Practice Doc: SNAP 2019 Quantitative Data Interpretation and Sufficiency | Additional Study Material for CAT PDF Download
1. Solve this:
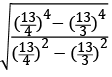
(a) 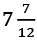
(b) 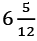
(c) 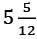
(d) 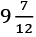
Ans: (c)
Solution: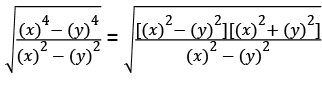
Putting the values: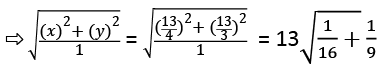
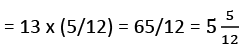
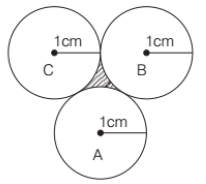
2. What is the area of the shaded portion.
(a) 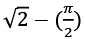
(b) 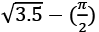
(c) 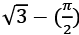
(d) 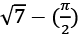
Ans. (c)
Solution:
ΔABC is equilateral triangle of side 2 cm.
Area of an equilateral triangle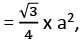
where a is the side of that triangle.
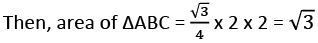
Area of 3 sector of angle 60° each and radius 1 cm each. = 3 x π (radius)2 × (θ/360°)
= 3 x π (1)2 × (60°/360°) = π/2
Area of shaded portion = Area of ΔABC – Area of 3 sectors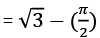
3. Length of two trains is 150 m each. When they are moving in opposite direction. They cross each other in 20 s and when they are moving in same direction. Then the faster train passed slower train in 40 s. Then find the speed of faster train.
(a) 10.50 m/s
(b) 11.25 m/s
(c) 30.75 m/s
(d) 25 m/s
Ans. (b)
Solution:
Let speed of faster train = x m/s
Let speed of slower train = y m/s
Distance = Speed × Time
Relative speed (in opposite direction) = (x + y) m/s
Relative speed (in same direction) = (x – y) m/s
In opposite direction
(x + y) = (150 + 150)/20 = 15 m/s
In same direction,
(x - y) = (150 + 150)/40 = 7.5 m/s
Using these two equations, we get x = 11.25 m/s
4. Brigadier Rastogi travels from A to Bat 40 km/h on bike. He travels from B to C at 10 km/h on cycle. The distance from A to B is equal to B to C. Then he travels from C to A via B at 24 km/h by auto-rickshaw. Find his average speed.
(a) 20.5 km/h
(b) 21 km/h
(c) 18 km/h
(d) 19.2 km/h
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Let distance from A to B LCM of 24, 10, 40 = 120 km
Time from A to B by bike = 120/40 = 3 h
Time from B to C by cycle = 120/10 = 12 h
All of us know that speed = Distance/time
Time from C to A by autorickshaw = 240/24 = 10 h
Average Speed = Total distance travelled/Total time taken
= (4 x 120)/(3 + 12 + 10) = 480/25 = 19.2 km/h
5. Rohan and Rahul are 144 km apart on point A and point B respectively. Rohan travels constantly at 8 km/h. Rahul travels 4 km in first hour, 5 km in second hour, 6 km in third hour and so on. Find the point where they well meet.
(a) 70 km from point A
(b) 74 km from point A
(c) 70 km from point B
(d) Exactly at midway between A and B
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Speed of Rohan = 8 km/h Speed of Rahul in start = 4 km/h and Rahul’s speed increases 1 km/h in every hour.
Relative speed in opposite direction AP series is formed = … 12, 13, 14 = Covered distance per hour
Let they meet after n hour.
According to the question, Distance between Rohan and Rahul = Covered distance in n hours
Here, we will use the formula of sum of n terms of an A.P., which is: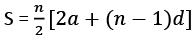
Where n = number of terms
a = First term of the A.P.
d = Common difference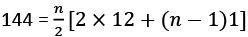
⇨ 288 = n(24 + n – 1)
Solving this equation,
n2 + 23n + 288 = 0
Splitting this quadratic equation,
(n – 9) (n + 32) = 0
Here, we have two values of n, which are -32 and 9, but negative value of n is not possible in this question.
So, after 9 h Rahul and Rohan meets, then distance covered by Rohan = 9 x 8 = 72 km.
It means, they meet exactly at midway between A and B.
