Power in an AC Circuit | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
7. Power in an AC circuit
In case of a steady current the rate of doing work is given by,
P = Vi
In an alternating circuit, current and voltage both vary with time, so the work done by the source in time interval dt is given by
dW= Vidt
Suppose in an ac, the current is leading the voltage by an angle φ. Then we can write,
V = V0 sinωt
and i = i0 sin(ωt + φ)
dW = V0i0 sin ωt sin (ωt + φ) dt
= V0 i0 (sin2 ωt cos f + sinωt cos ωt sin φ) dt
The total work done in a complete cycle is
W = V0i0 cos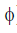
+ V0i0sin
+
=
The average power delivered by the source is, therefore,
P = =
=
= Vrms irms cos φ
or <P>one cycle = Vrms irms cos φ
Here, the term cos φ is known as power factor.
It is said to be leading if current leads voltage, lagging if current lags voltage. Thus, a power factor of 0.5 lagging means current lags the voltage by 60° (as cos-10.5 = 60°). The product of Vrms and irms gives the apparent power. While the true power is obtained by multiplying the apparent power by the power factor cos φ. Thus,
and apparent power = Vrms × irms
True power = apparent power × power factor
For φ= 0°, the current and voltage are in phase. The power is thus, maximum (Vrms× irms). For
φ = 90°, the power is zero. The current is then stated as wattless. Such a case will arise when resistance in the circuit is zero. The circuit is purely inductive or capacitive.
|
297 videos|953 docs|172 tests
|
FAQs on Power in an AC Circuit - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is power in an AC circuit? |  |
| 2. How is power factor related to power in an AC circuit? |  |
| 3. Can power flow in an AC circuit be negative? |  |
| 4. How does power factor correction improve the efficiency of an AC circuit? |  |
| 5. What are the different methods used for power measurement in an AC circuit? |  |

















