Practice Questions: Depreciation and Amortisation | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
Q1. State with reasons whether the following statements are True or False:
Reducing balance method of depreciation is followed to have a uniform charge for depreciation and repairs and maintenance together.
[Marks: 2 ]
Answer: True: In the early periods of useful life of a fixed assets, repairs and maintenance expenses are relatively low because the asset is new. Whereas in later periods, as the asset become old, repairs and maintenance expenses increase continuously. Under written down value method, depreciation charged is high in the initial period and reduces continuously in the later periods. Thus, depreciation and repair and maintenance expenses become more or less uniform throughout the useful life of the asset.
Q2. The balance of Machinery Account of a firm on 1st April, 2023 was ₹ 28,54,000. Out of this, a plant having book value of ₹ 2,16,000 as on 1st April, 2023 was sold on 1st July, 2023 for ₹ 82,000. On the same date a new plant was purchased for ₹ 4,58,000 and ₹ 22,000 was spent on its erection. On 1st November, 2023 a new machine was purchased for ₹ 5,60,000. Depreciation is written off @ 15% per annum under the diminishing balance method.
Calculate the depreciation for the year ended 31st March, 2024.
[Marks: 4]
Answer: Calculation of depreciation for the year ended 31.3.24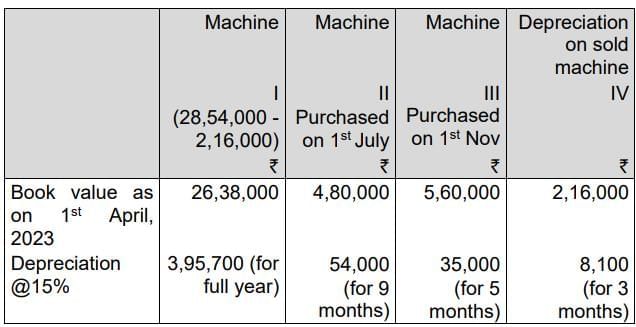 Total depreciation (I + II + III + IV) ₹ 4,92,800
Total depreciation (I + II + III + IV) ₹ 4,92,800
Q3. Discuss the factors taken into consideration for the calculation of depreciation.
[Marks: 5]
Answer: Following factors are taken into consideration for calculation of depreciation.
1. Cost of asset including expenses for installation, commissioning, trial run etc.- Cost of a depreciable asset represents its money outlay or its equivalent in connection with its acquisition, installation and commissioning as well as for additions to or improvement thereof for the purpose of increase in efficiency.
2. Estimated useful life of the asset - Useful Life’ is either
(i) the period over which a depreciable asset is expected to be used by the enterprise or
(ii) the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the use of the asset by the enterprise. Determination of the useful life is a matter of estimation and is normally based on various factors including experience with similar type of assets. Several other factors like estimated working hours, production capacity, repairs and renewals, etc. are also taken into consideration on demanding situation.
3. Estimated scrap value (if any) is calculated at the end of useful life of the asset. If such value is considered as insignificant, it is normally regarded as nil. On the other hand, if the residual value is likely to be significant, it is estimated at the time of acquisition/installation, or at the time of subsequent revaluation of asset.
Q4. M/s. Surya Lights purchased a second-hand machine on 1st January, 2020 for ₹ 3,20,000. Overhauling and erection charges amounted to ₹ 80,000.
Another machine was purchased for ₹ 1,60,000 on 1st July, 2020.
On 1st July, 2022, the machine installed on 1st January, 2020 was sold for ₹ 1,60,000. Another machine amounted to ₹ 60,000 was purchased and was installed on 30th September, 2022.
Under the existing practice the company provides depreciation @ 20% p.a. on original cost. However, from the year 2023 it decided to adopt WDV method and to charge depreciation @ 15% p.a.
You are required to prepare Machinery account for the years 2020 to 2023.