6. Find the unit’s digit of (1!)1! + (2!)2! + (3!)3! + …….. + (100!)100!.
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
Ans. (c)
Solution:
5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120
As we know, unit digit for (5!, 6!, 7!, 8! … ∞) is zero.
Also, (1!)1! + (2!)2! + (3!)3! + (4!)4! = 11 + 22 + 66 + 2424 ........(1)
Unit digit for (1): 1 + 4 + 6 + 6 = 17
∴ Required unit digit = 7.
7. In how many ways can 10 books on mechanics and 8 books on quantum physics be placed in a row such that two books on quantum physics may not be together?
(a) 180
(b) 170
(c) 165
(d) 175
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Required ways = 11c8 = (11 x 10 x 9)/(3 x 2 x 1) = 165
8. In an institute, MBA Exam is conducted and sectional cut off has been introduced into it. Any candidate appearing for the exam cannot qualify unless he clears the sectional cut off. If there are 4 sections in the paper, then what is the number of ways on applicant may fail in the exam.
Solution. There is two possibility pass (P) and Fail (F). Then, possibility of 4 sections:
Total possibility = 16
The number of way on applicant may fail in the exam = (16 – 1) = 15
9. In how many ways letters of word SOTICA can be arranged such that vowel occupy at odd positions?
(a) 36
(b) 15
(c) 42
(d) 21
Ans. (a)
Solution:
SOTICA has three vowel. Then, the required ways = 3! x 3! = 6 x 6 = 36
10. Square, Circle, Hexagon and Octagon has equal perimeter. Which has maximum area?
(a) Square
(b) Circle
(c) Hexagon
(d) Octagon
Ans. (b)
Solution.
If the perimeter of figures is same then, area of figure which has maximum number of sides is maximum.
Then, circle has maximum area.
11. In how many ways can one wrap 3 Kitkat, 2 Fivestar and 3 Bar one. If at least one Kitkat has to be there in the gift pack and the gift pack has three chocolates.
(a) 56
(b) 10
(c) 46
(d) 35
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Number of ways of the gift pack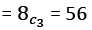
Number of ways of the gift pack without Kitkat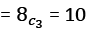
Then, number of ways of the gift pack with Kitkat = 56 – 10 = 46
12. The difference between compound and simple interest for a loan is 114 when invested for 2 yr. The rate of interest is 6% per annum. Find the loan amount.
Solution. Difference between compound and simple interest for 2 years of a principal P with interest rate r% per annum = P(r/100)2
Using this formula: 114 = P(6/100)2
⇨ P = (114 x 100 x 100)/(6 x 6) = 31666.66
13.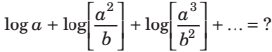
(a)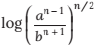
(b)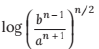
(c)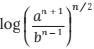
(d)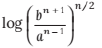
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Using the properties of Log, and simplifying this: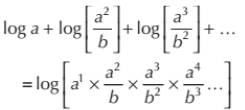
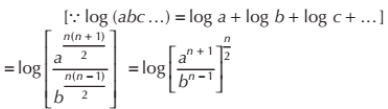
14. What is the coefficient of z3 in -7x y2 z3a2b2.
Solution. The given polynomial is -7x y2 z3a2b2
If we take z3 out of this, it becomes: z3 (-7x y2 a2b2)
Hence, (-7x y2 a2b2) is the coefficient of z3 in the given polynomial.
15. In a regular hexagon field, ropes are tied to connect all vertices (diagonal and side). What is the number of intersection points of ropes?
(a) 13
(b) 19
(c) 15
(d) 18
Ans. (b)
Solution: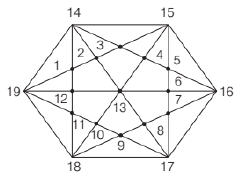
We can see that in above figure that there are 19 intersection points.
16. In the given diagram, ∠CAB = 60° and BC = a, AC = b, and AB = c.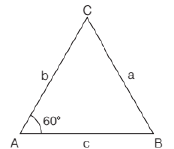
Then which of the following is correct?
