Quality of Sewage | Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Aerobic Decomposition
- Nitrogenous organic matter
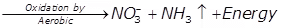
Nitrate - Carbonaceous organic matter
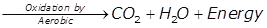
Carbon dioxide - Sulphurous organic matter
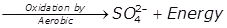
Sulphate
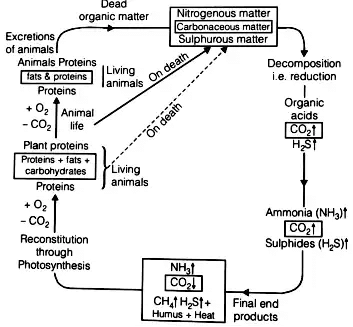
Anaerobic Decomposition
- Nitrogenous organic matter
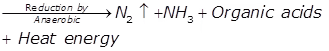
- Carbonaceous organic matter
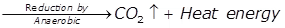
- Sulphurous organic matter
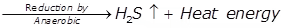
- Organic acids
Threshold Odour Number (TON)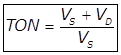
Vs = The volume of the sewage
VD = The volume of distilled water or odourless water.
Total Solids, Suspended Solids and Settleable Solids
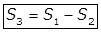
Where,
S3 = Dissolved solids plus colloidal or filterable solids in mg/lit
S2 = Non-filterable solids in mg/lit
S1 = The total amount of solids in mg/lit
S4 = Volatile suspended solids, in (mg/lit.)
S5 = Fixed solids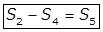
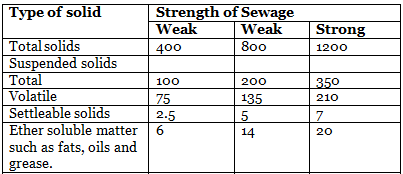
Total Solids
50% → Dissolved
25% → Suspended
25% → Settleable
Chemical Oxygen Demand
- Biodegradable + non Biodegradable O.M.
- K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 added and used is measured.
Theoretical Oxygen Demand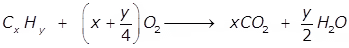
C6H6 + 7.5O2 → 6O2 + 3H2O
Benzene
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6O2 + 6H2O
Glucose
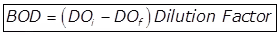
Where,
Biochemical oxygen demand in ppm or mg/lit.
Initial dissolved oxygen in mg/lit.
Final dissolved oxygen in mg/lit.
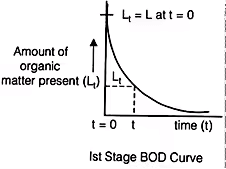
(i)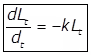
Where,
k = Rate constant signifying the rate of oxidation of organic matter and it depends upon the nature of organic matter and temperature. Its unit is per day.
Lt = O2 the equivalent of organic matter present after t days.
(ii) 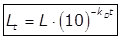
Where,
kD = Deoxygenation constant.
L = Organic matter present at t = 0
(iii) 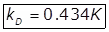
(iv) 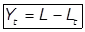
Where,
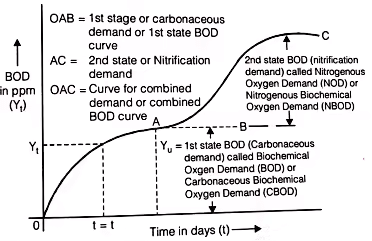
Yt = The total amount of organic matter oxidized int days i.e. BOD.
(v)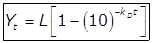
(vi) 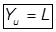
Where,
Yu = Ultimate B.O.D of days.
(vii) 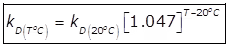
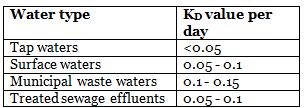
(viii) Laboratory Estimations of kD and L values
(Thomas Method)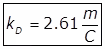
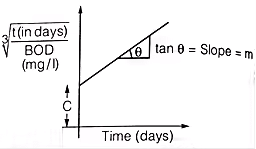
Where,
m = Slope of the line
C = Intercept of the line on the y-axis.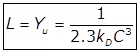
Relative Stability (s)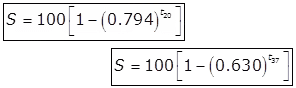
Where
t20 = time in days at 20oC.
t37 = time in days at 37oC.
|
14 videos|120 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Quality of Sewage - Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the importance of sewage civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How does sewage civil engineering contribute to sustainable development? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of a sewage system? |  |
| 4. How does sewage civil engineering mitigate the environmental impact of wastewater? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by sewage civil engineering? |  |
















