MANAGEMENT OF SPORTING EVENTS Chapter Notes | Physical Education Class 12(XII) - Notes & Model Test Papers - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Introduction
Managing sports events involves a series of structured activities designed to ensure smooth and successful conduct. It requires careful planning, efficient organization, proper staffing, clear direction, and effective control. This unit will guide you through the essential functions of sports event management, the formation and responsibilities of various committees, procedures for organizing tournaments, and the significance of intramural, extramural, and community sports.
Functions of Sports Events Management
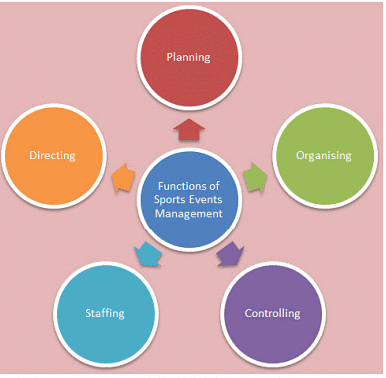
Planning
- Definition: Planning is the process of setting goals, developing strategies, and outlining tasks and schedules to achieve the goals.
- Importance: Planning ensures that events run smoothly, effectively, and without conflicts. It is the most crucial function as it lays the foundation for all other management activities.
- Elements:
- Specificity: Plans should be clear and precise.
- Logical Sequence: Steps should follow a logical order.
- Flexibility: Plans should be adaptable to changes.
- Comprehensiveness: Plans should cover all aspects of the event.
- Role in Sports Events: Effective planning ensures that the event runs smoothly by clearly defining aims, goals, and objectives. It includes setting the timeline, budget, and all necessary arrangements to achieve the desired outcome.
Organising
- Definition: Organising involves arranging resources and tasks to achieve the goals set in the planning stage.
- Key Activities:
- Distributing resources efficiently to various tasks.
- Organising personnel into teams or committees with specific roles.
- Creating organisational charts to define the hierarchy and reporting structure.
- Role in Sports Events: Ensures that all necessary resources and personnel are in place and know their roles. It involves coordinating different departments, such as logistics, technical, and finance, to work together seamlessly.
Staffing
- Definition: Staffing is the process of identifying and recruiting the necessary personnel.
- Activities:
- Recruitment and selection of qualified staff for various roles.
- Orientation to introduce new employees to the event's goals and procedures.
- Training and professional development to equip staff with the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Role in Sports Events: Ensures that qualified and trained personnel are available to carry out the tasks required for the event. This function is crucial for maintaining the quality and efficiency of the event.
Directing
- Definition: Directing involves guiding and motivating personnel to perform their tasks effectively.
- Activities:
- Supervision of tasks and personnel to ensure everything is on track.
- Providing guidance and inspiration to boost morale and productivity.
- Giving instructions to achieve organizational goals and addressing any issues that arise.
- Role in Sports Events: Ensures that all personnel know what to do and are motivated to do their best. Effective direction fosters a positive work environment and encourages teamwork.
Controlling
- Definition: Controlling involves monitoring performance to ensure that goals are being met.
- Activities:
- Establishing performance standards to measure success.
- Measuring actual performance against these standards.
- Comparing performance with standards and making necessary adjustments to improve efficiency.
- Role in Sports Events: Ensures that the event stays on track and any issues are promptly addressed. It involves continuous monitoring and evaluation to achieve the desired outcomes.
Formation of Committees
To organise any sports event effectively, various committees are formed. These committees ensure the smooth and systematic conduct of events. The formation of committees is based on three levels of management: top, middle, and lower levels. Depending on the level and area of the sports event, suitable people are chosen to staff these committees.
Types of Committees
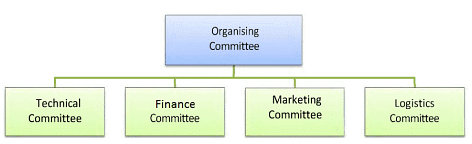
Technical Committee
- Pre-event:
- Procures sports equipment, ensuring that all necessary items are available and in good condition.
- Confirms officials like referees, umpires, and judges to oversee the event.
- Prepares fixtures, determining the schedule and matchups for the event.
- Sets rules and regulations to ensure fair play and safety.
- During event:
- Conducts matches according to the schedule.
- Ensures the presence of officials to enforce rules and make decisions.