(a) a2 + b2 + c2 = abc
(b) a2 = b2 + c2 – bc
(c) c2 = b2 + a2 – ab
(d) b2 = a2 + c2 = 2ac
Ans. (b)
Solution:
Here, we are using “Cosine rule”, which is as follows:
Cos 60° = (b2 + c2 - a2)/2bc
Putting the value of Cos 60°, which is 1/2 and doing the cross multiplication. a2 = b2 + c2 – bc
17.In a closed wooden box, length = 20 cm breadth = 14 cm and height = 10 cm and thickness = 5 mm. If weight of empty box is 3.462 kg, then what is the weight of 1 cm3 of wood (in gms)?
Ans: 6
Solution. Volume of cuboid = Length × Breath × Height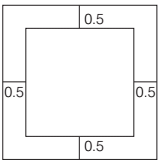
Volume of wood = External volume of box with wood – Internal volume of box without wood = (LBH)external – (LBH)internal
= 20 x 14 x 10 = 19 x 13 x 9
= 577 cm3
Total weight of wood = 3.462 kg
Weight of 577 cm3 of wood = 3462 gm
Then, weight of 1 cm3 of wood cm3 = 3462/577 = 6 gms
18. Find the number of zeros at the end of (5!)5! + (10!)10! + (50!)50! + (100!)100!
(a) 120
(b) 60
(c) 240
(d) 480
Ans. (a)
Solution:
(5!)5! is add in the remaining numbers then only we have to find number of zero in (5!)5!
5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120
Now, 120120 will have 120 zeroes.
19. Gitesh is twice as good as Jitesh. Gitesh takes 30 days less than Jitesh to finish a task. How long will Gitesh and Jitesh take to complete the task together.
(a) 30 days
(b) 20 days
(c) 60 days
(d) 15 days
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Let efficiency of Gitesh = 2x, and efficiency of Jitesh = x
Jitesh is half efficient as Gitesh, so he will take double time to finish the task.
And, difference between their time is 30 days.
So, Jitesh’s time = 2 x 30 = 60 days
And, Gitesh’s time = x = 30 days
Let us assume the total work to be 60 units.
Jitesh will do 1 unit per day.
Gitesh will do 2 units per day.
Together they will do 3 units per day.
Time taken by both, when working together = 60/3 = 20 days.
20. Mohan has a 200 L container. K L of milk is kept in the container. Mohan removes 6L milk and adds 6L water. He again replaces 6L of solution with water. Now milk and water are in the ratio 9: 16. What is the value of K?
Ans. 15
Solution:
Water which was added =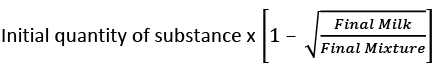
Putting the values: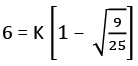
⇨ 6 = 2K/5
⇨ K = 15 litres
21. Indian express travels at 60 km/h and halts. For fixed time every hour. Due to halts, the average speed become 50 km/h. Find the time of halt.
(a) 10 min
(b) 20 min
(c) 15 min
(d) 12 min
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Halt time = [(Faster train’s speed – Slower train’s speed)/Faster train’s speed] x 60
[(60 – 50)/60] x 60 = 10 mins
Directions (Q. Nos. 22-25) Read the given information carefully and answer the given questions. In 2015, 100 aspirants appeared for an exam.
They had to answer four sections Maths, DI, LR and English.
The number of students who qualified in Maths = 55.
The number of students who qualified in LR= 38.
The number of students who qualified in (Maths + English) = 30.
The number of students who qualified in (LR + English) = 15.
The number of students who qualified in (Maths + LR) = 20.
The number of students who qualified in (Maths + LR + English) = 5.
The number of students who qualified in DI = 22.
The number of students who qualified in (DI + LR) = 5.
The number of students who qualified in (DI + Maths) = 5.
The number of students who qualified in (DI + Maths + LR) = 5.
The number of students who qualified in English = 50.
Those who qualified in English, could not qualify in DI section.
22. How many qualified at least two sections?
(a) 60
(b) 55
(c) 50
(d) 20
Ans. (b)
Solution:
Using the Venn Diagram concepts, we can draw a diagram like this: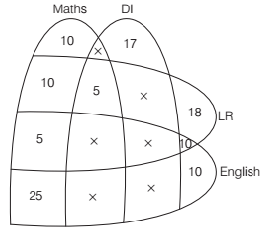
Qualified at least two section = 10 + 5 + 5 + 25 + 10 = 55 aspirants
23. How many qualified in both Maths and LR, but not in any other section?
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 5
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Using the Venn Diagram concepts, we can draw a diagram like this:
Qualified in both Maths and LR = 10 aspirants
24. How many did not qualify any section?
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 0
(d) 5
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Using the Venn Diagram concepts, we can draw a diagram like this:
None of the student failed i.e. 0.
