Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Agriculture
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Imagine you are travelling from Delhi to Chandigarh to attend a wedding, by road in January. Which of the following crops will you notice prominently in the fields during the journey?
(a) Paddy
(b) Maize
(c) Wheat
(d) Jowar
Ans: (c) Wheat
- January is the winter season in India, and during this time, rabi crops are grown in the northern plains, including the route from Delhi to Chandigarh (Punjab and Haryana).
- Wheat is a major rabi crop grown during the winter months (sown in October-November and harvested in March-April).
- Paddy and maize are kharif crops, grown during the monsoon season (June-September), so they are not prominent in January.
- Jowar is also a kharif crop and is less common in this region. Wheat fields will be green and noticeable during your journey in January.
Q2: Read the story of Rinjha and answer the question that follows:
Rinjha lived with her family in a small village at the outskirts of Diph in Assam. She enjoys watching her family members clearing, slashing and burning a patch of land for cultivation. She often helps them in irrigating the fields with water running through a bamboo canal from the nearby spring. She loves the surroundings and wants to stay here as long as she can, but this little girl has no idea about the declining fertility of the soil and her family's search for a fresh patch of land in the next season.
A. What type of farming is Rinjha’s family doing? Describe any two of its characteristics.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Rinjha’s family is practicing Primitive Subsistence Farming (Slash and Burn Agriculture).
Characteristics:
- Shifting Cultivation: Farmers clear a patch of land by cutting and burning vegetation, cultivate crops for a short period, and then move to a new patch when the soil fertility decreases. This allows the old land to regain fertility naturally.
- Low Productivity: This type of farming uses no modern inputs like fertilizers or machines, relying on natural soil fertility, which leads to low crop yields.
B. Suggest any three measures to Rinjha so that the fertility of the soil of her fields remains intact for a long time.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Rinjha’s family practices shifting cultivation (slash-and-burn), which depletes soil fertility over time. The following measures can help maintain soil fertility:
- Crop Rotation: Growing different crops in a sequence prevents the depletion of specific nutrients. For example, alternating cereals with leguminous crops like pulses restores nitrogen in the soil, enhancing fertility.
- Organic Farming: Using natural fertilizers like compost and manure instead of chemical fertilizers enriches the soil with organic matter, improving its structure and nutrient content. This reduces soil degradation caused by shifting cultivation.
- Contour Ploughing: Ploughing along the contours of the land reduces soil erosion, especially in hilly areas like Assam, by preventing runoff of topsoil during rains. This helps retain nutrients and maintain soil fertility for longer periods.
These measures promote sustainable agriculture, reducing the need to clear new land and preserving the soil’s productivity.
OR
Mrs. Monica, along with her family, clears a piece of land and grows grain and other food crops to feed her family. When the soil's fertility decreases, she prepares another piece of land for agriculture. Which of the following methods of agriculture does she use?
(a) Plantation farming
(b) Slash and burn farming
(c) Intensive subsistence farming
(d) Commercial farming
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Slash and burn farming
Mrs. Monica’s practice of clearing land, growing crops for family consumption, and moving to a new patch when soil fertility decreases is called slash and burn farming, a type of primitive subsistence farming. This method, also known as jhumming in northeastern India, involves cutting and burning vegetation to clear land for cultivation. It’s different from plantation farming (large-scale cash crops like tea), intensive subsistence farming (small plots with high labor input), and commercial farming (large-scale production for sale).
OR
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
Primitive Subsistence Farming
It is a 'slash and burn' agriculture. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family. When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation. This type of shifting allows Nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes; land productivity in this type of agriculture is low as the farmer does not use fertilisers or other modern inputs. It is known by different names in different parts of the country. It is jhumming in north-eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Nagaland; Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in Bastar district of Chhattisgarh, and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(i) 'Slash and Burn' system of agriculture comes under which type of farming?
(ii) Why is productivity low in 'Slash and Burn' system?
(iii) Describe any two features of 'Slash and Burn' system of agriculture.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Primitive Subsistence Farming
(ii) Productivity is low because farmers do not use fertilizers or modern inputs, relying only on natural soil fertility, which gets exhausted quickly.
(iii)
- Shifting Cultivation: Farmers clear land by slashing and burning vegetation, grow crops for a few years, and then shift to a new patch when soil fertility declines.
- No Modern Inputs: This farming uses traditional methods without fertilizers, pesticides, or machines, leading to low yields.
Q3: Swapna is a small farmer. Swapna wants to cultivate cotton. What kind of geographical conditions will be suitable for this? Choose the most appropriate option.
