water is 1000 kg/m3. The minimum mass of the gate in kg per unit width (perpendicular to the plane of paper), required to keep it closed
[2013 : 2 Marks]
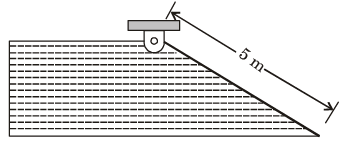
(a) 5000
(b) 6600
(c) 7546
(d) 9623
Ans. c
Solution:
Given data
l = 5 m
θ = 30°
ρ = 1000 kg/m3
h = 2.5 sin 30° = 1.25m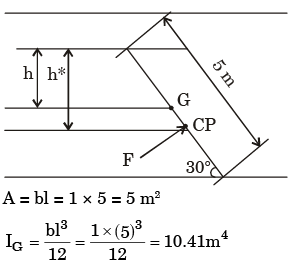
F = ρgAh = 1000 x 9.81 x 5 x 1.25 = 61312.5N
Q.12. A large tank with a nozzle attached contains three immiscible, inviscid fluids as shown. Assuming that the changes in h1, h2 and h3 are negligible, the instantaneous discharge velocity is
[2012 : 2 Marks]
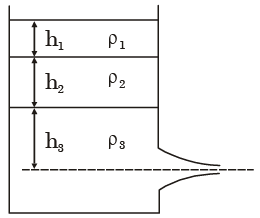
(a) 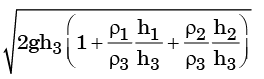
(b) 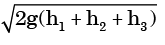
(c) 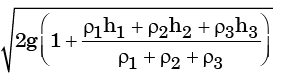
(d) 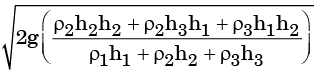
Ans. a
Solution: Applying Bernoulli’s equation at exit, we get
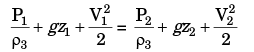
We know Z1 = Z2, V1 = 0 & P2 = Patm
Hence it reduce to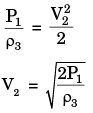
But P1 = ρ1gh1 + ρ2gh2 + ρ3gh3
Upon substituting, we get
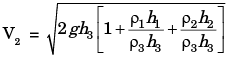
Q.13. For the stability of a floating body, under the influence of gravity alone, which of the following is TRUE?
[2010 : 1 Mark]
(a) Metacenter should be below centre of gravity.
(b) Metacenter should be above centre of gravity.
(c) Metacenter and centre of gravity must lie on the same horizontal line.
(d) Metacenter and centre of gravity must lie on the same vertical line.
Ans. b
Solution: For stable floating body metacentre should be above centre of gravity.
For unstable floating body, metacentre should be below centre of gravity.
For neutral equilibrium, both metacentre and centre of gravity should coincide.
Q.14. Oil in a hydraulic cylinder is compressed from an initial volume 2m3 to 1.96 m3. If the pressure of oil in the cylinder changes from 40 MPa to 80 MPa during compression, the bulk modulus of elasticity of oil is
[2007 : 2 Marks]
(a) 1000 MPa
(b) 2000 MPa
(c) 4000 MPa
(d) 8000 MPa
Ans. b
Solution:
Bulk modules of elasticity, 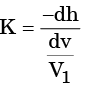
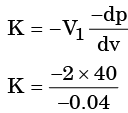
K = 2000 MPa
Q.15. The pressure gauges G1 and G2 installed on the system show pressure of ρG1 = 5.00 bar and ρG2 = 1.00 bar. The value of unknown pressure P is [Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 bar]
[2004 : 2 Marks]
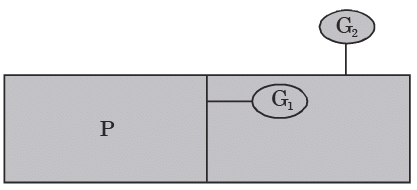
(a) 1.01 bar
(b) 2.01 bar
(c) 5.00 bar
(d) 7.01 bar
Ans. d
Solution:
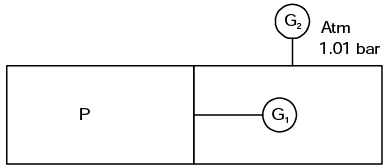
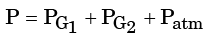
P = 5 + 1 + 1.01 = 7.01 bar
