RD Sharma Solutions (Part - 2)- Ex-22.1, Data Handling I Collection Organisation Data, Class 7 | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 7 Mathematics PDF Download
Question 7:
In a study of number of accidents per day, the observations for 30 days were obtained as follows:
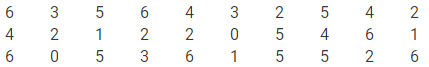
Prepare a frequency distribution table.
Answer 7:
Required frequency-distribution table:
| Number of Accidents | Number of Days |
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 6 |
Question 8:
Prepare a frequency table of the following ages (in years) of 30 students of class VIII in your school:
| 13, 14, 13, 12, 14, 13, 14, 15, 13, 14, 13, 14, 16, 12, 14 13, 14, 15, 16, 13, 14, 13, 12, 17, 13, 12, 13, 13, 13, 14 |
Answer 8:
Frequency Distribution Table is :
| Ages (in years) | Number of Students |
| 12 | 4 |
| 13 | 12 |
| 14 | 9 |
| 15 | 2 |
| 16 | 2 |
| 17 | 1 |
Question 9:
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
| 300, 250, 200, 250, 200, 150, 350, 200, 250, 200, 150, 300, 150, 200, 250 |
Prepare a frequency table.
(i) What is the range in wages (in Rs)?
(ii) How many Workers are getting Rs 350?
(iii) How many workers are getting the minimum wages?
Answer 9:
Frequency Distribution Table is
| Wages (in Rs.) | No. of Workers |
| 150 | 3 |
| 200 | 5 |
| 250 | 4 |
| 300 | 2 |
| 350 | 1 |
(i) The range in wages (in Rs.) = 350 -150 = 200.
(ii) Only 1 worker is getting Rs. 350.
(iii) 3 workers are getting the minimum wages, i.e, Rs. 150.
Question 10:
Construct a frequency distribution table for the following marks obtained by 25 students in a history test in class VI of a school:
| 9, 17, 12, 20, 9, 18, 25, 17, 19, 9, 12, 9, 12, 18, 17, 19, 20, 25, 9, 12, 17, 19, 19, 20, 9 |
(i) What is the range of marks?
(ii) What is the highest mark?
(iii) Which mark is occurring more frequently?
Answer 10:
Required frequency-distribution table:
| Marks | Frequency |
| 9 | 6 |
| 12 | 4 |
| 17 | 4 |
| 18 | 2 |
| 19 | 4 |
| 20 | 3 |
| 25 | 2 |
(i) Range of marks: 25-9=16.
(ii) The highest mark is 25.
(iii) 9 is occurring most frequently.
Question 11:
In a mathematis test following marks were obtained by 40 students of class VI. Arrange these marks in a table using, tally marks.

(i) Find how many students obtained marks equal to or more than 7?
(ii) How many students obtaned marks below 4?
Answer 11:
The Frequency Distribution Table is :
| Marks | Tally Marks | Frequency |
| 1 | II | 2 |
| 2 | III | 3 |
| 3 | III | 3 |
| 4 | 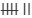 | 7 |
| 5 | 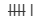 | 6 |
| 6 | 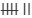 | 7 |
| 7 | 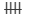 | 5 |
| 8 | IIII | 4 |
| 9 | III | 3 |
(i) 12 students obtained marks equal to or more than 7.
(ii) Only 8 students obtained marks below 4.
Question 12:
Following is the choice of sweets of 30 students of class VI: Ladoo, Barfi, Ladoo, Jalebi, Ladoo, Rasgulla, Jalebi, Ladoo, Barfi, Rasgulla, Ladoo, Jalebi, Jalebi Rasgulla, Ladoo, Rasgulla, Jalebi, Ladoo, Rasgulla, Ladoo, Rasgulla, Jalebi, Ladoo, Rasgulla, Ladoo, Ladoo, Barfi, Rasgulla, Rasgulla, Ladoo.
(i) Arrange the names of sweets in a table using tally marks.
(ii) Which sweet is preferred by most of the students.
Answer 12:

(ii) Ladoo is preferred by most of the students, 12 students.
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions (Part - 2)- Ex-22.1, Data Handling I Collection Organisation Data, Class 7 - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 7 Mathematics
| 1. What is data handling and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How can data be organized in data handling? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of data collection in data handling? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of data in data handling? |  |
| 5. How can data be analyzed in data handling? |  |
