(a) Laterite soil, Moderate rainfall, Low temperature and Bright sunshine
(b) Black soil, Light rainfall, High temperature and Bright sunshine
(c) Laterite soil, Light rainfall, High temperature and Moderate sunshine
(d) Black soil, High rainfall, Low temperature and Moderate sunshine
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Black soil, Light rainfall, High temperature and Bright sunshine
Cotton is a kharif crop that requires specific conditions to grow well. It thrives in black soil (also called regur soil), which is found in regions like Gujarat and Maharashtra. Cotton needs light rainfall (50-100 cm) because too much water can damage the crop. It also requires high temperatures (21°C to 30°C) and bright sunshine during the growing period for proper growth and boll formation. Option B matches these conditions perfectly. Laterite soil is not ideal for cotton, and high rainfall or low temperatures are unsuitable, ruling out the other options.
Q4: Identify the crop with the help of the below information:
- This crop is a major cash crop in India.
- It is cultivated mainly in the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- It is known for its aroma.
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Jute
(d) Cotton
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Coffee
Coffee is a major cash crop grown in India, particularly in Karnataka (which produces the most coffee) and Tamil Nadu. It is known for its aroma, especially in varieties like Arabica and Robusta. Tea is also a cash crop but is mainly grown in Assam and West Bengal. Jute is known as the “golden fibre” and is not aromatic, while cotton is a fibre crop, not known for aroma.
Q5: With the help of following information identify the agricultural crop from the given options:
I. It requires more than 200 cm rainfall and temperature above 25°C.
II. It is mainly used as raw material in industries.
III. It is primarily a crop of the equatorial region.
(a) Cotton
(b) Rubber
(c) Groundnut
(d) Mustard
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Rubber
Rubber is a crop that requires high rainfall (more than 200 cm) and high temperatures (above 25°C), typical of equatorial regions like Kerala in India. It is used as a raw material in industries (e.g., for making tires). Cotton needs less rainfall (50-100 cm), groundnut is a kharif crop with moderate rainfall needs, and mustard is a rabi crop grown in cooler, drier conditions.
Q6: Which among the following crop is known as 'Golden Fibre'?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wool
(c) Jute
(d) Silk
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Jute
Jute is called the “Golden Fibre” because of its shiny golden color and economic importance. It is a major cash crop grown in West Bengal and used to make products like sacks and bags. Cotton is a white fibre crop, wool comes from animals, and silk is a shiny but not golden fibre.
Q7: Examine the measures taken by the government to make agriculture profitable in India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government sets MSP for crops to ensure farmers get a fair price, protecting them from losses if market prices fall.
- Subsidies on Inputs: Farmers receive subsidies on fertilizers, seeds, and electricity to reduce the cost of farming and increase profits.
- Crop Insurance Schemes: Schemes like Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana provide insurance to protect farmers from losses due to natural calamities.
Q8: Explain any three features of intensive subsistence farming.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Small Land Holdings: Farmers cultivate small plots of land using family labor to grow food crops for their own consumption.
- High Labor Input: It involves intensive use of labor and traditional tools to maximize production from limited land.
- Multiple Cropping: Farmers grow more than one crop per year on the same land to meet family needs due to high population pressure.
Q9: Mention any three features of commercial farming.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Large-Scale Production: Commercial farming involves growing crops on large farms for sale in the market, not just for family use.
- Use of Modern Technology: Farmers use machines, fertilizers, and high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds to increase crop production.
- Cash Crops: Crops like cotton, sugarcane, or tea are grown for profit rather than personal consumption.
Q10: Explain any three features of Plantation Agriculture.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Large Estates: Plantation agriculture involves growing crops on large estates or plantations, often covering hundreds of hectares.
- Single Crop Cultivation: A single cash crop like tea, coffee, or rubber is grown for commercial purposes and export.
- High Investment: It requires significant capital for machinery, labor, and processing units to produce high-quality crops.
Q11: The Government of India has invited some suggestions for institutional reforms in agriculture. Propose any five institutional reforms to the Government for the betterment of agriculture.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Land Reforms: Distribute surplus land to landless farmers to increase their access to land and improve productivity.
- Access to Credit: Provide low-interest loans through banks or cooperatives to help farmers buy seeds, fertilizers, and equipment.
- Crop Insurance Schemes: Expand schemes like Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana to protect farmers from losses due to natural disasters.
- Marketing Support: Set up more regulated markets and improve storage facilities to ensure farmers get fair prices for their crops.
- Farmer Cooperatives: Encourage cooperatives to help farmers pool resources, share knowledge, and sell produce collectively for better profits.