- Collects score sheets and other related documents.
- Maintains the field or venue to ensure it is in optimal condition.
- Post-event:
- Cleans and maintains fields to prepare them for future use.
- Stores equipment properly to ensure it remains in good condition for future events.
Logistics Committee
- Pre-event:
- Arranges transportation for participants, officials, and equipment.
- Organizes lodging and refreshments for participants and officials.
- Sends invitations to participants, officials, and guests.
- Prepares first aid kits and medical facilities to ensure the safety of all participants.
- During event:
- Manages opening, closing, and award ceremonies.
- Handles registration of participants and officials.
- Distributes refreshments during the event.
- Controls spectators to ensure a safe and orderly environment.
- Post-event:
- Supervises cleaning of the venue.
- Manages the storage of items used during the event.
Finance Committee
- Pre-event:
- Prepares the budget, estimating all costs and revenues associated with the event.
- Finalizes sponsorship agreements to secure funding.
- Purchases equipment and other necessary items.
- Settles agreements with sponsors, ensuring all terms are clear and agreed upon.
- During event:
- Manages financial inflows and outflows, ensuring all transactions are tracked.
- Pays officials and other staff members as agreed.
- Post-event:
- Settles all bills and outstanding payments.
- Prepares financial reports to evaluate the financial success of the event.
Marketing Committee
- Pre-event:
- Develops strategies for sponsorship and publicity to promote the event.
- Arranges meetings with potential sponsors to secure funding and support.
- Prepares agreements with sponsors, outlining the terms and benefits of sponsorship.
- During event:
- Issues press releases to keep the media and public informed about the event.
- Manages media relations to ensure positive coverage.
- Fulfills sponsorship agreements, ensuring sponsors receive the agreed-upon benefits.
- Post-event:
- Continues publicity efforts to maintain interest and support for future events.
- Evaluates media coverage to assess the effectiveness of the marketing strategies.
Fixtures & Its Procedures
In sports, fixtures refer to the arrangement and scheduling of matches in a tournament. The way these fixtures are set up can impact the progression and elimination of teams or players. Different tournaments employ various types of fixtures based on factors like duration, cost, manpower, level of competition, and audience interest.
Tournaments
A tournament is a series of games or matches played among players or teams to determine the winner. Tournaments provide opportunities to demonstrate skills, evaluate performance, motivate players, attract audiences, and provide healthy entertainment.
Types of Tournaments
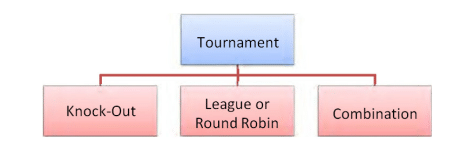
Knock-Out Tournament
- Definition: In a Knock-Out Tournament, a player or team continues to play matches until it is defeated. Once a team loses, it is eliminated from the tournament.
- Characteristics:
- Players or teams must consistently perform well to avoid elimination.
- This format saves cost and time and makes each match intensive due to the fear of elimination.
- Fixtures are drawn based on lots, which can result in early matches between two strong teams.
- A good team can be eliminated early due to chance or accident.
- Pros:
- Cost-effective and time-efficient.
- High intensity and excitement in each match.
- Cons:
- Potential for strong teams to be eliminated early.
- Less opportunity for teams to recover from a single loss.
League or Round Robin Tournament
- Definition: In a League or Round Robin Tournament, each player or team plays a predetermined number of matches against all other participants.
- Characteristics:
- Fixed number of matches are scheduled before the start of the tournament.
- Each team gets an equal chance to play against every other team.
- The true winner emerges from this format, and a ranking can be prepared for all participants.
- This format requires more money, time, and facilities compared to the Knock-Out Tournament.
- There is no provision for seeding extraordinary teams or players.
- Pros:
- Ensures equal opportunity for all teams.
- Provides a clear ranking of teams based on performance.
- Cons:
- More expensive and time-consuming.
- Requires extensive facilities.
Combination Tournament
- Definition: Combination Tournaments integrate elements of both Knock-Out and League formats.
- Characteristics:
- These tournaments can be designed as Knockout-League, League-Knockout, Knockout-League-Knockout, etc.
- Suitable for large numbers of participants or when participants are spread across different areas.
- Venues may be in different zones or places.