[Marks: 10]
Answer: In the books of M/s. Surya Lights
Machinery Account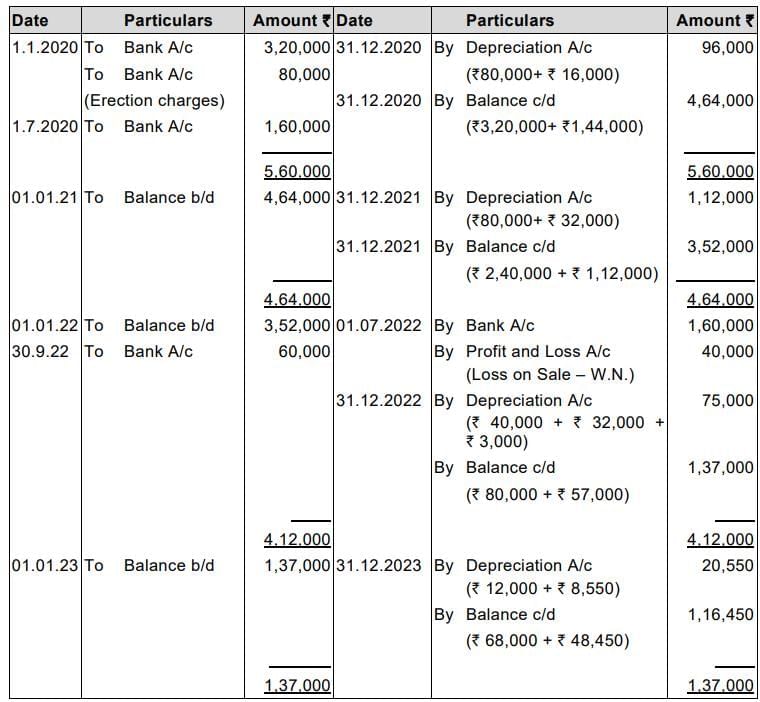
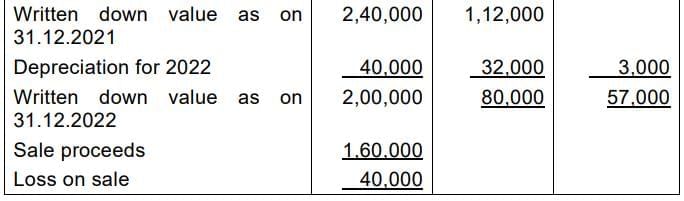
Working Notes: Book Value of machines (Straight line method)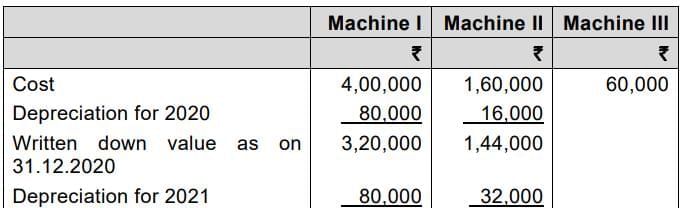
Q5. The details of Assets and Liabilities of Mr. Jalaj as on 31-3-2023 and 31-3-2024 are as follows:
| Particulars | 31-3-2023 (₹) | 31-3-2024 (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| Assets: | ||
| Furniture | 62,500 | |
| Building | 1,25,000 | |
| Stock | 1,25,000 | 3,12,500 |
| Sundry Debtors | 75,000 | 1,37,500 |
| Cash in hand | 14,000 | 16,500 |
| Cash at Bank | 75,000 | 93,750 |
| Liabilities: | ||
| Loans | 1,12,500 | 87,500 |
| Sundry Creditors | 62,500 | 1,00,000 |
Mr. Jalaj decided to provide depreciation on the building by 2.5% and furniture by 10% for the period ended on 31-3-2023. Mr. Jalaj purchased jewellery for ₹30,000 for his daughter in December 2022. He sold his car on 30-3-2023, and the amount of ₹50,000 is retained in the business.
You are required to:
(i) Prepare statement of affairs as on 31-3-2023 & 31-3-2024.
(ii) Calculate the profit received by Mr. Jalaj during the year ended 31-3-2024.
[Marks: 8]
Answer: In the books of Mr. Jalaj
Statement of Affairs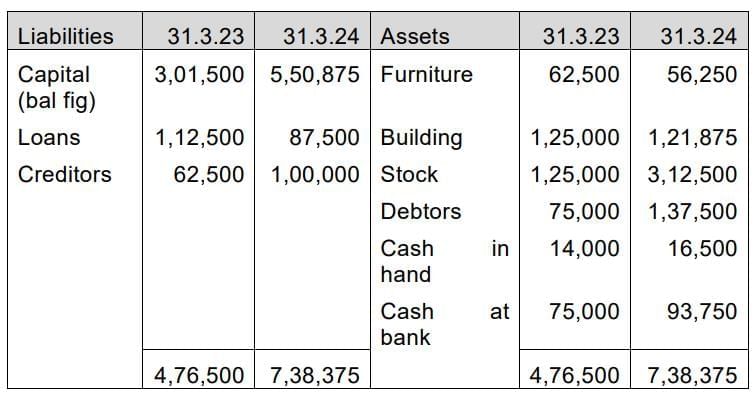
Capital A/c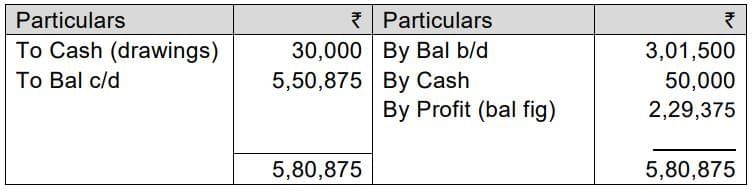
Q6. A Plant & Machinery costing ₹ 80,00,000 is depreciated on straight-line basis assuming 10-year working life and zero residual value, for four years. At the end of the fourth year, the machinery was revalued upwards by ₹ 3,20,000. The remaining useful life was reassessed at 8 years.