Q12: Suppose you are a farmer. You want to cultivate rice in India. Describe any three geographical conditions which will be suitable for rice cultivation in India and write the names of two leading rice-producing states of India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Geographical Conditions:
- High Rainfall or Irrigation: Rice requires 100-200 cm of rainfall or assured irrigation, as it is a water-intensive crop grown in flooded fields.
- High Temperature: It needs temperatures above 25°C during the growing season, typical of the kharif season in India.
- Alluvial Soil: Rice grows best in fertile alluvial soil, which retains water and is found in river plains.
Leading Rice-Producing States:
- West Bengal
- Uttar Pradesh
Q13: The Government of India has invited some suggestions for technological reforms in agriculture. Propose any five technological reforms to the Government for the betterment of agriculture.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- High-Yielding Variety (HYV) Seeds: Promote the use of HYV seeds to increase crop yields and improve food security.
- Modern Irrigation Systems: Encourage drip and sprinkler irrigation to save water and ensure crops get enough water in dry areas.
- Mechanization: Provide subsidies for tractors, harvesters, and other machines to reduce labor and increase efficiency.
- Use of Fertilizers and Pesticides: Educate farmers on the balanced use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to boost productivity without harming the soil.
- Weather Forecasting Technology: Improve access to accurate weather forecasts to help farmers plan sowing and harvesting.
Q14: Suppose you are a farmer. You want to cultivate tea in India. Describe any three geographical conditions which will be conducive for tea cultivation in India and write the names of two major tea-producing states of India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Geographical Conditions:
- High Rainfall: Tea requires 150-300 cm of rainfall, well-distributed throughout the year, to support its growth.
- Moderate Temperature: It grows best in temperatures between 20°C and 30°C, typical of hilly regions.
- Well-Drained Sloping Land: Tea needs well-drained, loamy soil on hill slopes to prevent waterlogging and ensure healthy roots.
Major Tea-Producing States:
- Assam
- West Bengal
Tea is a plantation crop that needs a lot of rain, moderate heat, and sloping land to grow well. Assam and West Bengal (especially Darjeeling) are famous for tea because they have the right climate and hilly terrain.
Q15: Describe the features of cropping patterns in India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: India’s cropping patterns are shaped by its diverse climate, soils, and seasons.
- Diverse Crops: India grows a variety of crops, including food crops (rice, wheat), cash crops (cotton, sugarcane), and plantation crops (tea, coffee), due to varied climate and soil.
- Seasonal Cropping: Crops are divided into kharif (monsoon, e.g., rice), rabi (winter, e.g., wheat), and zaid (summer, e.g., watermelon) based on seasons.
- Regional Specialization: Different regions grow specific crops based on soil and climate, e.g., rice in West Bengal, wheat in Punjab, and tea in Assam.
- Mixed Cropping: Farmers often grow multiple crops on the same land to reduce risk and meet food and cash needs.
- Dependence on Monsoon: Most cropping patterns rely on monsoon rains, with irrigation supporting rabi and zaid crops in dry areas.
Q16: Describe the main characteristics of major millet crops grown in India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Characteristics of Major Millet Crops (Jowar, Bajra, Ragi):
- Drought-Tolerant: Millets like jowar, bajra, and ragi can grow in areas with low rainfall (30-100 cm) and poor soils, making them suitable for dry regions.
- Nutritious Food Crops: Millets are rich in nutrients like proteins and fiber, used as food for humans and fodder for animals.
- Kharif Crops: These are mainly grown during the monsoon season in states like Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Karnataka.
Major Millet-Producing States:
- Rajasthan (bajra)
- Maharashtra (jowar)
Millets are hardy crops that don’t need much water or fertile soil, so they’re grown in dry areas like Rajasthan. Jowar and bajra are coarse grains used for food and animal feed, while ragi is known for its nutrition.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Read the following information and identify the crop.(I) It is the staple food crop of majority of people in India.
(II) India is the second largest producer of this crop.
(III) It is a Kharif crop.
(IV) It requires high humidity with 100 cm of annual rainfall. (CBSE 2024)
Crops:
(a) Ragi
(b) Bajra
(c) Wheat
(d) Rice
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Rice is the staple food for most people in India, making it essential for daily meals. India is the second-largest producer of rice in the world, and it is classified as a Kharif crop, which means it is grown during the monsoon season when conditions are humid and rainfall is abundant. Rice Farming
Rice Farming
Q2: Explain the initiation taken by the government to ensure the increase in agriculture production. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: India is essentially an agricultural country where two-third of its total population are engaged in agricultural activities. Considering, the importance of agriculture in India, following steps have been taken by the government to increase its production:
(1) Governments has established Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
(2) The government has founded veterinary clinics, animal breeding facilities, and agricultural universities.