- This format eliminates some demerits of pure Knockout and League Tournaments.
- Pros:
- Balances the advantages of both Knock-Out and League formats.
- Suitable for large-scale and geographically diverse tournaments.
- Cons:
- Complex to organize and manage.
- Requires detailed planning and coordination.
Fixtures, Byes, and Seeding
Fixtures
Fixtures are the systematic scheduling of matches or events in a tournament. They determine which teams or participants will compete against each other at specific times and venues.
Importance of Fixtures:
- Ensures an organized and orderly conduct of the tournament.
- Helps in managing time efficiently.
- Provides clarity to participants, officials, and spectators about the schedule.
- Ensures fair play by systematically rotating teams and participants.
Types of Fixtures:
- Knock-Out Fixtures: Teams are eliminated after a single loss.
- League Fixtures: All teams play against each other, and the team with the most points wins.
- Combination Fixtures: Combines elements of both knock-out and league formats.
Byes
Byes are given to teams or participants to automatically advance them to the next round without competing in the initial round(s). This is usually done when the number of participants is not a power of 2.
Purpose of Byes:
- To ensure that the number of teams progresses smoothly through the rounds.
- To balance the brackets when the number of participants is not even.
Allocating Byes:
- Determine Total Number of Byes Needed: Subtract the nearest lower power of 2 from the total number of teams.
- For example, if there are 14 teams, the nearest lower power of 2 is 8. Therefore, the number of byes needed is 14 - 8 = 6.
- Distribute Byes Fairly: Allocate byes in the first round to balance the brackets.
Procedure for Allocating Byes:
- Identify the total number of teams.
- Calculate the nearest lower power of 2.
- Subtract the nearest power of 2 from the total number of teams to find the number of byes.
- Allocate byes to the required number of teams.
Seeding
Seeding is the process of arranging teams or participants in a tournament based on their rankings or past performances. This ensures that the strongest teams or participants do not meet in the early rounds, thereby making the competition more exciting and fair.
Purpose of Seeding:
- To ensure that top-ranked teams do not face each other in the initial rounds.
- To maintain interest in the tournament by ensuring that stronger teams advance to the later stages.
- To provide a fair and balanced competition.
Procedure for Seeding:
- Rank the Teams: Based on previous performances, rankings, or qualifications.
- Place Seeds in the Draw: The highest-seeded team is placed in position 1, the second-highest in position 2, and so on, ensuring they are placed in opposite halves or quarters of the draw.
- Adjust for Byes: If byes are needed, ensure they are allocated such that seeded teams are not disadvantaged.
Example of Seeding and Byes Allocation:
- If there are 10 teams, the nearest lower power of 2 is 8, so 10 - 8 = 2 byes are needed.
- Rank the teams from 1 to 10 based on performance.
- Place the top 2 seeds such that they are in opposite halves.
- Allocate the byes to the lower-ranked teams in the first round to balance the draw.
Seeding Benefits:
- Fair Competition: Ensures that stronger teams have a better chance of progressing based on merit.
- Audience Engagement: Keeps the audience engaged by having stronger teams potentially face off in the later rounds.
- Balanced Matches: Prevents early elimination of strong teams, maintaining the quality of competition throughout the tournament.
Procedure for Drawing Knock-Out Fixture
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Teams
- Identify the total number of teams that will participate in the knockout tournament.
- If the number of teams is a power of two (e.g., 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, etc.), there is no need for byes.
- If the number of teams is not a power of two, byes will be given according to the draw of lots.
Examples:
- If there are 8 teams, no byes are needed.
- If there are 15 teams, byes will be required.
Step 2: Determine the Total Number of Matches
- Use the formula: Total Number of Matches = Number of teams - 1
- This formula does not include a third-place match.
Examples:
- For 8 teams: 8 - 1 = 7 matches.
- For 12 teams: 12 - 1 = 11 matches.
- For 15 teams: 15 - 1 = 14 matches.
Step 3: Divide Teams into Upper and Lower Halves
- Even Number of Teams: Divide the total number of teams by 2 to get the number of teams in each half.
- Formula: Number of teams / 2 = Teams in Upper Half or Lower Half
- Example: For 12 teams: 12 / 2 = 6 (6 teams in Upper Half and 6 teams in Lower Half).
- Odd Number of Teams: Adjust the formula to account for the odd number.
