Past Year Questions: Hydrostatic Forces | Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A 5 m × 5 m closed tank of 10 m height contains water and oil, is connected to an overhead water reservoir as shown in the figure. Use = 10kN/m3 and specific gravity of oil = 0.8. [2024, Set-I]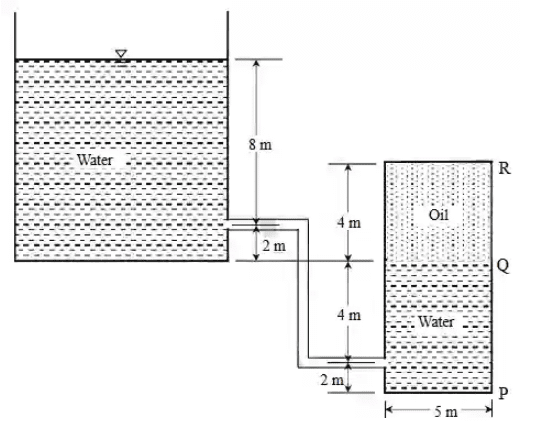
The total force (in kN) due to pressure on the side PQR of the tank is ______ (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Ans: 5575 to 5585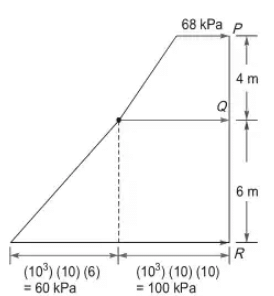 PP + (800)(10)(4) = (103)(10)(10), where Pp is pressure at P
PP + (800)(10)(4) = (103)(10)(10), where Pp is pressure at P
PP + (32 × 103 = 100 × 103
PP = 68 × 103 Pa
PP = 68kPa
Now, force on PQR, F =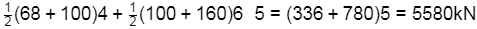
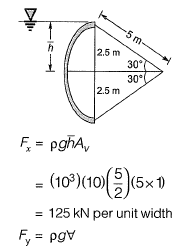
Q2: A sector gate is provided on a spillway as shown in the figure. Assuming g = 10 m/s2, the resultant force per meter length (expressed in kN/m) on the gate will be_______. [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
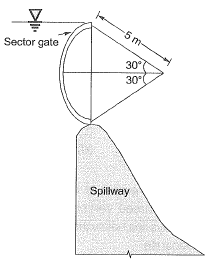
Ans:
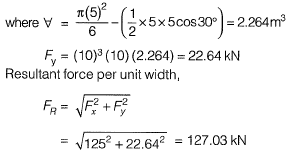
Q3: A triangular gate with a base width of 2 m and a height of 1.5 m lies in a vertical plane. The top vertex of the gate is 1.5 m below the surface of a tank which contains oil of specific gravity 0.8. Considering the density of water and acceleration due to gravity to be 1000 kg/m3 and 9.81 m/s2, respectively, the hydrostatic force (in kN) exerted by the oil on the gate is _________. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: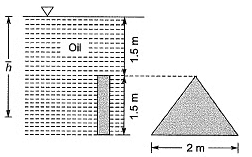
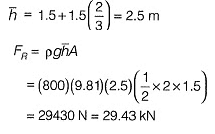
Q4: Three rigid buckets, shown as in the figures (1), (2) and (3), are of identical heights and base areas. Further, assume that each of these buckets have negligible mass and are full of water. The weight of water in these buckets are denoted as W1, W2, and W3 respectively. Also, let the force of water on the base of the bucket be denoted as F1, F2, and F3 respectively. The option giving an accurate description of the system physics is [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
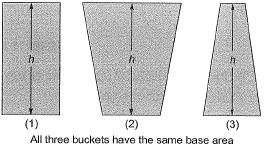
(a) W2 = W1 = W3 and F2 > F1 > F3
(b) W2 > W1 > W3 and F2 > F1 > F3
(c) W2 = W1 = W3 and F1 = F2 = F3
(d) W2 > W1 > W3 and F1 = F2 = F3
Ans: (d)
Bucket → identical height → identical base area
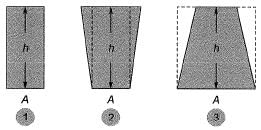
⇒ w2> w1> w3
Force on the base in each case will be equal to = 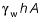
Hence, F1 = P2 = F3
|
54 videos|127 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Hydrostatic Forces - Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is hydrostatic force? |  |
| 2. How is hydrostatic force calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the principle of buoyancy? |  |
| 4. How does the shape of an object affect hydrostatic force? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of hydrostatic forces? |  |
