Q.16. A closed cylinder having a radius R and height H is filled with oil of density ρ. If the cylinder is rotated about its axis at an angular velocity of ω, the thrust at the bottom of the cylinder is
[2004 : 2 Marks]
(a) πR2rgH
(b)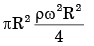
(c) πR2(rw2R2 + ρgH)
(d)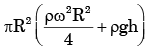
Ans. d
Solution: We know that
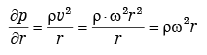 [∵ v = ω × r]
[∵ v = ω × r]
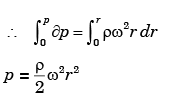
Area of circular ring = 2πrdr
Force on elementry ring
= Intensity of pressure × Area of ring

∴ Total force on the top of the cylinder
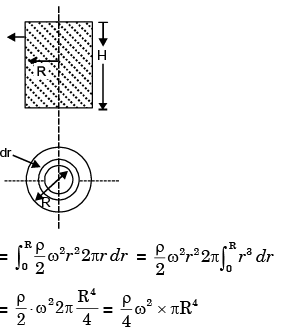
Thrust at the bottom of the cylinder
= Weight of water in cylinder + Total force on the top of cylinder
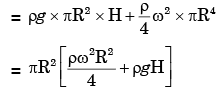
Q.17. A cylindrical body of cross-sectional area A, height H and density ρs, is immersed to a depth h in a liquid of density ρ, and tied to the bottom with a string. The tension in the string is ____.
[2003 : 1 Mark]
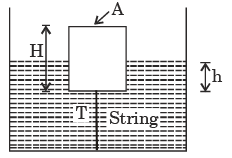
(a) ρghA
(b) (ρs - p)ghA
(c) (ρ - ρs)ghA
(d) (ρh - ρsH)gA
Ans. d
Solution: Let T = Tension in string
T1 = Mg = Buoyancy force
T + ρsH.A.g = ρ.h A.g
∴ T = g.A(ρh - ρs.H)
Q.18. A static fluid can have
[2001 : 1 Mark]
(a) Non-zero normal and shear stress
(b) Negative normal stress and zero shear stress
(c) Positive normal stress and zero shear stress
(d) Zero normal stress and non-zero shear stress
Ans. c
Q.19. The horizontal and vertical hydrostatic forces Fx and Fy on the semicircular gate, having a width w into the plane of figure, are
[2001 : 2 Marks]
(a) Fx = ρghrw and Fy = 0
(b) Fx = 2ρghrw and Fy = 0
(c) Fx = ρghrw and Fy = ρgwr2
(d) Fx = 2ρghrw and Fy = πρgwr2/2
Ans. d
Solution: Fx = 2rghrw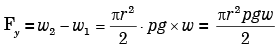
Q.20. In given figure, if the pressure of gas in bulb A is 50 cm Hg vacuum and patm = 76 cm Hg, then height of column H is equal to
[2000 : 2 Marks]
(a) 26 cm
(b) 76 cm
(c) 50 cm
(d) 126 cm
Ans. c
Solution:
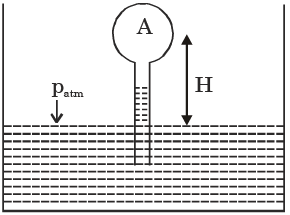
PA = 50 cm Hg vacuum = pH
Q.21. Refer to figure, the absolute pressure of gas A in the bulb is
[1997 : 2 Marks]
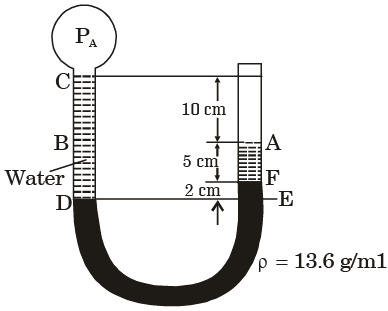
(a) 771.2 mm Hg
(b) 767.35 mm Hg
(c) 752.65 mm Hg
(d) 748.8 mm Hg
Ans. a
Solution: Patm = 760 mm Hg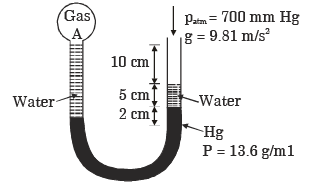
Let PA be the absolute pressure at 'A'
Pressure at D = Pressure at E
or PA + PCD = Patm + PAF + PFE
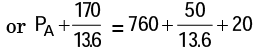
PA= 771.2 mm Hg
Q.22. A mercury manometer is used to measure the static pressure at a point in a water pipe as shown in figure. The level difference of mercury in the two limbs is 10 mm. The gauge pressure at that point is