- Formulas:
- (Number of teams + 1) / 2 = Teams in Upper Half
- (Number of teams - 1) / 2 = Teams in Lower Half
- Example: For 15 teams:
- (15 + 1) / 2 = 8 Teams in Upper Half
- (15 - 1) / 2 = 7 Teams in Lower Half
- Formulas:
Step 4: Allocate Byes
- Calculate the difference between the number of participating teams and the next higher power of 2.
- Example: For 12 teams, the next power of 2 is 16. Thus, 16 - 12 = 4 byes.
- Distribution of Byes:
- Even Number of Byes: Divide the byes equally between the upper and lower halves.
- Example: For 4 byes: 4 / 2 = 2 byes in each half.
- Odd Number of Byes: Allocate one additional bye to the lower half.
- Formulas:
- (Total byes - 1) / 2 = Byes in Upper Half
- (Total byes + 1) / 2 = Byes in Lower Half
- Example: For 13 byes:
- (13 - 1) / 2 = 6 byes in Upper Half
- (13 + 1) / 2 = 7 byes in Lower Half
- Formulas:
- Even Number of Byes: Divide the byes equally between the upper and lower halves.
Step 5: Allotment of Byes
- Follow a specific order for allotting byes to ensure fairness.
- Order:
- First bye to the last team of the Lower Half.
- Second bye to the first team of the Upper Half.
- Third bye to the last team of the Upper Half.
- Fourth bye to the first team of the Lower Half.
- Repeat the pattern until all byes have been allotted.
- Order:
Alternative Order:
- First bye to the last team of the Lower Half.
- Second bye to the first team of the Upper Half.
- Third bye to the first team of the Lower Half.
- Fourth bye to the last team of the Upper Half.
- Continue this pattern for the remaining byes.
Step 6: Finalize and Draw Fixtures
- Write the serial number (number of participants) in vertical order.
- Divide into two halves as per Step 3.
- Place byes as per Step 5.
- Allocate the remaining teams through a random lottery system, placing them from top to bottom or following the same pattern used for allotting byes.
- Teams with byes will not play in the first round.
- Assign the date, time, and venue for each match in the fixture.
Illustration 1:
- Total Number of Teams: 4
- Total Number of Matches: 4 - 1 = 3
- Total Number of Byes: None (as the number is a power of two)
- Number of Teams in Upper Half: 4 / 2 = 2
- Number of Teams in Lower Half: 4 / 2 = 2
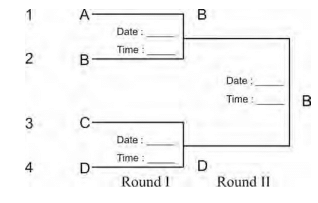
Round I Matches:
- First match: A vs. B (Winner: B)
- Second match: C vs. D (Winner: D)
Round II (Final):
- Third match: B vs. D (Winner: B)
Illustration 2:
- Total Number of Teams: 8
- Total Number of Matches: 8 - 1 = 7
- Total Number of Byes: None (as the number is a power of two)
- Number of Teams in Upper Half: 8 / 2 = 4
- Number of Teams in Lower Half: 8 / 2 = 4
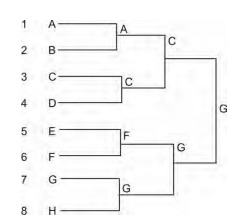
Round I Matches:
- First match: A vs. B (Winner: A)
- Second match: C vs. D (Winner: C)
- Third match: E vs. F (Winner: F)
- Fourth match: G vs. H (Winner: G)
Round II Matches:
- Fifth match: A vs. C (Winner: C)
- Sixth match: F vs. G (Winner: G)
Round III (Final):
- Seventh match: C vs. G (Winner: G)
Illustration 3:
- Total Number of Teams: 11
- Total Number of Matches: 11 - 1 = 10
- Total Number of Byes: 16 - 11 = 5
- Number of Byes in Upper Half: (5 - 1) / 2 = 2
- Number of Byes in Lower Half: (5 + 1) / 2 = 3
- Number of Teams in Upper Half: (11 + 1) / 2 = 6
- Number of Teams in Lower Half: (11 - 1) / 2 = 5
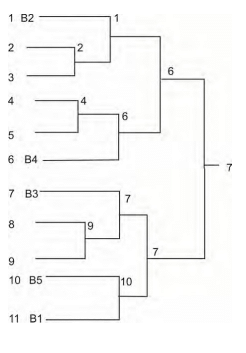
Round I Matches:
- First match: 2 vs. 3 (Winner: 2)
- Second match: 4 vs. 5 (Winner: 4)
- Third match: 8 vs. 9 (Winner: 9)
Round II Matches:
- Fourth match: 1 vs. 2 (Winner: 1)
- Fifth match: 4 vs. 6 (Winner: 6)
- Sixth match: 7 vs. 9 (Winner: 7)
- Seventh match: 10 vs. 11 (Winner: 10)
Round III (Semi-finals):
- Eighth match: 1 vs. 6 (Winner: 6)
- Ninth match: 7 vs. 10 (Winner: 7)
Round IV (Final):
- Tenth match: 6 vs. 7 (Winner: 7)
Procedure to Draw League or Round Robin Fixture:
In a League or Round Robin Tournament, each team plays once with all the remaining teams of the tournament.