25. How many qualified only DI section?
(a) 10
(b) 25
(c) 20
(d) 17
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Using the Venn Diagram concepts, we can draw a diagram like this:
Qualified only in DI = 17
Directions (Q. Nos. 26-28) 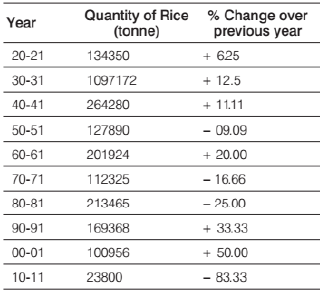
26. What is the approximate production of rice in year 1949-50?
(a) 132650 tonne
(b) 160479 tonne
(c) 140679 tonne
(d) 120659 tonne
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Production of rice in year 1950-51= 127890 tonne Production of rice in year 1950-51 is 09.09% less than that of in year 1949-50
As we know that 09.09% is 1/11. Using it below:
Then, production of rice in 1949-50
= (11/10) x Production of rice in year 1950-51
= (11/10) x 127890 = 140679 tonne
27. What is the difference in the production of rice in 1969-70 and 1979-80?
(a) 149830 tonnes
(b) 125600 tonnes
(c) 143980 tonnes
(d) 162500 tonnes
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Required difference = (Production of rice in 1979-80) − (Production of rice in 1969-70)
Using the fraction values of %:
= 213465 x (4/3) – 112325 x (6/5)
= 284620 – 134790 = 149830 tonne
28. What is the approximately production in 1959-60?
(a) 168270 tonnes
(b) 148070 tonnes
(c) 157270 tonnes
(d) 1382890 tonnes
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Production of rice in 1960-61= 201924 tonne
The production in 1959-60:
5/6 of 201924 = 168270 tonne
29. What is the sum of integers from 113 to 113113, which are divisible by 7?
(a) 899235637
(b) 867265029
(c) 913952088
(d) 752643214
Ans. (c)
Solution:
119 + 126 + …….. + 113113
This is the series of AP.
Let total number of terms be n.
Last number of an AP = a + (n – 1)d
Where a = first term
n = number of terms
d = common difference
Putting the values in the formula:
113113 = 119 + (n – 1) x 7
n = 16143
There is another formula, and it is for sum of n terms of an AP when first and last terms are given.
Sum = n/2(a + l)
= 16143/2 x (119 + 113113)
= 913952088
30. Robot is 4 m in length and placed at corner of 16 m × 30 m field. The robot is facing diagonally opposite corner and reaches the diagonally opposite corner in 15 s. What is the speed (in m/s) of robot?
(a) 5
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 1
Ans. (b)
Solution: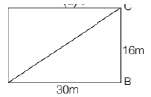
ABCD is rectangle. Then, ∠B = 90°
Using the Pythagoras Theorem: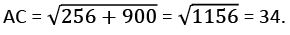
Length of the Robot = 4 m.
Travelled distance by the Robot = 34 – 4 = 30 m
Speed of the Robot = 30/15 = 2 m/s
31. In a smart phone factory, Robot A, B, and C manufacture 25%, 35% and 40% circuit board respectively. for each of the robot faulty circuit board = 5%, 4% and 2% respectively. What is the probability that the printed circuit board is defective if 1 circuit board is picked at random?
(a) 0.034
(b) 0.027
(c) 0.091
(d) 0.030
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Let total circuit board manufacture in factory = 100k
Then, the circuit board manufactured by the Robots:
A = 100k (25/100) = 25k
B = 100k (35/100) = 35k
C = 100k (40/100) = 40k
Number of faulty circuit boards by Robots:
A = 25k (5/100) = 1.25k
B = 35k (4/100) = 1.4k
C = 40k (2/100) = 0.8k
Total faulty boards = 3.45k
Probability = 3.45k/100k = 0.034
32. Average stipend of a group of students is 50 per day. The difference between maximum and minimum stipend is 45. If these 2 students are excluded, the average decreases by 1. Minimum earning lie between 42 to 47 and the number of students is a prime number, where both the digit is also prime. What is the number of students initially?
