Class 10 Civics Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Gender Religion and Caste (Old Syllabus)
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Suggest any two measures to remove gender inequality.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Increase women's education and enforce equal pay for equal work.
Promote Women's Education:
- Education empowers women to challenge stereotypes and access better opportunities.
- Gender inequality stems from societal norms that limit women’s access to education. Providing scholarships and free schooling for girls can bridge this gap.
- Educated women are more likely to participate in economic and political activities, reducing dependency and inequality.
Enforce Equal Pay for Equal Work:
- Economic disparities are where women are often paid less than men for similar work.
- Implementing and enforcing laws like the Equal Remuneration Act ensures women receive fair wages, promoting financial independence.
- This reduces economic inequality and enhances women’s status in society.
Q2: Suggest any two measures to increase the number of women in legislatures of India.
Or
Suggest any two measures to ensure participation of women in public life.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Introduce reservation of seats for women and provide leadership training programs.
Reservation of Seats for Women:
- There is a low representation of women in Indian legislatures (e.g., less than 12% in Lok Sabha as per historical data).
- Reserving a percentage of seats (e.g., 33% as proposed in the Women’s Reservation Bill) ensures more women are elected to legislative bodies.
- This measure directly addresses structural barriers to women’s political participation.
Leadership Training Programs:
- Women often face societal and institutional barriers, such as lack of political experience or networks.
- Organizing training programs to develop leadership, public speaking, and political skills can empower women to contest elections.
- Such initiatives, supported by NGOs or government, help build confidence and capability, as noted in the chapter’s discussion on feminist movements.
Q3: Suggest any two measures to prevent violence against women.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Strengthen legal enforcement and promote gender sensitization programs.
Explanation:
Strengthen Legal Enforcement:
- Violence against women, including domestic violence, is a significant issue rooted in patriarchal norms.
- Strict implementation of laws like the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005, and fast-track courts for gender-based violence cases can deter perpetrators.
- Ensuring swift justice and support for victims (e.g., shelters, legal aid) reduces the incidence of violence.
Promote Gender Sensitization Programs:
- Societal attitudes that normalize violence against women need to change, as highlighted in the chapter’s discussion on gender inequality.
- Conducting awareness campaigns and gender sensitization workshops in schools, workplaces, and communities can challenge stereotypes.
- These programs educate men and women about equality and respect, reducing instances of violence.
Q4: Suggest any two measures to promote secularism as mentioned in the Indian Constitution.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ensure equal treatment of all religions and promote interfaith dialogue.
Ensure Equal Treatment of All Religions:
- The Indian Constitution, promotes secularism by guaranteeing equality of all religions under Article 14 and freedom of religion under Articles 25-28.
- The state must avoid favoring any religion in policies, laws, or public funding to maintain neutrality.
- For example, ensuring no religious community is discriminated against in access to education or jobs upholds secular principles.
Promote Interfaith Dialogue:
- Communalism is a threat to secularism, where religious differences are exploited.
- Organizing interfaith dialogues and cultural exchange programs fosters mutual understanding among communities.
- Such initiatives, supported by government or civil society, reduce communal tensions and strengthen constitutional secularism.
Q5: How did the feminist movements help to enhance the role of women in public life? Explain.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Feminist movements raised awareness about women’s rights and pushed for legal reforms to increase women’s participation in public life.
Explanation:
Raising Awareness About Women’s Rights:
- Feminist movements highlighted issues like gender discrimination, unequal pay, and limited political representation.
- By organizing protests, campaigns, and advocacy, these movements educated society about women’s rights, challenging patriarchal norms.
- This increased public support for women’s participation in politics, education, and employment.
Pushing for Legal Reforms:
- Feminist movements, were instrumental in advocating for laws like the 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992) for women’s reservation in local governance.
- They also supported policies for equal wages and protection against violence, creating a safer environment for women to engage in public life.