(3) It has prioritised the advancement of meteorology and weather forecasting research and development.
(4) The infrastructure in rural areas has been enhanced.
(5) Indian farmers now have access to lowcost finance to purchase essential inputs like machinery, fertiliser, seeds, etc.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q3: Explain any two features of Intensive Subsistence farming. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two features of Intensive Subsistence farming are:
(i) It is practiced in densely populated area.
(ii) It involves high degree of use of bio-chemical inputs and irrigation.
Q4: Identify the crop with the help of the following information and choose the correct option. (2023)
- This is the second most important Cereal Crop.
- This a Rabi crop.
- It requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- It requires 50 to 75 cm annual rainfall.
(a) Wheat
(b) Maize
(c) Rice
(d) Sugarcane
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Wheat is the second most important cereal crop in India, following rice. It is classified as a Rabi crop, which means it is sown in the winter and harvested in the spring. Wheat thrives in a cool growing season and needs plenty of sunshine during ripening, along with an annual rainfall of 50 to 75 cm for optimal growth.
Q5: Explain any three institutional reforms taken for the development of Indian agriculture. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The institutional reforms introduced by the Government, to help the farmers are given below.
(i) Crop insurance was provided for disease, fire, cyclone, flood, and drought.
(ii) To provide loans to farmers at low interest rates, banks, cooperative societies, grameen banks were established.
(iii) For the benefit of farmers, some of the schemes introduced were the Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS), Kissan Credit Card (KCC).
(iv) To help the farmers, special agricultural programmes and special weather bulletins were introduced on television and radio.
(v) To check exploitation of farmers by middlemen and speculators, procurement and remunerative prices, minimum support price was introduced by the Government for many important crops
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q6: Which of the following is not a characteristic of 'Intensive Subsistence Farming’? (2021)(a) This is practised in areas of high population.
(b) It is an example of labour-intensive farming.
(c) High doses of biochemical inputs are used,
(d) It is an example of commercial farming
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Intensive subsistence farming is not considered commercial farming because it primarily focuses on producing enough food for the farmer's family rather than for sale. This type of farming typically occurs in densely populated areas and relies heavily on labor and biochemical inputs to maximize crop yields.

Q7: Read the following passages and answer the questions that follow:
Jhumming : The ‘slash and burn’ agriculture is known as ‘Milpa’ in Mexico and Central America, ‘Conuco’ in Venezuela, ‘Roca’ in Brazil, ‘Masole’ in Central Africa, ‘Ladang’ in Indonesia, ‘Ray’ in Vietnam. In India, this primitive form of cultivation is called ‘Bewar’ or ‘Dahiya’ in Madhya Pradesh, ‘Podu’ or ‘Penda’ in Andhra Pradesh, ‘Pama Dabi’ or ‘Koman’ or ‘Bringa’ in Odisha, ‘Kumari’ in Western Ghats, ‘Valre’ or ‘Waltre’ in South-eastern Rajasthan, ‘Khil’ in the Himalayan belt, ‘Kuruwa’ in Jharkhand, and ‘Jhumming’ in the North-eastern region.
(i) How is Primitive Subsistence Agriculture related to Jhumming?
(a) It is based on shifting cultivation.
(b) It is intensive in nature.
(c) It is based on plantation cultivation.
(d) It depends upon the cash crop. (CBSE 2021)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Primitive Subsistence Agriculture, also known as shifting cultivation, is a type of farming where farmers clear a patch of land, cultivate it for a few years, and then move to a new area once the soil fertility declines. Jhumming is a traditional form of shifting cultivation practiced in various parts of India, especially in the northeastern states. In this method, a piece of land is cleared by cutting and burning vegetation, crops are grown for a few seasons, and then the land is left fallow to regain fertility.
Thus, the correct answer is (a) It is based on shifting cultivation.
(ii) Identify the major problem of Jhumming cultivation.
(a) Single crop dominance
(b) Modern inputs
(c) High cost
(d) Low production
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Jhumming Cultivation or the primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family/community labour. This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown. Hence, the crop production is low.
(iii) In India ‘slash and burn’ agriculture is known as ‘Bewar’, in which one of the following States?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jharkhand
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In India, slash and burn agriculture is known by different names in various regions. In Madhya Pradesh, this form of agriculture is called Bewar (or sometimes Dahiya). It involves clearing a patch of land by cutting and burning vegetation, then cultivating it for a few seasons before moving to a new plot when the soil loses fertility.