(a) 47
(b) 43
(c) 31
(d) 37
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Let the minimum stipend = x
Then, the maximum stipend = x + 45
Let number of students = n
Then, total stipend of a group of students = 50n …(i)
New average = 49
Then, total stipend of a group of students = 49 (n – 2) ….. (ii)
By Equations. (i) and (ii), we get
The stipend of two students
50n - 49 (n – 2) = n + 98
As per the question,
n + 98 = x + x + 45
Minimum earning lie between 42 to 47. Putting x = 45.
n + 98 = 2(45) + 45
n = 37
For x = 45, n is a prime number. Number of students = 37.
33. Valve A fills a bathtub in 10 h and Valve B fills the bathtub in 15 h. When A and B are opened together, later B closed after some time. Total time taken to fill the bathtub is 5h. After how much time was B closed?
(a) 5 h
(b) 3 h
(c) 8 h
(d) 6 h
Ans. (b)
Solution:
Valve A fills a bathtub = 10 h Valve B fills the bathtub = 15 h Let us assume the capacity of the bathtub = 150 litres A’s 1 hour filling work = 15 litres B’s 1 hour filling work = 10 litres A was on for 5 hours, it would have filled 15 x 5 = 75 litres.
Remaining 75 litres were filled by A + B, time taken by them to fill this: 75/(15 + 10) = 3 h B was on for 3 hours.
Directions (Q. Nos. 34 and 35) Refer to the pie-chart and answer the given questions.
Percentage of employees in different departments of branch ‘XYZ’ in the year 2014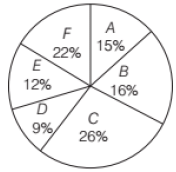
Total number of employees = 450
34. In 2014, the number of female employees in department C was 5/13 of the total number of employees in same department. If the number of female employees in department F was 4 less than that in department C, what is the number of male employees department F?
(a) 41
(b) 42
(c) 58
(d) 54
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Total number of employees in department C
450 x 0.26 = 117
Female employees in department C = 117 x (5/13) = 45
Now, total number of employees in department F = 450 x (22/100) = 99
Female employees in department F = 45 – 1 = 41
Male employees in F department = 99 – 41 = 58
35. The number of employees in department E is what per cent less than the number of employees in departments A and C together?
(a) 72
(b) 60
(c) 65
(d) 70
Ans. (d)
Solution:
As per the pie chart, E has 12%.
A and C together have 26 + 15 = 41%
Required Percentage = [(41 – 12)/41] x 100 = 70% (Approximately)
Directions (Q. Nos. 36-39) The following pie chart shows the analysis of the result of an examination in which 5 candidates have failed. Study the chart and answer the questions given below.
36. The total number of examinees was
(a) 100
(b) 120
(c) 135
(d) 150
Ans. (b)
Solution:
Full circle pie chart makes the angle of 360. 15 degree is for failed students, and as per the question, there are 5 failed students.
15 degree means 5 students.
360 degree means (5/15) x 360 = 120.
37. Percentage of passed female candidates with respect to total examinees is
(a) 30
(b) 37
(c) 40
(d) 45
Ans. (b)
Solution:
135 degree is for passed female candidates.
Calculating the percentage = (135/360) x 100 = 37.5%
38. Percentage of passed male candidates with respect to total passed candidates is
(a) 60.8
(b) 56
(c) 71
(d) 58
Ans. (a)
Solution:
210 degree is for passed male candidates.
Percentage of passed male candidates with respect to total passed candidates is: (210/345) x 100 = 60.8 %
39. Ratio of passed male candidates to the successful female candidates is
(a) 9: 1
(b) 1: 14
(c) 14: 9
(d) 9: 14
Ans. (c)
Solution:
Ratio of passed male candidates to the successful female candidates is: 210/135 = 14 : 9
40. Find the value of m – n, if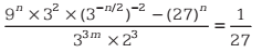
(a) 1
(b) -2
(c) -1
(d) 2
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Simplifying for n, and using the properties of powers: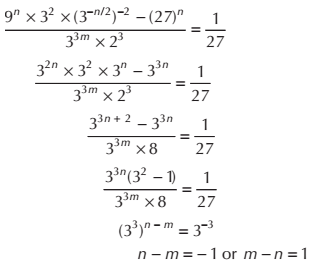
|
5 videos|385 docs|204 tests
|




