Step 1: Determine the Number of Matches
- Use the formula: Total number of matches = n(n-1)/2, where n is the number of teams.
- Example:
- If there are 6 teams:
- Total matches = 6(6-1)/2 = 30/2 = 15 matches.
- If there are 7 teams:
- Total matches = 7(7-1)/2 = 42/2 = 21 matches.
- If there are 6 teams:
- Example:
Step 2: Methods to Fix Teams in League Tournament
Cyclic Method
- In the Cyclic Method, one team is fixed in position and the others are placed in rotation to complete the cycle.
Even Number of Teams
- No byes are needed.
- The number of rounds is calculated using the formula: Number of teams - 1.
- Example:
- Total number of teams: 6
- Total number of rounds: 6 - 1 = 5
- Example:
Odd Number of Teams
- One bye is given to one team each round, rotating each round.
- The number of rounds is equal to the number of teams.
- Example:
- Total number of teams: 7
- Total number of rounds: 7
- Example:
Staircase Method
- In the Staircase Method, one team is fixed on the highest step, and that team plays with all the teams in the tournament. The next team is fixed on the next step down, playing with the remaining teams, and so on.
Example:
- Total number of Teams: 7
- A vs. B
- A vs. C, B vs. C
- A vs. D, B vs. D, C vs. D
- A vs. E, B vs. E, C vs. E, D vs. E
- A vs. F, B vs. F, C vs. F, D vs. F, E vs. F
- A vs. G, B vs. G, C vs. G, D vs. G, E vs. G, F vs. G
Details of Matches:
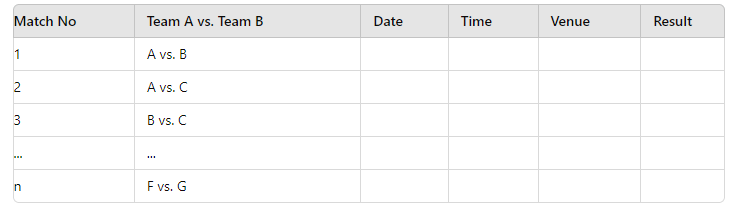
Step 3: Determining the Winner/Merit in League Tournament
- The winner or merit in a League or Round Robin Tournament is decided based on points awarded to the teams.
- Example Point System:
- Winner = 5 points
- Draw = 3 points
- Loser = 0 points
- Example Point System:
Points Tally Example:
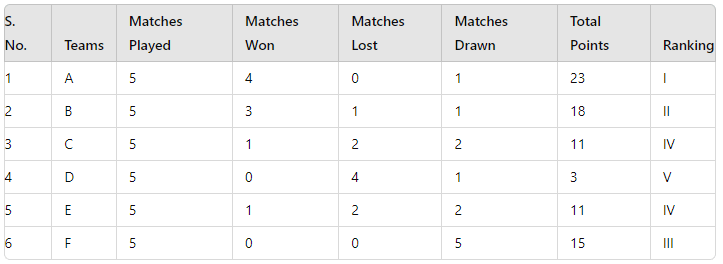
Tiebreaker Rules: Tournament organizers should frame rules for resolving ties before the start of the tournament.