Calculate Depreciation for the fifth year.
[Marks: 4]
Answer: Calculation of depreciation for 5th year
Depreciation per year charged for four years = ₹ 80,00,000 / 10 = ₹ 8,00,000
WDV of the machine at the end of fourth year = ₹ 80,00,000 – ₹ 8,00,000 × 4 = ₹ 48,00,000.
Depreciable amount after revaluation = ₹ 48,00,000 + ₹ 3,20,000 = ₹ 51,20,000
Remaining useful life as per previous estimate = 6 years
Remaining useful life as per revised estimate = 8 years
Depreciation for the fifth year and onwards = ₹ 51,20,000 / 8 = ₹ 6,40,000.
Q7. Savin & Co. purchased a machine for ₹ 1,00,000 on 1.4.2021. Another machine costing ₹ 1,50,000 was purchased on 1.10.2022. On 31.3.2024, the machine purchased on 1.4.2021 was sold for ₹ 50,000. The company provides depreciation at 15% on Written Down Value Method. Prepare –
(i) Machinery Account
(ii) Machinery Disposal Account
(iii) Provision for Depreciation Account
[Marks: 10]
Answer: Savin &Co.
Machinery Account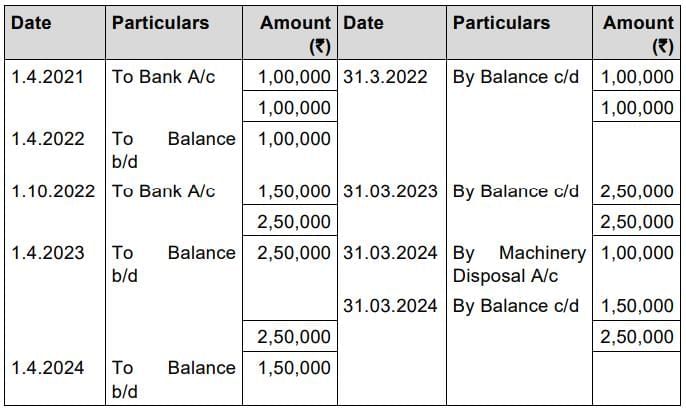
Provision for Depreciation Account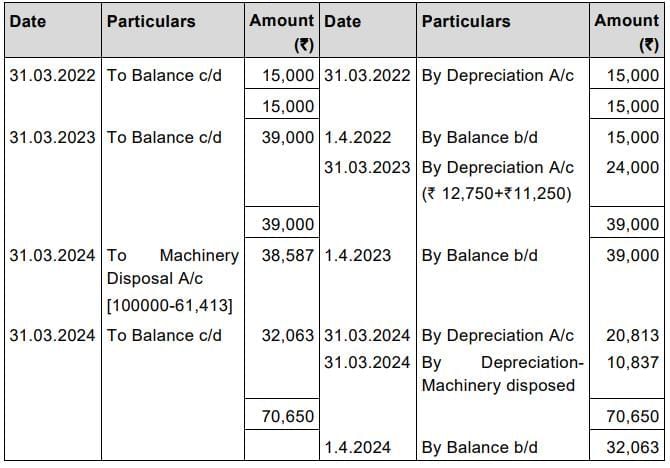
Machinery Disposal Account 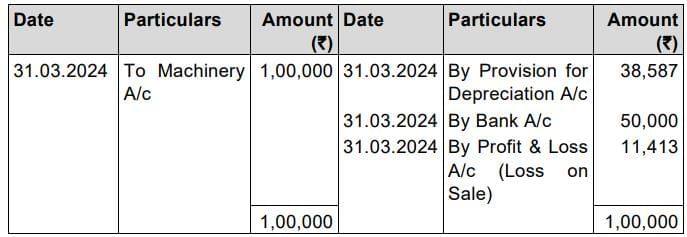
Working Notes:
1. Depreciation for the machine purchased on 1.10.2022.
For the year 2022-23 (used for 6 months) = ₹ 1,50,000 x 15% x 6/12 = ₹ 11,250
For the year 2023-24 (used for full year) = ₹ 1,38,750 x15 % = ₹ 20,813
2. Depreciation for the machine purchased on 1.4.2021.
Depreciation = ₹ 1,00,000 x 15% = ₹ 15,000
So, Depreciation for 2nd year = ₹ 85,000 x15% = ₹ 12,750
Depreciation for 3rd year = ₹ 72,250x15% = ₹10,837
Q8. S Chand & Associates purchased a machine for ₹ 3,00,000 on 1.1.2021. Another machine costing ₹ 4,50,000 was purchased on 1.7.2022. On 31.12.2023 the machine purchased on 1.1.2021 was sold for ₹ 1,50,000. The company provides depreciation at 15% on Written Down Value Method. The company closes its accounts on 31st December every year.
Prepare –
(i) Machinery Account
(ii) Machinery Disposal Account
(iii) Provision for Depreciation Account
[Marks: 10]
Answer: S Chand & Associates
Machinery Account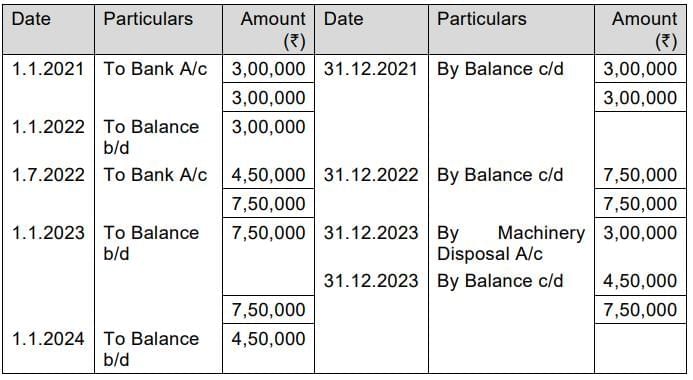
Provision for Depreciation Account 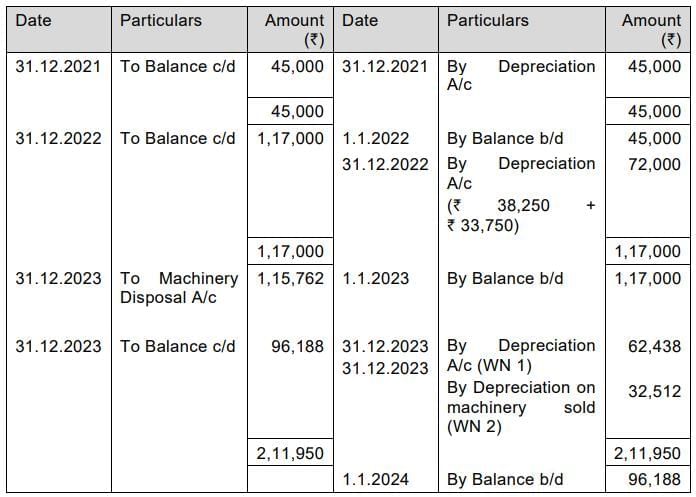
Machinery Disposal Account 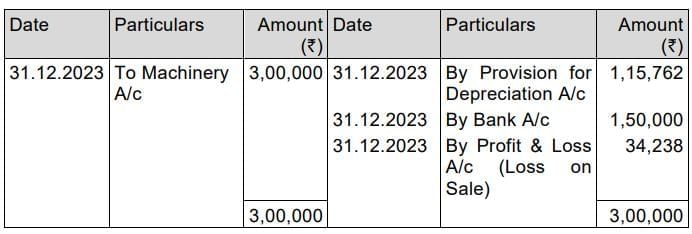
Working Notes:
1. Depreciation for the machine purchased on 1.7.2022.
For the year 2022 (Used for 6 months) = ₹ 4,50,000 x 15% x 6/12 = ₹ 33,750
For the year 2023 (Used for full year) = ₹ 4,16,250 x15 % = ₹ 62,438
2. Depreciation for the machine purchased on 1.1.2021.
Depreciation for the year 2021 = ₹ 3,00,000 x 15% = ₹ 45,000
Depreciation for the year 2022 = ₹2,55,000 x15% = ₹ 38,250
Depreciation for the year 2023 = ₹ 2,16,750 x15% =₹ 32,512
Q9. On 1st April, 2022, LMP Co. which depreciates its machinery @10% p.a. on diminishing balance method, had ₹ 9,72,000 to the debit of Machinery Account. On 1st October, 2022, part of machinery purchased on 1st April, 2020 for ₹ 80,000 was sold for ₹ 45,000. Also, a new machinery at a cost of ₹ 1,50,000 was purchased on 1st October, 2022 and installed on the same date and installation charges being ₹ 8,000.