- These reforms empowered women to take up leadership roles in politics, workplaces, and community activities.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: “Role of women is gradually enhancing in the politics of the country.” Examine the statement. (CBSE 2024) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, the number of women involved in politics has significantly increased in the past few years. The increasing number of women running for office, holding elected positions, and actively participating in decision-making processes at all levels of government is evidence of this growing trend.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q2: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option. (2023)Assertion (A): Women in different parts of the world organised themselves and agitated for equal rights.
Reason (R): Women’s movement aimed at equality in personal and family life as well.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Assertion (A) is true, as women globally have indeed organised to fight for equal rights.
- Reason (R) is also true, highlighting that the women's movement focused on achieving equality in personal and family life.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct choice.
Q3: "Women face discrimination in various ways in our society" Explain any two ways. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two ways in which women face discrimination in our society are:
- Limited access to education: A smaller proportion of girls students go for higher studies compared to boys. Due to various social and cultural norms, girls often face restrictions in pursuing education beyond a certain level. This discrimination deprives them of opportunities for personal and professional growth.
- Occupational segregation: The proportion of women among highly paid and valued jobs is still very small. Women often face discrimination in the workplace, where they are confined to certain industries and job roles that are considered traditionally feminine. This limits their chances of career advancement and equal pay.
Q4: Which one of the following matters do not deal with the 'Family Laws?' (2023)
(a) Marriage
(b) Adoption
(c) Inheritance
(d) Finance
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Family laws typically cover personal matters related to family life, such as marriage, adoption, and inheritance. These laws focus on how families are structured and how issues like property and custody are handled. However, finance relates to money management and economic matters, which are not specifically included in family laws, making it the correct answer.
Q5: How has caste system in modern India undergone great change? Explain. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Partly due to the efforts of political leaders and social reformers like Jotiba Phula, Gandhiji, B.R. Ambedkar etc. and partly due to other socio-economic changes castes and caste system in modern India have undergone great changes.
(i) With the economic development, large scale urbanisation, growth of literacy and education, occupational mobility and the weakening of the position of landlords in the villages, the old notions of caste hierarchy are breaking down.
(ii) Now, most of the times, in urban areas it does not matter much who is walking along next to us on a street or eating at the next table in a restaurant.
(iii) The Constitution of India also prohibits any caste based discrimination and lays down the foundations of policies to reverse the injustices of the caste system.
In spite of these changes yet caste has not disappeared from contemporary India. Some of the older aspects of caste have persisted.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q6: Suggest any one way to protect women from domestic oppression. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Women can seek assistance from NGOs or the Mahila Aayog to protect themselves from domestic oppression.
Q7: Suggest any one way to pay equal wages to women in all areas of work as men. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Better implementation of 'Equal Remuneration Act, 1976 which provides equal wages to be paid to equal work.
Q8: What percentage of reservations is given to women in local administration in India? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 33% or one-third of reservation is given to women in local administration in India. This reservation is provided to ensure adequate representation of women in decision-making bodies at the grassroots level, such as Panchayats and Municipalities.
Q9: Suggest any one way to increase the participation of women in the legislative domain of India. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: One way to solve this problem is to make it legally binding to have a fair proportion of women in the elected as well as nominated bodies.
Q10: Describe the problems of low representation of women in Indian legislature. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Political parties are not giving tickets to women candidates to fight elections in proportion to their population.
- The lack of representation has led many feminists and women's movements to conclude that unless women control power, their issues will not receive adequate attention.
- India is lagging behind the averages for several developing countries in terms of women's representation in the legislature, placing India among the bottom group of nations in the world.