Procedure to Draw Combination Fixture
Combination fixtures are a mix of Knockout and League tournaments. The steps followed are similar to those used in both Knockout and League fixtures. The process for drawing League-Knockout fixtures is outlined below:
League-Knockout
Example:
- Total Teams: 8
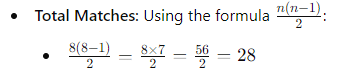
- Rounds in League: 7
League Stage
The league stage is conducted first, where each team plays against every other team in a round-robin format.
Rounds:
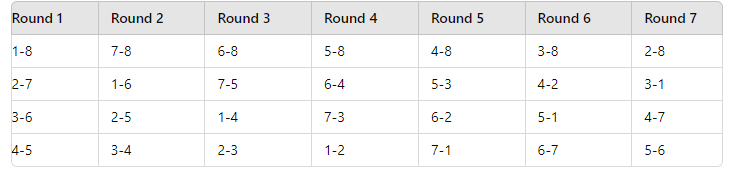
Points System:
- Winner = 5 points
- Draw = 3 points
- Loser = 0 points
Points Table Example:
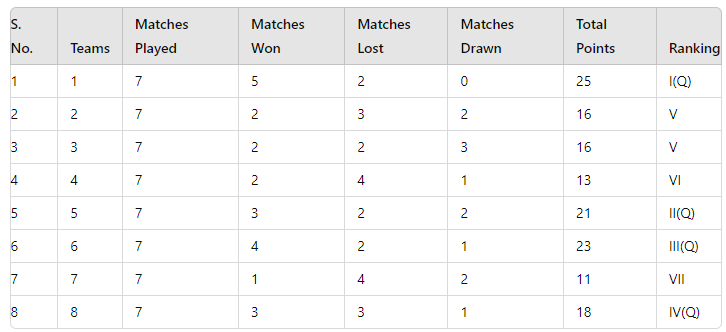
Top Four Teams: 1, 5, 6, and 8 qualify for the knockout rounds.
Knockout Stage
- The top four teams from the league stage advance to the knockout rounds.
- Tournament Committee: Forms rules regarding the placement of teams in the semifinals before the tournament. Possible patterns include:
- The first team may play with the third, and the second may play with the fourth-ranked team.
- The first-ranked team may play with the fourth, and the second-ranked team may play with the third-ranked team.
- Draw of lots.
Example Pattern:
- First Semifinal: 1 vs. 5 (Winner: 5)
- Second Semifinal: 6 vs. 8 (Winner: 8)
- Final Match: 5 vs. 8 (Winner: 8)
- Third Place Match: 1 vs. 6 (optional)
Results:
- Winner: Team 8
- Runner-up: Team 5
Example of a Major Tournament
FIFA World Cup:
- The FIFA World Cup uses a League-Knockout combination fixture.
- League Stage: The initial rounds are based on the league system, with eight groups (A to H), each consisting of four teams.
- Group Stage: Every team in a group plays against the other three teams.
- Qualification: The top two teams from each group advance to the pre-quarterfinals based on the points table.
- Knockout Stage: From the pre-quarterfinals onwards, the tournament follows a knockout format until the final.
Intramural
The word ‘intramural’ means “within the walls”. In the context of sports, it refers to a tournament conducted within the walls of a single institution, school, or community. Intramural competitions/tournaments are conducted among players of one institution. The tournament may be an event/game/more than one game and sports conducted in one day or more, or in a month or a year. Examples include Sports Day, Sports Festival, Athletics Meet, Swimming Meet, and Badminton Tournament conducted among Houses, Classes, Hostels, Residents, etc., of a school/institution.
Objectives of Intramural Tournaments
Intramurals are common and integral parts of educational organizations and communities, where teams are constituted among classes, houses, or groups, and competitions are conducted for engaging children and youth and for deriving various types of benefits for the participants.
Objectives:
- To encourage mass participation in sports in an institution.
- To focus on the all-round development of children.
- To develop values like fair play, respect, and friendship through sports.
- To provide the first opportunity to compete in a controlled environment.
- To focus on fitness, wellness, and health aspects of children.
- To promote curricular integration through sports.
- To help children develop personality (first stage of leadership, control of emotions, cooperation, etc.)
Significance of Intramural Tournaments
With all the above-discussed objectives of intramural tournaments being implemented successfully, it surely brings lots of benefits to the participants. Such competitions conducted in a controlled environment with enough scope for all-round development deliver significant advantages.