The company changed the method of depreciation from diminishing balance method to straight line method on 1st April, 2022. The rate of depreciation remains the same.
Show the Machinery Account and ascertain the amount chargeable to Profit and Loss Account as depreciation in the year 2022-23.
[Marks: 10]
Answer: In the books of LMP Co.
Machinery Account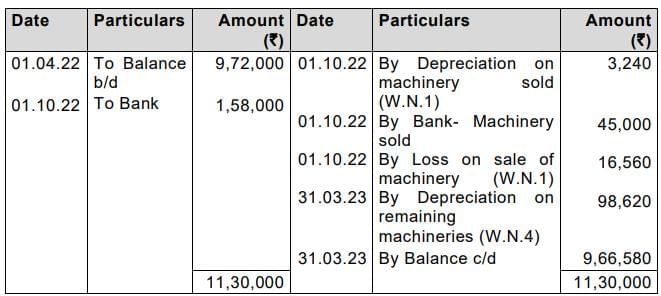
Working Note:
1. Calculation of amount of Depreciation, written down value and loss on sale of the part of the machinery
2. Computation of written-down value of the remaining asset as on 01.04.2022

3. Computation of the written-down value of the machinery as on 31.03.2023
4. Total Depreciation to be charged to Profit and Loss Account during the year 2022-2023 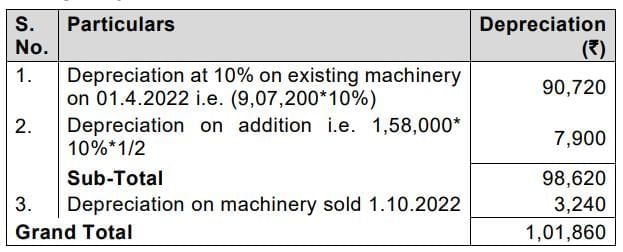
Q10. PQR associates bought a computer set on 01.04.2020 for ₹ 2,00,000 and charged depreciation @ 20% p.a. on diminishing balance method. They made further additions as follows:
| Date | Amount |
|---|---|
| 01.04.2021 | ₹ 1,50,000 |
| 01.04.2023 | ₹ 1,00,000 |
On 01.04.2023, it was decided to change the method to straight line basis and charge depreciation assuming the expected life of all the computers to be 8 years from 01.04.2023.
Prepare Computers A/c for year ending 31.03.2024.
[Marks: 5]
Answer: Calculation of Depreciation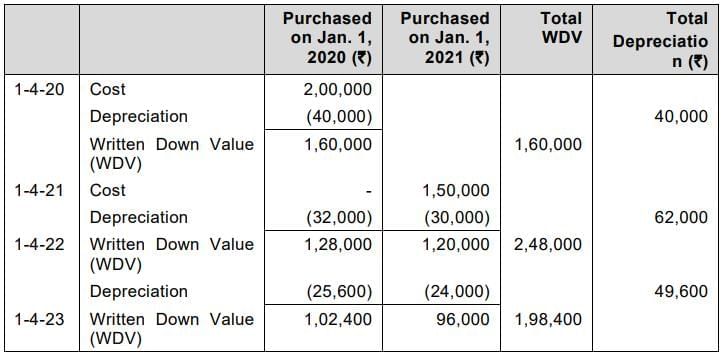
Computers Account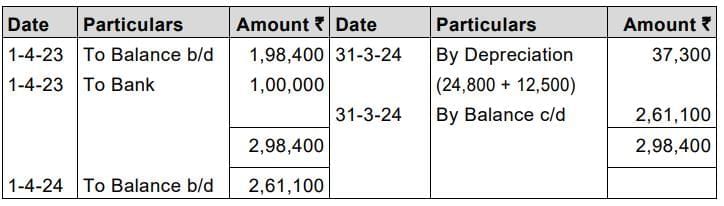
|
68 videos|265 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions: Depreciation and Amortisation - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What is the difference between depreciation and amortisation ? |  |
| 2. How is depreciation calculated for fixed assets ? |  |
| 3. What are the common methods of amortisation ? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to record depreciation and amortisation in financial statements ? |  |
| 5. What is the impact of depreciation and amortisation on taxable income ? |  |
