[1996 : 1 Mark]
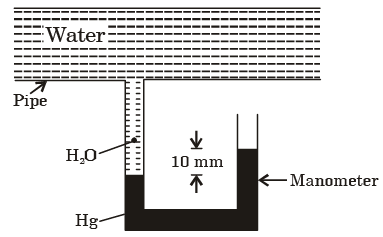
(a) 1236 Pa
(b) 1333Pa
(c) Zero
(d) 98 Pa
Ans. a
Solution: Gauge pressure = (δm - δw)gh
= (13600 - 1000) × 9.81 × 10 × 10-3 = 1236 Pa
Q.23. The force F needed to support the liquid of density ρ and the vessel on top (fig.) is
[1995 : 2 Marks]
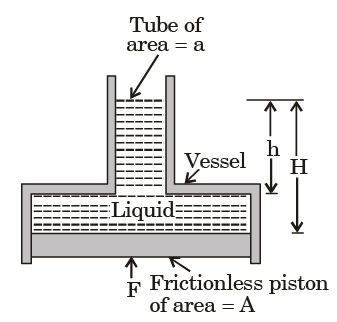
(a) ρg[ha-(H-h)A
(b) ρgHa
(c) ρgHA
(d) ρg(H-h)A
Ans. c
Solution:
Height of water column over plate is H.
F = P × A = ρgHA
Q.24. Bodies in flotation to be in stable equilibrium the necessary and sufficient condition is that the centre of gravity is located below the ____.
[1994 : 1 Mark]
Ans. Located below the metacentre.
Q.25. Shown below are three cylindrical gates which restrain water in a 2–D Channel. Which gate experiences the maximum vertical component, the minimum vertical component and the maximum horizontal component of the hydrostatic force?
[1993 : 1 Mark]
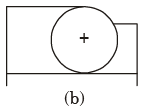
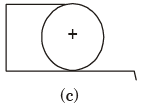
Ans. A → Experiences Maximum vertical hydrostatic force component
B → Experiences Maximum horizontal hydrostatic force component
C → Experiences minimum vertical component of force
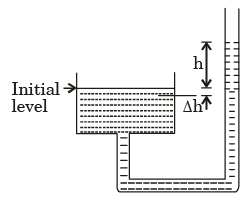
Q.26. The cross-sectional area of one limb of a U-tube manometer (figure shown below) is made 500 times larger than the other, so that the pressure difference between the two limbs can be determined by measuring h on one limb of the manometer. The percentage error involved is
[1990 : 2 Marks]
(a) 1.0
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.2
(d) 0.05
Ans. c
Solution: Fall in larger limb = Rise in smaller limb
A1 Δh = A2h
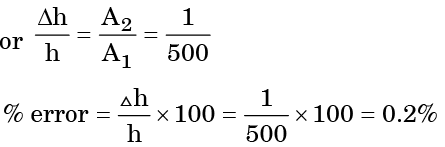
Q.27. A circular plate 1 m in diameter is submerged vertically in water such its upper edge is 8 m below the free surface of water. The total hydrostatic pressure force on one side of plate is
[1988 : 2 Marks]
(a) 6.7 kN
(b) 65.4 kN
(c) 45.0 kN
(d) 77.0 kN
Ans. b
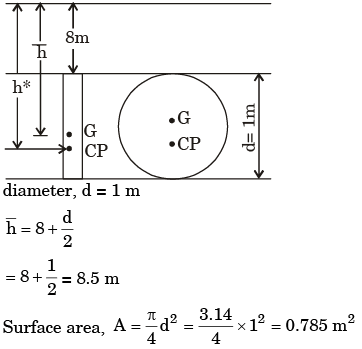
Total hydrostatic pressure force, F = ρghA
F = 1000 × 9.81 × 8.5 × 0.785 = 65458 N
or
F = 65.45 KN
|
54 videos|127 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Fluid Statics - Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is fluid statics in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How is fluid pressure calculated in fluid statics? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of fluid statics in civil engineering? |  |
| 4. How is buoyancy force determined in fluid statics? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of fluid statics in civil engineering design? |  |
