Thus, the correct answer is (b) Madhya Pradesh.
(iv) Match Column (A) with Column (B) and choose the correct options :
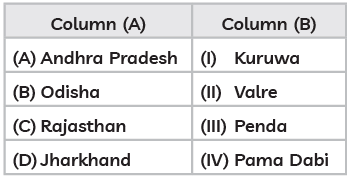
(a) (A)–(III) (B)–(IV ) (C)–(II) (D)–(I)
(b) (A)–(I) (B)–(II) (C)–(III) (D)–(IV )
(c) (A)–(II) (B)–(I) (C)–(IV ) (D)–(III)
(d) (A)–(IV ) (B)–(III) (C)–(I) (D)–(II)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The practice of slash and burn agriculture is given different names as mentioned in the question. Apart from them, this practice of farming is also known as jhumming in north-eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland; Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in Bastar district of Chhattisgarh, and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q8: Describe any three main features of ‘Rabi crop season.’ (Delhi 2020, 2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Rabi crops are also known as winter crops. They are sown from October to December and harvested from April to June.
(b) Wheat, barley, pea, gram and mustard are the important rabi crops. Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are the important producers of rabi crops.
(c) Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western disturbances helps in the success i of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh ; and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above mentioned rabi crops.
 Rabi Crops
Rabi Crops
Q9: Analyse any five features of Commercial Farming. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) In commercial farming, most of the produce is sold in the market to earn money (as opposed to subsistence farming).
(ii) In this system, farmers use inputs like irrigation, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, and high yielding varieties of seeds, etc.
(iii) Some of the major commercial crops grown in different parts of India are cotton, jute, sugarcane, groundnut, etc.
(iv) Rice farming in Haryana is mainly for commercial purpose as people of this area are predominantly wheat eaters.
(v) However, in East and North-Eastern states of India, rice cultivation would be largely of subsistence type.
Q10: Write the temperature requirement of Maize crop. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It requires the temperature range between 21°C - 27°C.
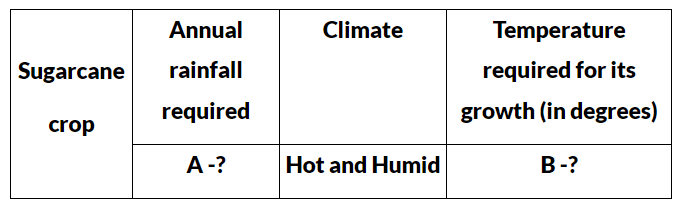
Q11: Complete the following table with correct information for A and B: (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A-75cm to 100 cm
B-21° to 27°C
Q12: Why is agriculture called the backbone of the Indian economy? Explain. (Delhi 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Agriculture is called the backbone of the Indian economy due to the following reasons:
- It is the main occupation of the majority of people in India, providing employment to a significant portion of the population.
- Agriculture provides raw materials to the manufacturing sector, supporting industrial development.
- It ensures food security by producing food grains for the growing population.
- Agriculture contributes to the development of the tertiary sector, as it requires services like transportation, storage, and marketing of agricultural produce.
- It is the main source of the country's national income, contributing to the GDP.
- Agriculture also plays a crucial role in the country's export sector, earning foreign exchange.
- It helps in the overall development of rural areas and contributes to poverty alleviation.
Q13: There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below:
Assertion (A): The Government of India buys wheat and rice from farmers at a fair price.
Reason ( R): The public sector contributes to economic development.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A): The statement is true. The Government of India buys wheat and rice from farmers at a fair price, known as the Minimum Support Price (MSP), to ensure farmers get a stable income and are protected from market fluctuations.
Reason (R): This statement is also true. The public sector contributes to economic development by providing essential services, stabilizing prices, and supporting various sectors, including agriculture.
However, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). The government’s action of buying wheat and rice at a fair price is more specifically aimed at supporting farmers and ensuring food security, rather than being solely about the public sector's contribution to economic development.
Thus, the correct answer is (b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Q14: Write the amount of annual rainfall required for the cultivation of wheat. (CBSE 2020, 11)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 50-75 cm of rainfall is the amount of rainfall required for the cultivation of wheat.
Q15: Describe the technological reforms taken by the Indian Government in the field of agriculture. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: To improve the Indian agriculture, the government of India began introducing technological reforms in the 1960s. Some of them have been listed below:
(1) Widespread use of radio and television for providing knowledge to farmers about new and improved techniques of cultivation and introduction of special weather bulletins.