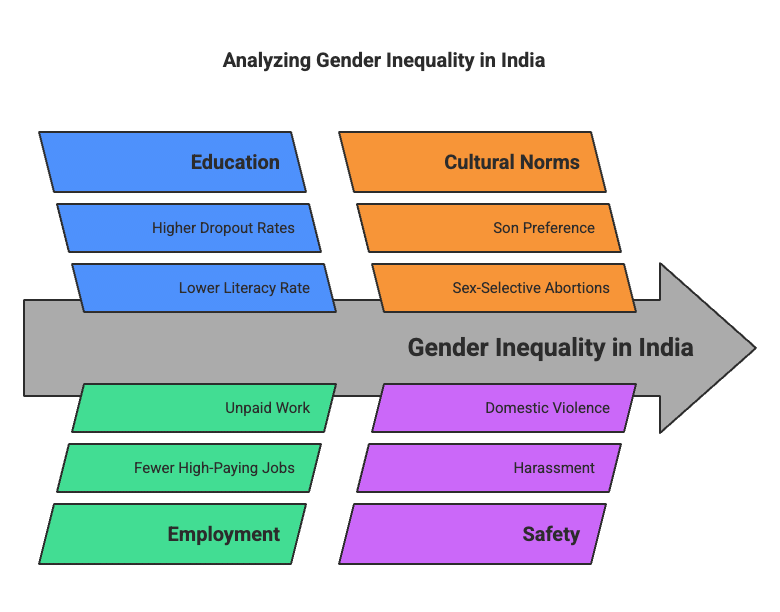
Q11: Describe the ways of discrimination faced by women in India. (2020)
OR
"Women still lag much behind men in India despite some improvements since independence" Analyse the statement. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, women continue to face significant disadvantages and discrimination despite some progress since Independence.
The following points highlight the various forms of inequality:
- The literacy rate for women stands at only 64.60%, compared to 80.90% for men (2011 Consensus data).
- A smaller number of girls pursue higher education. Although they perform well in school, many drop out as families prioritise spending on boys' education.
- Women occupy a minority of high-paying jobs. On average, an Indian woman works one hour more than a man daily, yet much of her work remains unpaid and undervalued.
- In some regions, there is a preference for sons, leading to sex-selective abortions and a declining child sex ratio.
- Women frequently experience harassment, exploitation, and violence, particularly within the home.
Q12: Suggest any one way to create communal harmony among various communities of India. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Spread awareness about unity and integrity.
Q13: Suggest any one way to change the 'family laws' of all religions. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Enforcement of Dowry Prohibition Act can bring a remarkable change in the family law of all religions.
Q14: Fill in the blank: The Indian Constitution provides to all individuals and communities the freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion because of ____ . (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Indian Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practise and propagate any religion because of secularism. Secularism is one of the fundamental principles of the Indian Constitution, which ensures that the state remains neutral in matters of religion and treats all religions equally. This allows individuals and communities to freely exercise their religious beliefs without any discrimination or interference from the state.
Q15: Describe any three problems of communalism in Indian politics. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Problems of communalism in Indian politics:
- Religious Prejudices: Communalism often involves biases and stereotypes against different religious communities, fostering a belief in the superiority of one's own religion.
- Desire for Separation: Members of minority communities may seek to create separate political units, driven by a sense of alienation.
- Communal Violence: This ideology can escalate into severe violence, including riots and massacres, as seen during the Partition of India and in subsequent years.
