Power Flow in Synchronous motor | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Losses in Synchronous Motor |

|
| Copper Losses or I2R Losses |

|
| Core Losses |

|
| Mechanical Losses |

|
| Miscellaneous Losses |

|
| Power Flow in a Synchronous Motor |

|
Losses in Synchronous Motor
The losses that occur in a synchronous motor can be divided into the following categories −
Copper Losses or I2R Losses
Copper losses or I2R losses occur in the armature winding and rotor winding of the motor. These losses occur due to the resistance of the windings.
Core Losses
Core losses or iron losses occur in the iron parts of the synchronous motor. The core losses in the motor occur because the various iron parts of the machine are subjected to the varying magnetic field. The core losses consist of eddy current loss and hysteresis loss.
Mechanical Losses
In the synchronous motor, there are two types of mechanical losses viz. friction losses and windage losses. The friction losses occur due to the friction in the moving parts such as bearings etc. while the windage losses occur due to the friction between the moving parts of the machine and the air inside the motor’s casing.
Miscellaneous Losses
All the losses in the synchronous motor which cannot be easily accounted for are known as miscellaneous losses.
Power Flow in a Synchronous Motor
The input power (Pi) in a synchronous Motor is electrical in nature. There occurs armature copper loss in the resistance of the armature winding. If the armature copper losses are subtracted from the input power, then we get the mechanical power (Pm) developed by the motor.
Further, core losses (i.e., eddy current and hysteresis losses) and mechanical losses (i.e., friction and windage losses) occur in the motor due to rotation of the moving parts. Thus, if the core losses and mechanical losses are subtracted from the developed mechanical power, then we get the mechanical power output (Po) of the synchronous motor. This output power is available at the shaft of the synchronous motor.
The power flow diagram of the synchronous motor is shown in Figure-1.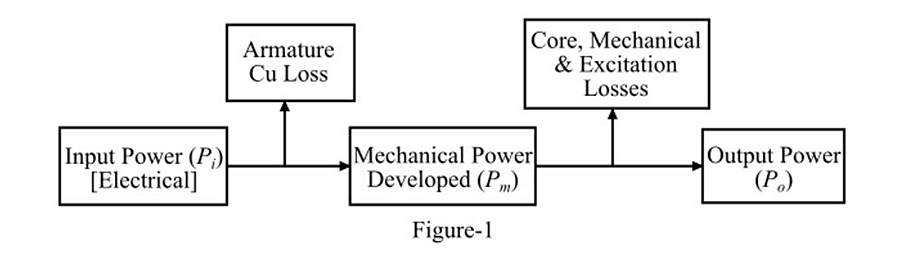
Consider an under-excited synchronous motor (i.e.,Ef<V) driving a mechanical load. Figure-2 shows the per phase phasor diagram of the motor.
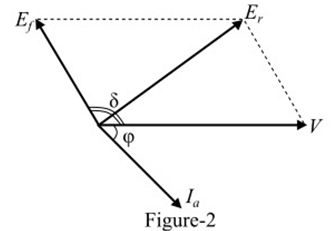
As the synchronous motor is under-excited, thus it being operating at a lagging power factor cosφ. Also, in practice,XS>>Ra, therefore, the armature current (Ia) lags the resultant voltage (Er)by about 90°. As we know, the input power to the synchronous motor is electrical while the output power is mechanical. Hence, the power flow equations of a synchronous motor are given as follows: Input power per phase, 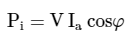 Mechanical power developed,
Mechanical power developed,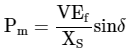
Armature Cu loss per phase 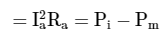
Output power per phase, 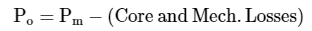
|
19 videos|124 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Power Flow in Synchronous motor - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the different types of losses in a synchronous motor? |  |
| 2. What are copper losses in a synchronous motor? |  |
| 3. What are core losses in a synchronous motor? |  |
| 4. What are mechanical losses in a synchronous motor? |  |
| 5. What are miscellaneous losses in a synchronous motor? |  |