(2) The Green Revolution based on the use of package technology was one of the best strategies of government to improve agriculture sector.
(3) The White Revolution with some technical innovation increased the production in dairy industry which somehow give a direct boost to the Indian agriculture sector.
Q16: Describe any five features of primitive subsistence farming. (CBSE 2020, 12)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The features of primitive subsistence farming are:
(1) Primitive subsistence farming is a type of farming practice in which the farmer and his family raise crops for home consumption and not trade.
(2) This is practiced with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks. The farming totally depends on the monsoon and natural fertility of the soil.
(3) It is done on small areas of land and is labour intensive.
(4) It is practiced as a ‘slash and burn’ agriculture. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce crops for their sustenance.
(5) Land productivity is low. No artificial fertilisers are used.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q17: Describe any three main features of ‘Rabi crop season.’ (Delhi 2020, 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Rabi crops are also known as winter crops. They are sown from October to December and harvested from April to June.
(b) Wheat, barley, pea, gram and mustard are the important rabi crops. Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are the important producers of rabi crops.
(c) Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western disturbances helps in the success i of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh ; and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above mentioned rabi crops.
Q18: Describe any three main features of 'Kharif crop season.’ (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Kharif crops are also known as summer crops. They are sown at the beginning of monsoon and harvested in September-October.
(ii) Paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soybean are important kharif crops. Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are important rice growing states.
(iii) In Assam, West Bengal and Odisha; three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are called Aus, Aman and Boro.
Q19: Describe the geographical conditions required for rubber cultivation. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Rubber is a crop that is primarily grown in equatorial regions, but it can also be cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. The geographical conditions required for rubber cultivation are as follows:
- Moist and humid climate: Rubber plants thrive in areas with high humidity and abundant rainfall. The annual rainfall should be more than 200 cm.
- Temperature: Rubber cultivation requires a temperature range above 25°C. It cannot withstand extreme cold temperatures.
- Soil: Rubber plants prefer well-drained, fertile soil. Sandy loam and laterite soils are suitable for rubber cultivation.
- Growing regions in India: Rubber is mainly grown in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands. The Garo hills of Meghalaya also have rubber plantations.
Q20: Categorise the following as 'Rabi crops' and 'Zaid crops': (Al 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Wheat - Rabi crop
(ii) Watermelon - Zaid crop
(iii) Fodder crops - Rabi crop
(iv) Mustard - Rabi crop
(v) Cucumber - Zaid crop
(vi) Peas - Rabi crop
Q21: Describe the geographical conditions required for tea cultivation. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The geographical conditions required for tea cultivation are as follows:
(a) Temperature: Tea bushes require a hot and wet climate. The ideal temperature range for their growth is between 20°C to 30°C. Extreme temperatures below 10°C and above 35°C can be harmful to the plants.
(b) Rainfall: Tea plants need a good amount of rainfall ranging between 150-300 cm. The annual rainfall should be well-distributed throughout the year, as long dry spells can be detrimental to tea cultivation
(c) Soil: Tea bushes thrive in well-drained, deep, and loamy soil. The presence of humus and iron content in the soil is beneficial for tea cultivation. Shady areas with trees are preferred for tea plantations.
Q22: Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of 'wheat' in India. (2019 C, 2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The geographical conditions required for the growth of wheat in India are as follows:
- Cool growing season: Wheat requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine during the ripening period.
- Rainfall: Wheat cultivation requires an annual rainfall of 50 to 75 cm, which should be evenly distributed throughout the growing season.
- Soil: Wheat grows well in fertile alluvial soil or mixed soil. Well-drained plain lands or gentle slopes are ideal for wheat cultivation.
- Growing regions in India: The major wheat-producing regions in India are the Ganga-Satluj plains in the northwest and the black soil region of the Deccan. The states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, and parts of Madhya Pradesh are the main wheat-producing states.
Q23: Name the two major beverage crops grown in India. Describe their growing areas. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The two major beverage crops grown in India are tea and coffee.
Tea cultivation is mainly done in Assam, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala. Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh, and Tripura are also tea-producing states in the country. India is the second-largest producer of tea after China.
Coffee cultivation is confined to the Nilgiri in Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. Karnataka accounts for 70% of the coffee produced in India.

Q24: Name the two major fibre crops grown in India. Describe the conditions required for the growth of these two crops with their growing areas. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The two major fibre crops grown in India are cotton and jute.
Conditions required for cotton:
- Temperature: Cotton is the crop of tropical and subtropical areas and requires uniformly high temperature varying between 21°C and 30°C.