Q16: Mention any three features of 'secularism’ described in the Indian Constitution. (2020)
OR
Secularism is not an ideology of some political parties, but it is one of the foundations of a country. Examine the statement. (2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
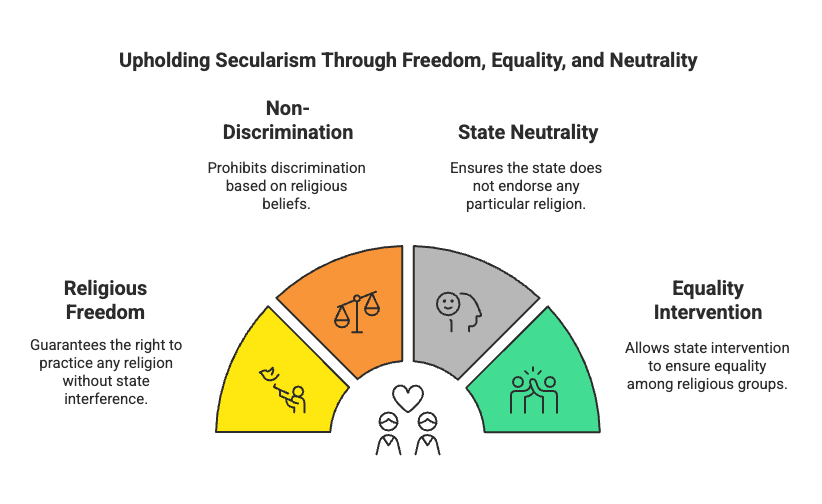
Ans: The makers of our Constitution were aware of religion related challenge. That is why they chose the model of a secular state. The important provisions that makes India a secular state are:
(i) There is no official religion for the Indian states. Unlike the status of Buddhism in Sri Lanka, that of Islam in Pakistan and that of Christianity in England, our Constitution does not give a special status to any religion.
(ii) The Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
(iii) The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
(iv) At the same time the Constitution allows the state to intervene in the matters of religion in order to ensure equality within religious communities. For example, it bans untouchability.
Q17: 'Communalism can take various forms in politics'. Explain. (2020)
OR
What form does communalism take in politics? (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- The most common expression of communalism is in everyday beliefs. These involve the spread of religious prejudices, stereotypes of religious belief, and the superiority of one's religion over other religions. This is so common that we often fail to notice it, even when we do not believe in it.
- It often leads to a quest for political dominance of one's own religious community. This takes the form of majoritarian dominance. For those belonging to the minority community, it leads to the formation of a separate political unit.
- Political mobilization on religious lines is another frequent form of communalism. This involves the use of sacred symbols by religious leaders. Emotional appeals are made to bring the followers of one religion together in the political arena.
- Sometimes communalism can lead to communal violence, riots, and massacres.
Q18: "The caste system is still prevalent in Indian society.” Suggest any one measure to abolish it. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: One measure to abolish caste system is increasing the literacy rates in our country.
Q19: "Sometimes elections are all about caste in India.” How can this situation be avoided? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Proper laws should be passed to separate elections from casteism.
- Implement strict regulations to limit caste-based campaigning.
- Encourage political parties to focus on issues and policies rather than caste affiliations.
- Promote awareness about the detrimental effects of casteism in politics.
- Support candidates based on their qualifications and integrity, not caste.
Q20: Fill in the blank: Castes and Caste system in modern India have undergone a great change because____ . (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Castes and Caste system in modern India have undergone a great change because
- Occupational mobility: This refers to the ability of individuals to change their jobs, often leading to new generations pursuing different careers than their ancestors.
- Implementation of laws: The Indian Constitution prohibits caste-based discrimination, promoting equality and social justice.
Q21: Describe the influence of Politics in the Caste system. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Politics significantly influences the caste system, but it is not the only factor at play.
- Caste affects electoral politics, influencing voting behaviour.
- Other factors, such as economic status and gender, also shape voting patterns.
- Individuals from the same caste may have different interests based on their economic conditions.
- Caste groups often form coalitions, leading to new classifications like 'backward' and 'forward' castes.
- Political dynamics can lead to the politicisation of caste identities.
In summary, while caste plays a role in politics, it interacts with various other factors that influence electoral outcomes.
Q22: Mention the problem of 'Casteism' in Indian politics. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Problems of casteism in India:
(i) There is discrimination between upper and lower castes. There is still a wide gap and difference between different castes.
(ii) Upper castes still enjoy respectable position in the society.
(iii) Political leaders contest election in the name of castes, for the vote bank.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q23: "Gender division is not based on biology but on social expectations and stereotypes." Support the statement. (2019 C, 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Gender division is a form of hierarchical social division based on social expectation and stereotypes.