Significance:
- Selection for Extramural: Intramural Tournaments provide an opportunity to select a player or team to participate in Extramural Tournaments. Players demonstrate skill and fitness in events, which become the base for selection.
- Group Cohesion: Students from different classes or houses come together in a team, share experiences, display cooperation and coordination, and lead the team to win the game. Students from different backgrounds and communities come together, gaining self-confidence, developing social relations, and tolerance in culture.
- Professional Experience: Students become a helping hand in conducting the tournament, which gives them good experience in officiating and event management. This experience helps them in professional and personal aspects.
- Health: Intramurals help in developing a healthy and active lifestyle. Children enjoy sports events because it is a medium to display their desired skills. It contributes to the physical, mental, social, and spiritual well-being of children.
- Recreation: Joy and entertainment are the outcomes of intramural physical activities. The elements of happiness and enjoyment are always there because activities are not so competitive, which makes intramural events successful.
- Mass Participation: Such activities are meant for all the students of the institution, not only for sportspersons or players.
Extramural Tournaments
The word ‘extramural’ means “outside the boundary or walls”. In sports, Extramural Tournaments are conducted outside or beyond the walls of the organizing unit, which may be a school, college, or institution. These tournaments are held between two or more players/teams of different schools, colleges, or institutions. Examples include Zonal, Inter-District, State, National, or International Tournaments.
Objectives of Extramural Tournaments
Extramural tournaments are very popular and an essential part of educational organizations and communities, where a common team represents a school, college, or group and promotes participation or organization of various inter-institution competitions for engaging children and youth.
Objectives:
- To achieve high performance at the highest level of the tournament.
- To develop the feeling of integration with other institutions.
- To provide opportunities for choosing a career in sports.
- To promote social, cultural, and economic development through sports.
Significance of Extramural Tournaments
With all the above-discussed objectives of extramural tournaments being implemented successfully, it brings many benefits to the participants. Participation and organization of such inter-competitions focus on showcasing talent and exploring potentials among talented athletes.
Significance:
- Progression in Performance: Extramural Tournaments help to lift the level of performance as athletes and sportspersons gain experience, learn to prepare tactics and strategies, and develop fitness and psychological preparation.
- Psychological Factors: Extramural events help balance psychological factors like stress, confidence, self-esteem, emotions, and promote qualities like leadership and team building in students.
- Level of Fitness: As the level of the tournament increases, the level of fitness improves, making an individual physically and mentally strong to compete at higher levels.
- Socialization: Such tournaments held among different communities, regions, and countries increase cross-cultural exchange and inter-community association, allowing individuals to know and understand different places and cultures, leading to closer ties.
Community Sports
Community sports events should be held at residential societies, villages, cities, schools where the purpose is not only to demonstrate the skills and abilities of children, but create harmony among people of all age groups including of senior citizens, women and differently-abled population.
Types of Community Sports Event
The various important specific programs are:-
Sports Day–
A. School–Annual Sports Day
B. NATIONAL SPORTS DAY
Health Run: These are organized by health departments to ameliorate the standard of health in a country along with raising funds for charity.
Run For Fun: It is also organised to spread the message among masses to remain healthy and fit. It may be organised to motivate the people to remain fit.
Run For Unity: It is organised to show unity and peace among the people of different religions. Its purpose may be national and international integration and brotherhood.
Run For Specific Cause: This is the run related to specific or noble cause. Most of the social non- profit organizations organise these runs for creating awareness about AIDS, Educating the girl child, Cancer, etc.Mumbai and Chennai Marathons are organised for such a noble purpose.
Games and Sports :
Different games and sports events can be organized with the aim of wholesome development of the community.
Indigenous Games: Indigenous games like kho-kho, kabaddi, marbles, Gilli danda, etc., may be introduced to keep people familiar with the cultural heritage of the nation.
|
12 videos|72 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on MANAGEMENT OF SPORTING EVENTS Chapter Notes - Physical Education Class 12(XII) - Notes & Model Test Papers - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the key functions of sports events management? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of committees involved in sports events management? |  |
| 3. How are fixtures determined and what procedures are followed in sports events management? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of tournaments commonly organized in sports events management? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of seeding and byes in sports events management? |  |

