- Rainfall: It grows mostly in the areas having at least 210 frost-free days in a year. It requires a modest amount of rainfall of 50 to 100 cm.
- Soil: Cotton cultivation is closely related to Black soils of Deccan and Malwa plateau.
Conditions required for jute:
- Jute grows well on well-drained fertile soils in the flood plains where soils are renewed every year.
- High temperature is required during the time of growth.
Q25: Categorise the following as kharif crops and rabi crops:
(I) Wheat
(II) Maize
(III) Barley
(IV) Peas
(V) Bajra
(VI) Tur (arhar) (CBSE 2019)
Ans:
(I) Wheat – Rabi crop
(II) Maize – Kharif crop
(III) Barley – Rabi crop
(IV) Peas – Rabi crop
(V) Bajra - Kharif crop
(VI) Tur (arhar) - Kharif crop
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q26: The government of India has introduced various institutional and technological reforms to improve agriculture in the 1980s and 1990s. Support this statement with examples. (Delhi 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The government of India introduced various institutional and technological reforms to improve agriculture in the 1980s and 1990s. Some examples of these reforms are:
- Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, and disease to protect farmers from crop losses.
- Establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies, and banks for providing loan facilities to farmers at lower interest rates.
- Introduction of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) to provide financial support and insurance coverage to farmers.
- Special weather bulletins and agricultural programs for farmers on radio and television to provide them with timely information and guidance.
- Announcement of minimum support price (MSP) and remunerative prices for important crops to ensure fair prices for farmers' produce and protect them from exploitation by intermediaries.
- Promotion of technological advancements in agriculture, such as the use of improved seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation techniques to increase productivity.

Q27: Explain any three steps for agriculture reforms taken by the Government of India, after the independence. (Delhi 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three steps taken for agriculture reforms by the Government of India after independence are as follows: (i) From the earliest days, agriculture was given great importance in the "five year plans". Other important steps included: (ii) Abolishment of zamindari system. The right to own the land was given to the actual cultivators which then led to an increase in the production. (iii) Cooperative societies were formed which provided quality seeds and fertilizers to farmers at a low price. (iv) Another act called 'land ceiling act' was passed, according to which the land could not be held by a person beyond a defined limit.
Q28: Compare ‘intensive subsistence farming’ with that of ‘commercial farming’ practiced in India. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 'Intensive Subsistence farming’ and ‘Commercial farming’ can be compared and described using these points:
(1) In regions of intensive subsistence farming, pressure of population on land is high whereas in commercial farming, population density is low.
(2) In intensive subsistence farming, farming is labour-intensive whereas in commercial farming, mechanised form of farming is used.
(3) In intensive subsistence farming, there is low capital investment whereas in commercial farming, high capital investment is seen.
(4) In intensive subsistence farming, farmers produce for their own consumption whereas in commercial farming, production is mainly for the market.
(5) In intensive subsistence farming, processing industries are not associated with farms whereas in commercial farming, processing industries are associated with plantations.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q29: By which name is specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables known? (2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Horticulture
Q30: Describe 'Jhumming cultivation' in one sentence. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Jhumming cultivation, also known as the slash and burn agriculture, is the process of growing crops by first clearing the land of trees and vegetation and burning them thereafter.
Q31: Which factors has helped Punjab and Haryana to grow more and more of rice? (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Development of dense canal network and inputs like fertilisers and pesticides.
Q32: What is the importance of pulses in our country? Why are pulses grown as a rotation crop? (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Pulses hold great importance in our country due to the following reasons:
- Protein source: Pulses are rich in proteins and serve as a significant source of protein in the Indian diet. They are the second most important constituent after cereals.
- Soil fertility: Pulses are grown as rotation crops because they help in restoring soil fertility. Being leguminous crops, they have the ability to fix nitrogen from the air, which improves soil health.
- Water requirement: Pulses require less moisture compared to other crops, making them suitable for dry conditions.
- Major pulse-producing states: Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh are the major pulse-producing states in India.
Q33: Name any four oilseeds produced in India. Explain the importance of oilseeds in our day to day life. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Four oilseeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard, coconut, and sesamum.
Importance of oilseeds:
- Most of these oilseeds are edible in the form of oil, which is an essential ingredient in cooking.
- They are used as raw materials for manufacturing paints, varnishes, soaps, perfumes, etc.
- Oil cake, the by-product of oilseeds, is used as cattle feed and fertilizer.
Q34: What are millets? Give a brief description of the climatic conditions and producing states of the millets grown in India. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Millets are coarse grains that have high nutritional value, such as ragi, which is rich in iron and calcium.