(ii) Boys and girls are brought up to believe that the main responsibilities of women are house work and bringing up children.
(iii) There is a sexual division of labour in most families where women do all the household chores and men work outside the home.
(iv) Majority of women may do some paid work in addition of domestic labour both in rural and Urban areas but their work is not valued and does not get recognition.
Q24: Explain any five methods to raise the political representation of women in India. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: To enhance the political representation of women in India, several methods can be implemented:
- Improve literacy rates: Currently, the literacy rate for women is only 65.46%, compared to over 82% for men. Increasing literacy among women will boost their political awareness.
- Ensure equal pay: Many women are still paid less than men for the same jobs. Achieving equal pay will strengthen women's voices in society.
- Amend inheritance laws: The Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005, grants daughters equal rights to inherit their father's estate. This legal change has enhanced women's political power.
- Increase representation in politics: Women are underrepresented in Indian legislatures. Political parties should nominate more female candidates for elections, and the Supreme Court should enforce this change.
- Expand reservation in local bodies: Currently, one-third of seats in local government bodies are reserved for women. This should be increased to 50% to further enhance women's representation in panchayats and municipalities.
Q25: "Politics and social divisions should not be allowed to mix.” Justify the statement. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It is absolutely correct to say that politics and social divisions should not be allowed to mix. This is because:
- Mixing these can transform social divisions into political conflicts, leading to violence and instability.
- In Northern Ireland, a long-standing ethno-political conflict has caused significant turmoil.
- The disintegration of Yugoslavia into six countries illustrates the dangers of politicising social divides.
- In Sri Lanka, the politicisation of tensions between Sinhalas and Tamils resulted in a devastating civil war.
Q26: Examine the different forms of ‘Casteism’ in Indian politics. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Different forms of casteism in Indian politics:
- Candidate Selection: Political parties consider the caste makeup of the electorate when choosing candidates, aiming to secure votes from various castes.
- Government Formation: When forming governments, parties ensure representation from different castes and tribes to reflect the electorate's diversity.
- Campaigning: Political parties often appeal to caste sentiments during campaigns, with some parties seen as representatives of specific castes.
- Electoral Dynamics: The principle of universal adult franchise has led leaders to address caste-based issues to gain support, raising awareness among historically marginalised castes.
Q27: What does the term ‘Scheduled’ denote in ‘Scheduled castes’ and ‘Scheduled tribes’ ? (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: These groups include hundreds of castes or tribes whose names are listed in an official Schedule in the Indian Constitution. Hence, they are called Scheduled.
Q28: Read the following information and write a single term for it. The Constitution of India provides freedom to profess and practice any religion to all its citizens. The Constitution of India prohibits discrimination on religious grounds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Constitution of India promotes secularism.
- It grants freedom to all citizens to profess and practice any religion.
- Discrimination based on religion is prohibited.
- There is no official religion for the Indian state.
- The Constitution allows state intervention to ensure equality among religious communities.
Q29: “The caste system is still prevalent in Indian society.” Suggest any one measure to abolish it. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Casteism can be abolished by:
- Providing educational opportunities to everyone.
- Ensuring employment access without discrimination.
- Offering health facilities to all citizens equally.
Q30: ‘‘Sexual division of labour is not based on biology but on social expectations and stereotypes.’’ Support the statement. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sexual division is not based on biology. This can be supported by the following points:
- Women are often expected to handle housework and childcare, yet they are seen as too emotional for important decision-making roles.
- Men have successfully taken on traditional roles of women, and vice versa, showing that these roles are not biologically determined.
- Women's participation in politics is limited due to stereotypes that they are weak and unable to cope with stress.
- Historically, only men were permitted to engage in public affairs.
- Women face unequal opportunities to demonstrate their capabilities outside of their biological differences. Although there are biological distinctions, cultural norms and social expectations play a more significant role in defining roles and responsibilities in society.
Q31: “In India, women still lag behind men despite some improvement since Independence.” Support the statement with examples. (CBSE 2019, 13, 11)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, women lag behind men in various fields and sectors including political participation:
(1) Women legislators in our parliament are lower than in most of the other democracies. India is placed among the bottom few countries in the world.
(2) Women have less knowledge about their rights and duties as a citizen. The literacy rate of women is much lower than men in our country.
(3) They also face discrimination in terms of economic and social opportunity.
(4) The proportion of women working in influential positions in famous companies is comparatively lower than that of men.
(5) Women are paid less than their counterparts despite working equally hard.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q32: Women face disadvantage, discrimination, and oppression in various ways even today. Assess the statement by giving five suitable arguments. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Education:
(a) Women are deprived of an equal access to education. Thus, the literacy rate among women is only 54 per cent as compared to 76 per cent among men.
(b) A smaller proportion of girl students go for higher education because in spite of their better performance parents prefer to spend their resources on son’s higher education.
(ii) The number of women on highly paid jobs is less than men.
(iii) In spite of the Equal Remuneration Act 1976, women are paid less than men even when both do exactly the same work.
(iv) Parents prefer sons and get girl child aborted before she is born. This has led to decline in child sex ratio to merely 919 (2011 census).
(v) Women are exploited by their employers. They are sexually assaulted and do not feel safe while travelling at night. They are subjected to various forms of domestic-violence such as beating and harassment.
Q33: What is a secular state? Explain factors that make India a secular state. (CBSE 2016-17)
Or
“Secularism is not an ideology of some political parties or persons, but it is one of the foundations of our country.” Examine the statement. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) A secular state is a concept of secularism, whereby a state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. It grants equal status to all religions.
(b) (i) There is no official religion in India like Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
(ii) The Constitution grants every individual freedom to profess, preach and practice their own religion.
(iii) The Constitution prohibits discrimination on the grounds of religion.
(iv) The Constitution allows the state to intervene in the matters of religion in order to ensure equality within religious communities. For example it bans untouchability.
Thus, Our Constitution makers choose the model of a secular state. It is one of the foundations of our country.
Q34: Describe any three factors that are responsible for breaking down the caste system in India. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three factors that contribute to the breakdown of the caste system in India are:
- Reformers: Social reformers like Gandhiji and B.R. Ambedkar promoted the idea of a classless society and actively worked towards achieving it.
- Socio-economic changes: Urbanisation, increased literacy, and educational opportunities have helped to challenge and reduce caste-based prejudices.
- The Constitution of India: It prohibits caste-based discrimination and has established policies, such as reservations, to address historical injustices.
Q35: Describe the solution provided by the Constitution framers of India to meet the challenge of communalism. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The makers of our Constitution were aware of the challenge of communalism. The model of secular state was chosen to prevent these conflicts.
This choice was reflected in several constitutional provisions like:
(1) There is no official religion for the Indian state.
(2) The Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
(3) The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion. (4) At the same time, the Constitution allows the state to intervene in the matters of religion in order to ensure equality within religious communities.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q36: ‘Gender division is not based on biology but on social expectations and stereotypes.’ Support the statement. (CBSE 2016-17)Or
What is Gender division? How is it practised? What are its consequences?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Gender division is a hierarchical social structure that is often seen as natural and unchangeable. However, it is primarily shaped by social expectations and stereotypes rather than biology.
Here are some key points:
- Domestic Roles: Women are typically responsible for household tasks such as cooking and cleaning.
- Public Roles: Men are generally seen as the breadwinners, working outside the home.
- Paid Work: Men may engage in cooking or domestic work if it is paid, while women often juggle both paid work and household responsibilities.
- Urban Dynamics: In urban areas, women may work in offices but their contributions often go unrecognised.
Consequences of gender division include:
- Minimal representation of women in politics.