- (i) Jowar: It is a rain-fed crop that mostly grows in moist areas. It is grown in states like Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- (ii) Bajra: It grows well on sandy soils and shallow black soil. It is grown in states like Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- (iii) Ragi: It grows well in dry regions on red, black, sandy, and loamy soils. It is grown in states like Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
Q35: Explain any five initiatives taken by the government to ensure an increase in agricultural production. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Five initiatives taken by the government to ensure an increase in agricultural production are:
- Land reforms: The government implemented collectivization, consolidation of land holdings, cooperation, and abolition of zamindari to improve land productivity and reduce inequalities.
- Agricultural reforms: The introduction of the Green Revolution and White Revolution (Operation Flood) aimed at increasing agricultural productivity and promoting dairy farming.
- Land development programs: The government provided crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, etc., and established Grameen banks, cooperative societies, and banks to provide financial support and loans to farmers.
- Introduction of schemes like Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) to provide financial assistance and insurance coverage to farmers.
- Promotion of modern agricultural practices and technologies such as soil testing facilities, cold storage, and transportation to improve agricultural productivity and reduce post-harvest losses.

Previous Year Questions 2016
Q36: Which is the leading coffee producing state in India? (2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Karnataka
Q37: What is the importance of millets? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In addition to their good nutritional value, an important feature of these crops is that they require much less water to grow than rice and wheat. They can be successfully cultivated in semi-arid tropics and on poor soils
Q38: Which crop is known as the 'golden fibre'? Explain any two geographical conditions essential for the cultivation of this crop. Mention its any four uses. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Jute is known as the 'golden fibre'.
(ii) Geographical conditions required for the cultivation of jute:
- It grows well in drained fertile soil of the flood plains where the soil is renewed every year.
- High temperature is required during the time of growth.
Uses of jute:
- Jute can be used to manufacture gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets, and other artifacts.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q39: What are the growing conditions required for the main staple food crop of India? Mention the main growing regions. (2015) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The main staple food crop of India is rice. The growing conditions required for rice cultivation are as follows:
(a) High temperature: Rice is a Kharif crop and requires high temperatures above 25°C for its growth.
(b) High humidity and rainfall: Rice cultivation requires high humidity and an annual rainfall of over 100 cm. It thrives in areas with a high water table or near river valleys.
(c) Main growing regions: Rice is grown in various regions of India, including the northern plains, northeastern India, coastal areas, deltaic plains, and river valleys.
Q40: How many cropping seasons are found in India? Name them and write a short note on each. (CBSE 2015, 2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: India has three cropping seasons, namely:
(i) Rabi: The rabi season begins with the onset of winter in October-November and lasts until March-April. It is characterized by low-temperature conditions, which are suitable for the cultivation of temperate and subtropical crops. Major rabi crops include wheat, gram, and mustard.
(ii) Kharif: The kharif season largely coincides with the southwest monsoon, which provides the necessary water for cultivation. It is suitable for the cultivation of tropical crops such as rice, cotton, jute, jowar, bajra, and tur.
(iii) Zaid: The zaid season is a short-duration summer cropping season that begins after the harvesting of rabi crops. It includes crops such as watermelon, cucumber, and other vegetables that can be grown during the summer months.
Q41: Mention any two geographical conditions required for the growth of the maize crop in India. Describe any three factors that have contributed to an increase in maize production. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Geographical conditions required for the growth of the maize crop in India:
- It is a kharif crop that requires a temperature between 21°C to 27°C.
- It grows well in alluvial soil.
Factors contributing to the increase in maize production:
- Use of modern inputs such as high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation.
- Adoption of improved farming techniques and practices.
- Government support through subsidies and incentives to maize farmers.
Q42: Explain any three geographical conditions required for the growth of rice in India. How is it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall? Explain with examples. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three geographical conditions required for the growth of rice in India:
- High temperature (above 25°C)
- Annual rainfall above 100 cm
- High humidity
Rice can be grown in areas of less rainfall with the help of irrigation. For example, in Punjab and Haryana, rice cultivation is possible despite receiving less rainfall because these states have a well-developed canal irrigation system. Water is supplied to the fields through canals, ensuring sufficient moisture for rice cultivation.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Agriculture
| 1. What are some important topics covered in the Class 10 Agriculture exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 10 Agriculture exam? |  |
| 3. What is the marking scheme for the Class 10 Agriculture exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific books or resources recommended for Class 10 Agriculture preparation? |  |
| 5. How important is practical knowledge in Class 10 Agriculture examinations? |  |

