- Formation of feminist movements advocating for women's rights and opportunities.
- Demands for improved educational and career prospects for women.
Q37: How can communalism take various forms in politics? Explain. (CBSE 2016-17)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Majoritarian dominance: A majority community tries to dominate other communities in politics. This may compel the minority community to form a separate political unit. The example in Sri Lanka and Yugoslavia or India and Pakistan.
(ii) Religious appeals are made to voters to attract their votes. Sometimes sacred symbols and religious leaders are used to bring the followers of one religion together in the political arena.
(iii) Sometimes communalism takes most ugly form of communal violence, riots and massacre. India and Pakistan suffered some of the worst communal riots at the time of the partition. Even after independence, riots on communal lines have taken place in India.
Q38: Explain the reasons for the decline of the caste system in India. (CBSE 2016-17)
Or
Assess the circumstances prevalent in contemporary India which are responsible for bringing about a change in the caste system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The decline of the caste system in India can be attributed to several factors:
- In urban areas, people often ignore caste distinctions, travelling together on public transport like buses and metros.
- The economic conditions of lower castes have improved, allowing them to reside in areas with upper castes in cities.
- Individuals from lower castes are now changing their professions based on their qualifications and experience, rather than adhering to ancestral occupations.
- The Indian Constitution prohibits discrimination based on caste, and the practice of untouchability has been abolished.
- Social reformers and political leaders, such as Jyotiba Phule, Mahatma Gandhi, and B.R. Ambedkar, have played a significant role in advocating for equality.
Q39: Discuss various forms of caste in politics. (CBSE 2016-17)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) At the time of election, parties select their candidates on the basis of caste of the voters in a constituency to muster support to win election.
(ii) At the time of formation of government or Council of Ministers, effort is made to have representatives from all castes and communities.
(iii) During election campaign, appeals are made to voters to caste their vote in favour of the candidate of their own caste.
(iv) Universal adult franchise and the principle of one-person-one vote compelled political leaders to gear up to the task of mobilising and securing political support.
(v) Political parties are also formed on the basis of caste to attract the voters in the elections. The BSP in UP, DMK and AIADMK are examples o f such political parties.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q40: Suggest any three measures to enhance the participation of women in politics. (CBSE 2015) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three such measures are:
(1) Women should be educated and made aware of their rights and responsibilities towards the society and the country.
(2) Women should be made self reliant and self independent.
(3) Women should be encouraged and promoted to positions of greater influence to encourage their participation.
Q41: Suppose a politician seeks your vote on religious grounds. Why is his act considered against the norms of democracy? Explain. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: His act is against the spirit of democracy as the said politician is not working as per the Constitution. This is also because:
(1) It also exploits the social difference.
(2) It may create social discard and may lead to social division.
(3) It is also biased and neglects the principle of equality.
Previous Year Questions 2012
Q42: How can the relationship between politics and religion be beneficial and problematic at the same time? Explain. (CBSE 2012) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The relationship between politics and religion can have both benefits and drawbacks:
Benefits:- Religion can encourage ethical behaviour in politics.
- Religious communities can express their needs and interests politically.
- Politics can help protect the freedom and equality of religious groups.
- Political authorities can intervene to prevent religious oppression.
- Religion may foster nationalist sentiments, leading to conflicts.
- Political parties might exploit religion for electoral gains, favouring some groups over others.
- State power can be misused to dominate one religious group over another.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Civics Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Gender Religion and Caste (Old Syllabus)
| 1. What are the key themes covered in the Class 10 Gender, Religion & Caste chapter? |  |
| 2. How does the chapter explain the relationship between gender and social status? |  |
| 3. What examples are provided in the chapter to illustrate caste discrimination? |  |
| 4. How can understanding gender, religion, and caste contribute to social justice? |  |
| 5. What are some suggested measures to promote equality in terms of gender, religion, and caste? |  |






















